
Contributions
Abstract: S103
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA23: On Friday, June 15, 2018 from 12:15 - 12:30
Location: Room A1
Background
Although the majority of SMZL displays an indolent course, the disease is still incurable. Moreover, a significant proportion of patients (~25-30%) experience poor outcome and survive <5 years. Molecular aspects of SMZL have been claimed as promising biomarkers and their incorporation into prognostic models for SMZL might improve risk stratification of patients.
Aims
The main objective of the study is to test the impact of molecular alterations on overall survival (OS) prognostication in newly diagnosed SMZL.
Methods
IELSG46 is a multicentre, international, retrospective, observational study in which already existing and coded health-related personal and biological material is further used. The study included adults, who received a diagnosis of SMZL on spleen histology, and for whom tumor material collected before initiation of medical therapy and clinical annotations were available. Mutation analysis was performed by CAPP-seq targeted deep next generation sequencing of tumor genomic DNA was performed on the NexSeq500 sequencer (Illumina). A stringent bioinformatic pipeline was applied to suppress the background noise allowing to call variants with a sensitivity of 5x10-2 in FFPE derived DNA. Deletion of 17p and of 7q were identified by using the sequencing reads-based GATK4-CNV algorithm. The adjusted association between exposure variables and OS was estimated by Cox regression. Cox regression included exposure variables showing an univariate association with OS with a Bonferroni corrected significant level <0.1.
Results
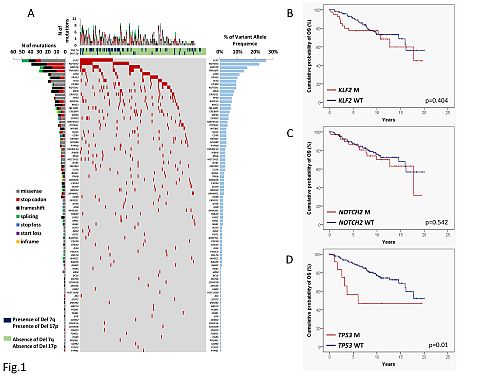
This interim analysis included 162 of the 316 cases enrolled in the study. The sample size allowed to identify 30% differences in OS for genetic lesions represented in at least 5% of cases. Median follow-up was 10 years. At 10 years, 74.6% of cases were alive, consistent with the general indolent behavior of this lymphoma. Genes recurrently affected by non-synonymous somatic mutations in >10% of SMZL included KLF2 (25.9%), NOTCH2 (22.2%), KMT2D (15.4%), TNFAIP3 (13.5%), ATM (11.1%) (Fig. 1A). Deletion 7q was documented in 31.5% of cases. OS was not affected by either KLF2 mutations (Fig. 1B), NOTCH2 mutations (Fig 1C), or the co-occurrence on NOTCH2 and KLF2 mutations. The only recurrent (>5%) lesion associated with inferior OS was TP53 mutation, which occurred in 7.4% cases (Fig. 1D). Among TP53 mutated cases, the median OS was 6 years (10-year OS: 46%), while it was not reached among TP53 wild type cases (10-year OS: 76.9%, p=.01).
Conclusion
The large sample size and the inclusion of SMZL confirmed on spleen pathology allowed to precisely estimate the prevalence of KLF2 and NOTCH2 mutations in this lymphoma, which were previously reported in the range of 10-40%. NOTCH2 and KLF2 mutations do not affect disease course, consistent with the hypothesis that they are early and founding molecular events in SMZL. As in other mature B-cell tumor, also SMZL outcome is affected by TP53 mutations.
Session topic: 19. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Outcome, Somatic mutation, Splenic marginal zone lymphoma
Abstract: S103
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA23: On Friday, June 15, 2018 from 12:15 - 12:30
Location: Room A1
Background
Although the majority of SMZL displays an indolent course, the disease is still incurable. Moreover, a significant proportion of patients (~25-30%) experience poor outcome and survive <5 years. Molecular aspects of SMZL have been claimed as promising biomarkers and their incorporation into prognostic models for SMZL might improve risk stratification of patients.
Aims
The main objective of the study is to test the impact of molecular alterations on overall survival (OS) prognostication in newly diagnosed SMZL.
Methods
IELSG46 is a multicentre, international, retrospective, observational study in which already existing and coded health-related personal and biological material is further used. The study included adults, who received a diagnosis of SMZL on spleen histology, and for whom tumor material collected before initiation of medical therapy and clinical annotations were available. Mutation analysis was performed by CAPP-seq targeted deep next generation sequencing of tumor genomic DNA was performed on the NexSeq500 sequencer (Illumina). A stringent bioinformatic pipeline was applied to suppress the background noise allowing to call variants with a sensitivity of 5x10-2 in FFPE derived DNA. Deletion of 17p and of 7q were identified by using the sequencing reads-based GATK4-CNV algorithm. The adjusted association between exposure variables and OS was estimated by Cox regression. Cox regression included exposure variables showing an univariate association with OS with a Bonferroni corrected significant level <0.1.
Results
This interim analysis included 162 of the 316 cases enrolled in the study. The sample size allowed to identify 30% differences in OS for genetic lesions represented in at least 5% of cases. Median follow-up was 10 years. At 10 years, 74.6% of cases were alive, consistent with the general indolent behavior of this lymphoma. Genes recurrently affected by non-synonymous somatic mutations in >10% of SMZL included KLF2 (25.9%), NOTCH2 (22.2%), KMT2D (15.4%), TNFAIP3 (13.5%), ATM (11.1%) (Fig. 1A). Deletion 7q was documented in 31.5% of cases. OS was not affected by either KLF2 mutations (Fig. 1B), NOTCH2 mutations (Fig 1C), or the co-occurrence on NOTCH2 and KLF2 mutations. The only recurrent (>5%) lesion associated with inferior OS was TP53 mutation, which occurred in 7.4% cases (Fig. 1D). Among TP53 mutated cases, the median OS was 6 years (10-year OS: 46%), while it was not reached among TP53 wild type cases (10-year OS: 76.9%, p=.01).

Conclusion
The large sample size and the inclusion of SMZL confirmed on spleen pathology allowed to precisely estimate the prevalence of KLF2 and NOTCH2 mutations in this lymphoma, which were previously reported in the range of 10-40%. NOTCH2 and KLF2 mutations do not affect disease course, consistent with the hypothesis that they are early and founding molecular events in SMZL. As in other mature B-cell tumor, also SMZL outcome is affected by TP53 mutations.
Session topic: 19. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Outcome, Somatic mutation, Splenic marginal zone lymphoma


