
Contributions
Abstract: PB2181
Type: Publication Only
Background
Aims
Methods
Results
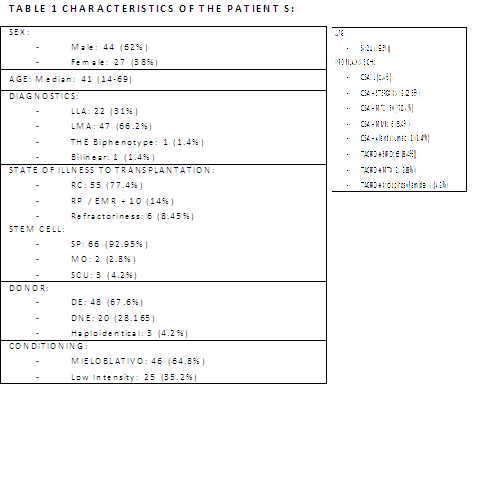
After analyzing the product infused we observe a relationship between LT and lymphocyte recovery on day + 30 (p: 0097, cor: 0223) and day +60 (p = 0.059, cor: 0257) but not with the CD34 + / Kg r. Table 2 shows the patient characteristics in lymphocyte absolute count in the day +60. We analyzed the overall survival (OS) and disease - free survival (DFS) and a decrease in OS with statistical difference was evident in patients with <.300 (p = 0.0029) on day +60 and day + 30 (p: 0.05), a decline also in DFS, with no statistically significant difference (p = 0.1). Multivariate analysis to determine which factors could influence the lymphoid recovery on day +60 and SG, we observed that the type of unrelated donor, myeloablative conditioning and ATG administration can influence a delay in this recovery. No differences were observed in the rest of the variables.
Conclusion
A delay in lymphocyte recovery is associated with a decrease in survival rates in our patients. Measures favoring an accelerated lymphocyte recovery (judicious use of thymoglobulin, adequate donor selection, and transplantation modality) could affect the post-transplant survival. It appears that the amount of infused product could play an important role in reconstitution, so it would be a factor to take into account prior to infusion.
Session topic: 22. Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Abstract: PB2181
Type: Publication Only
Background
Aims
Methods
Results
After analyzing the product infused we observe a relationship between LT and lymphocyte recovery on day + 30 (p: 0097, cor: 0223) and day +60 (p = 0.059, cor: 0257) but not with the CD34 + / Kg r. Table 2 shows the patient characteristics in lymphocyte absolute count in the day +60. We analyzed the overall survival (OS) and disease - free survival (DFS) and a decrease in OS with statistical difference was evident in patients with <.300 (p = 0.0029) on day +60 and day + 30 (p: 0.05), a decline also in DFS, with no statistically significant difference (p = 0.1). Multivariate analysis to determine which factors could influence the lymphoid recovery on day +60 and SG, we observed that the type of unrelated donor, myeloablative conditioning and ATG administration can influence a delay in this recovery. No differences were observed in the rest of the variables.

Conclusion
A delay in lymphocyte recovery is associated with a decrease in survival rates in our patients. Measures favoring an accelerated lymphocyte recovery (judicious use of thymoglobulin, adequate donor selection, and transplantation modality) could affect the post-transplant survival. It appears that the amount of infused product could play an important role in reconstitution, so it would be a factor to take into account prior to infusion.
Session topic: 22. Stem cell transplantation - Clinical


