
Contributions
Abstract: PB2174
Type: Publication Only
Background
Hemorrhagic cystitis (HC) is a serious complication ocurring after allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) more frequent on haploidentical (haplo) HSCT, with an incidence of 10% to 70%(Silva et al Haematologica 2010;95(7):1183–1190) associated mainly with the effect of cytotoxic agents such as Cyclophosphamyde (Cy). The conditioning regimen, BKPyV infection and graft versus host disease have an implication in the incidence. Other authors related the reactivation of CMV and a previous transplantation as risk factors to HC development(Ruggeri et al Transplant Infectious Disease 2015:17:822–830).
Aims
With this study we aim to describe the HC incidence and risk factors in all haplo-HSCT performed in the Canary Islands.
Methods
We analyzed all consecutive haplo-HSCT from family donors performed at our Hospital between 2013 and 2016. The conditioning regimen used for the transplant was the Hopkins haplo protocol with high dose Cy (50 mg/kg on days 3 and 4) posttransplantation (PTCy). We used as HC prophylaxis intense hydratation on the Cy administration day and the following 24 hours (using bladder wash only in 1 patient with cardiac dysfunction) and perfused MESNA at 100% of Cy dose beginig 15 minutes before the Cy administration on 16 pts and at 20% of the last dose at 0, 4 and 8 hours on all pts. We used SPSS V.23 to determine the cumulative incidence (CI) of HC.
Results
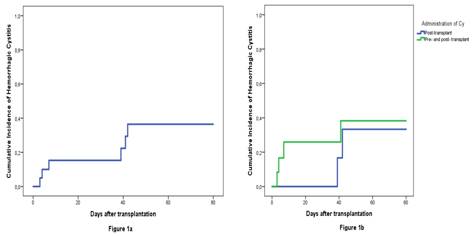
Conclusion
Session topic: 22. Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Keyword(s): Hemorrhagic cystitis, Haploidentical stem cell transplantation
Abstract: PB2174
Type: Publication Only
Background
Hemorrhagic cystitis (HC) is a serious complication ocurring after allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) more frequent on haploidentical (haplo) HSCT, with an incidence of 10% to 70%(Silva et al Haematologica 2010;95(7):1183–1190) associated mainly with the effect of cytotoxic agents such as Cyclophosphamyde (Cy). The conditioning regimen, BKPyV infection and graft versus host disease have an implication in the incidence. Other authors related the reactivation of CMV and a previous transplantation as risk factors to HC development(Ruggeri et al Transplant Infectious Disease 2015:17:822–830).
Aims
With this study we aim to describe the HC incidence and risk factors in all haplo-HSCT performed in the Canary Islands.
Methods
We analyzed all consecutive haplo-HSCT from family donors performed at our Hospital between 2013 and 2016. The conditioning regimen used for the transplant was the Hopkins haplo protocol with high dose Cy (50 mg/kg on days 3 and 4) posttransplantation (PTCy). We used as HC prophylaxis intense hydratation on the Cy administration day and the following 24 hours (using bladder wash only in 1 patient with cardiac dysfunction) and perfused MESNA at 100% of Cy dose beginig 15 minutes before the Cy administration on 16 pts and at 20% of the last dose at 0, 4 and 8 hours on all pts. We used SPSS V.23 to determine the cumulative incidence (CI) of HC.
Results

Conclusion
Session topic: 22. Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Keyword(s): Hemorrhagic cystitis, Haploidentical stem cell transplantation


