
Contributions
Abstract: PB2172
Type: Publication Only
Background
Herpes simplex virus(HSV)-1/2 can still be reactivated after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) even when the prophylactic acycloviris used. However, the risk factors for HSV-1/2 viremia and the clinical outcomes following unmanipulated haploidentical HSCT remain unknown.
Aims
The aim of this study was to explore the risk factors for HSV-1/2 viremia and to evaluate clinical outcomes following haplo-HSCT.
Methods
Nineteen patients with HSV-1/2 viremia and fifty-seven patients without HSV-1/2 viremia which were selected using the case-pair method after haploidentical HSCT were enrolled. We analysed the risk factors for HSV-1/2 viremia and compared clinical outcomes between the two patient groups.
Results
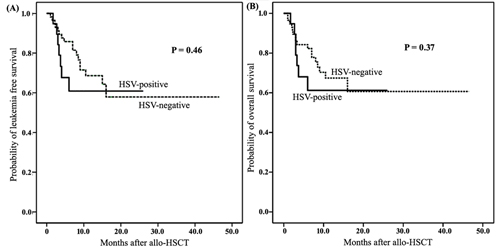
The risk factors for HSV-1/2 viremia included HLA disparity ≥2 loci(p=0.049)and cytomegalovirus (CMV)reactivation(p=0.028). The incidences of platelet engraftment, oral mucositis and severe haemorrhagic cystitis(HC) in patients with and without HSV-1/2 viremia were77% and 94%(p=0.003),78% and 13%(p = 0.000), and 25% and 6%(p=0.04), respectively. Moreover, the median time to platelet engraftment in patients with and without HSV-1/2 viremia was 25 d(range,11–80 d) and 17 d(range, 8–67 d) (p=0.004).In a multivariate analyses, HSV-1/2 viremia was associated with delayed platelet engraftment(p=0.038), a higher incidence of oral mucositis(p=0.000) and severe HC (p=0.038). However, HSV-1/2 viremia was not associated with non-relapse mortality (34.0%vs.31.5%,p=0.26),leukaemia-free survival (60.9%vs.57.9%,p=0.46)and overall survival (61.2%vs. 60.7%,p=0.37).
Conclusion
Based on our study results, we recommend that HSV-1/2 PCR should be performed on clinical suspicion.
Session topic: 22. Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Keyword(s): Herpesvirus, Haploidentical stem cell transplantation
Abstract: PB2172
Type: Publication Only
Background
Herpes simplex virus(HSV)-1/2 can still be reactivated after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) even when the prophylactic acycloviris used. However, the risk factors for HSV-1/2 viremia and the clinical outcomes following unmanipulated haploidentical HSCT remain unknown.
Aims
The aim of this study was to explore the risk factors for HSV-1/2 viremia and to evaluate clinical outcomes following haplo-HSCT.
Methods
Nineteen patients with HSV-1/2 viremia and fifty-seven patients without HSV-1/2 viremia which were selected using the case-pair method after haploidentical HSCT were enrolled. We analysed the risk factors for HSV-1/2 viremia and compared clinical outcomes between the two patient groups.
Results
The risk factors for HSV-1/2 viremia included HLA disparity ≥2 loci(p=0.049)and cytomegalovirus (CMV)reactivation(p=0.028). The incidences of platelet engraftment, oral mucositis and severe haemorrhagic cystitis(HC) in patients with and without HSV-1/2 viremia were77% and 94%(p=0.003),78% and 13%(p = 0.000), and 25% and 6%(p=0.04), respectively. Moreover, the median time to platelet engraftment in patients with and without HSV-1/2 viremia was 25 d(range,11–80 d) and 17 d(range, 8–67 d) (p=0.004).In a multivariate analyses, HSV-1/2 viremia was associated with delayed platelet engraftment(p=0.038), a higher incidence of oral mucositis(p=0.000) and severe HC (p=0.038). However, HSV-1/2 viremia was not associated with non-relapse mortality (34.0%vs.31.5%,p=0.26),leukaemia-free survival (60.9%vs.57.9%,p=0.46)and overall survival (61.2%vs. 60.7%,p=0.37).

Conclusion
Based on our study results, we recommend that HSV-1/2 PCR should be performed on clinical suspicion.
Session topic: 22. Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Keyword(s): Herpesvirus, Haploidentical stem cell transplantation


