
Contributions
Abstract: PB2055
Type: Publication Only
Background
JAK2 V617F is the most common genetic mutation in myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) and included in the major diagnostic criteria. Beyond the description of existence, quantification of mutational load is proposed as a useful information to classify subgroups of MPN and to predict prognosis. Droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) is a novel assay which has an advantage in accurate and reproducible quantitative analysis.
Aims
This study was planned to verify the correlation of ddPCR with pyrosequencing in diagnosis of MPN and to investigate clinical implication of the mutation burden in disease course.
Methods
Between 2012 and 2016, peripheral blood or bone marrow samples were obtained from 56 patients at diagnosis and every 3 months after enrollment. Inclusion criteria were 1) older than 20 years, 2) who were newly diagnosed with MPN and 3) diagnosed with MPN before, not met the indication of JAK2 inhibitor treatment yet. JAK2 V617F mutation was detected by pyrosequencing as diagnostic work-up. The ddPCR was performed using the same samples with pyrosequencing to prove correlations between assays and to establish a detection sensitivity cutoff. Clinical aspects and hematologic profiles of enrolled patients were reviewed.
Results
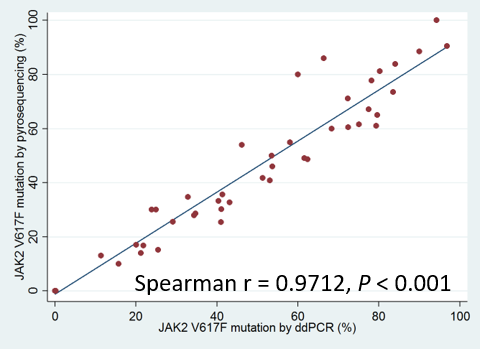
The lowest value of measured JAK2 V617F allele by ddPCR except negative samples in our study was 0.01%, which was approximately 0.07 copies/uL of mutant allele. Some discrepancies were observed from 0.0001% to 0.01% concentration between the expected and measured values in ddPCR detection sensitivity assay, 0.1% was determined as the cutoff. Forty-two patients (75%) were positive for JAK2 V617F by pyrosequencing and 46 (82.1%) were positive by ddPCR. The mean mutated allele at diagnosis was 37.5% ± 30.08%. With ddPCR, the mean was 40.7% ± 31.2%. Pyrosequencing and ddPCR were highly correlated (r = 0.9712, P<0.001). JAK2 V617F burden measured with ddPCR was significantly different by subgroups (P<0.001). In comparison of one disorder with another, polycythemia vera (PV) had more amount of mutant allele than essential thrombocytosis (ET) (P=0.001), however, differences between PV-myelofibrosis (MF) and ET-MF were not statistically significant. Follow-up samples were available in 12 patients and 8 were JAK2 V617F positive. Among them, reduction of mutant burden after treatment was observed in 6 patients (75%). JAK2 V617F burden showed initial reduction in a MF patient treated with JAK2 inhibitor, however, after dose reduction for toxicities, the JAK2 V617F mutation increment with hematologic aggravation was discovered. Mutation burden decrease showed a tendency consistent with hematologic improvement.
| Pt.No | Sex/Age | Subgroup | Initial JAK2 V617F allele (%) | Follow-up JAK2 V617F allele (%) | Difference | Initial CBC (WBC-Hb-Plt) | Follow-up CBC (WBC-Hb-Plt) | Treatment |
| 1 | F/56 | PV | 15.67 | 53.64 | +37.97 | 15700-16.1-429K | 4270-14.1-314K | Interferon alpha |
| 2 | F/63 | PV | 46.11 | 76.28 | +30.17 | 10090-20.2-491K | 6350-13.5-329K | Hydroxyurea, phlebotomy |
| 3 | M/72 | PV | 61.56 | 43.25 | -18.31 | 15740-19.8-304K | 7840-14.8-268K | Phlebotomy |
| 4 | F/52 | PV | 60.00 | 46.95 | -13.05 | 18060-19.2-605K | 6100-14.2-339K | Hydroxyurea |
| 5 | F/68 | ET | 11.35 | 4.94 | -6.41 | 11620-11.5-780K | 7270-12.3-540K | Hydroxyurea |
| 6 | F/49 | ET | 34.68 | 28.25 | -6.33 | 6630-14.7-600K | 5200-14.5-89K | Hydroxyurea |
| 7 | M/75 | MF | 21.23 | 16.55* | -4.68 | 8700-8.5-124K | 7370-10.1-176K | Ruxolitinib |
| 25.71† | +9.16 | 11080-12.3-169K | ||||||
| 8 | F/51 | ET | 0.17 | 0.00 | -0.17 | 6920-10.8-396K | 5940-9.7-329K | Hydroxyurea |
Conclusion
Quantitative analysis of JAK2 mutation using ddPCR was highly correlated with pyrosequencing and might reflex clinical treatment response.
Session topic: 16. Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Keyword(s): Myeloproliferative disorder, Mutation, Assay
Abstract: PB2055
Type: Publication Only
Background
JAK2 V617F is the most common genetic mutation in myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) and included in the major diagnostic criteria. Beyond the description of existence, quantification of mutational load is proposed as a useful information to classify subgroups of MPN and to predict prognosis. Droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) is a novel assay which has an advantage in accurate and reproducible quantitative analysis.
Aims
This study was planned to verify the correlation of ddPCR with pyrosequencing in diagnosis of MPN and to investigate clinical implication of the mutation burden in disease course.
Methods
Between 2012 and 2016, peripheral blood or bone marrow samples were obtained from 56 patients at diagnosis and every 3 months after enrollment. Inclusion criteria were 1) older than 20 years, 2) who were newly diagnosed with MPN and 3) diagnosed with MPN before, not met the indication of JAK2 inhibitor treatment yet. JAK2 V617F mutation was detected by pyrosequencing as diagnostic work-up. The ddPCR was performed using the same samples with pyrosequencing to prove correlations between assays and to establish a detection sensitivity cutoff. Clinical aspects and hematologic profiles of enrolled patients were reviewed.
Results
The lowest value of measured JAK2 V617F allele by ddPCR except negative samples in our study was 0.01%, which was approximately 0.07 copies/uL of mutant allele. Some discrepancies were observed from 0.0001% to 0.01% concentration between the expected and measured values in ddPCR detection sensitivity assay, 0.1% was determined as the cutoff. Forty-two patients (75%) were positive for JAK2 V617F by pyrosequencing and 46 (82.1%) were positive by ddPCR. The mean mutated allele at diagnosis was 37.5% ± 30.08%. With ddPCR, the mean was 40.7% ± 31.2%. Pyrosequencing and ddPCR were highly correlated (r = 0.9712, P<0.001). JAK2 V617F burden measured with ddPCR was significantly different by subgroups (P<0.001). In comparison of one disorder with another, polycythemia vera (PV) had more amount of mutant allele than essential thrombocytosis (ET) (P=0.001), however, differences between PV-myelofibrosis (MF) and ET-MF were not statistically significant. Follow-up samples were available in 12 patients and 8 were JAK2 V617F positive. Among them, reduction of mutant burden after treatment was observed in 6 patients (75%). JAK2 V617F burden showed initial reduction in a MF patient treated with JAK2 inhibitor, however, after dose reduction for toxicities, the JAK2 V617F mutation increment with hematologic aggravation was discovered. Mutation burden decrease showed a tendency consistent with hematologic improvement.
| Pt.No | Sex/Age | Subgroup | Initial JAK2 V617F allele (%) | Follow-up JAK2 V617F allele (%) | Difference | Initial CBC (WBC-Hb-Plt) | Follow-up CBC (WBC-Hb-Plt) | Treatment |
| 1 | F/56 | PV | 15.67 | 53.64 | +37.97 | 15700-16.1-429K | 4270-14.1-314K | Interferon alpha |
| 2 | F/63 | PV | 46.11 | 76.28 | +30.17 | 10090-20.2-491K | 6350-13.5-329K | Hydroxyurea, phlebotomy |
| 3 | M/72 | PV | 61.56 | 43.25 | -18.31 | 15740-19.8-304K | 7840-14.8-268K | Phlebotomy |
| 4 | F/52 | PV | 60.00 | 46.95 | -13.05 | 18060-19.2-605K | 6100-14.2-339K | Hydroxyurea |
| 5 | F/68 | ET | 11.35 | 4.94 | -6.41 | 11620-11.5-780K | 7270-12.3-540K | Hydroxyurea |
| 6 | F/49 | ET | 34.68 | 28.25 | -6.33 | 6630-14.7-600K | 5200-14.5-89K | Hydroxyurea |
| 7 | M/75 | MF | 21.23 | 16.55* | -4.68 | 8700-8.5-124K | 7370-10.1-176K | Ruxolitinib |
| 25.71† | +9.16 | 11080-12.3-169K | ||||||
| 8 | F/51 | ET | 0.17 | 0.00 | -0.17 | 6920-10.8-396K | 5940-9.7-329K | Hydroxyurea |

Conclusion
Quantitative analysis of JAK2 mutation using ddPCR was highly correlated with pyrosequencing and might reflex clinical treatment response.
Session topic: 16. Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Keyword(s): Myeloproliferative disorder, Mutation, Assay


