
Contributions
Abstract: PB2044
Type: Publication Only
Background
Thrombocytosis is defined as an abnormally increased number of platelets (>450x109/L) in the blood counts, whose cause can be primary or secondary, hereditary or acquired. Hereditary thrombocytosis is a rare congenital disease due to germ line mutations affecting thrombopoietin signaling genes such as THPO, MPL and, more recently, JAK2.
Aims
To describe five cases of persistent thrombocytosis in young patients with JAK2 mutations.
Methods
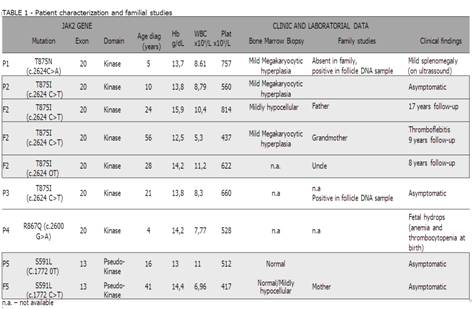
Four children (2F: 2M), median age of 8,8 years and 1 young adult (F) 21 years-old, with sustained elevation of platelet counts. None had previous history of thrombo-hemorragic events. Main causes of secondary thrombocytosis were excluded, and all patients tested negative for BCR-ABL1, JAK2V617F, CALR and MPL mutations. Sanger sequencing of exons 12 to 20 of JAK2 was performed in all patients. Family studies were possible in 3 families.
Results
Conclusion
In vitro studies performed by other authors have demonstrated that JAK2 R867Q and JAK2 S591L, described in familial thrombocytosis, promote JAK-STAT activation. The germline nature of JAK2 T875N mutation, previously described in an acute megakaryoblastic leukemia primary cell line, was confirmed in DNA obtained from hair follicle. Two patients presented a non-described JAK2 T875I mutation. Familial studies clarified the etiology of thrombocytosis in 3 adults previously diagnosed as ET triple negative.
Session topic: 16. Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Keyword(s): Thrombocytosis, Myeloproliferative disorder, Mutation
Abstract: PB2044
Type: Publication Only
Background
Thrombocytosis is defined as an abnormally increased number of platelets (>450x109/L) in the blood counts, whose cause can be primary or secondary, hereditary or acquired. Hereditary thrombocytosis is a rare congenital disease due to germ line mutations affecting thrombopoietin signaling genes such as THPO, MPL and, more recently, JAK2.
Aims
To describe five cases of persistent thrombocytosis in young patients with JAK2 mutations.
Methods
Four children (2F: 2M), median age of 8,8 years and 1 young adult (F) 21 years-old, with sustained elevation of platelet counts. None had previous history of thrombo-hemorragic events. Main causes of secondary thrombocytosis were excluded, and all patients tested negative for BCR-ABL1, JAK2V617F, CALR and MPL mutations. Sanger sequencing of exons 12 to 20 of JAK2 was performed in all patients. Family studies were possible in 3 families.
Results

Conclusion
In vitro studies performed by other authors have demonstrated that JAK2 R867Q and JAK2 S591L, described in familial thrombocytosis, promote JAK-STAT activation. The germline nature of JAK2 T875N mutation, previously described in an acute megakaryoblastic leukemia primary cell line, was confirmed in DNA obtained from hair follicle. Two patients presented a non-described JAK2 T875I mutation. Familial studies clarified the etiology of thrombocytosis in 3 adults previously diagnosed as ET triple negative.
Session topic: 16. Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Keyword(s): Thrombocytosis, Myeloproliferative disorder, Mutation


