
Contributions
Abstract: PB2028
Type: Publication Only
Background
Aims
Investigate the mRNA expression levels of HIF-1a and HIF-2a, MDR1 and CALR genes in whole blood samples from patients with JAK2 V617F positive MPN.
Methods
Real-time PCR was performed to detect of HIF1a, HIF2a, MDR1 and CALR mRNA transcripts levels in white blood cells 14 healthy volunteers (median age 22 years, range 21-58 years, 57% males) and 11 (median age 44 years, range 20-77 years, 45% males) patients with JAK2 V617F-positive MPN, median of allelic burden is 36%, range 9-87%. Venous blood were collected in tube with RNAse inhibitor. Total RNA was isolated using “RIBO-zol-D” (Aplisens) and were transcribed using “Reverta-L” (Aplisens). PCR was optimized for the thermocycler CFX96 (Bio-Rad). The results were calculated utilizing the delta Ct method in the software package of “R”. The threshold cycles (Ct) genes and housekeeping genes (TBP, GUS, ABL) determined using Cy0 method. The results was normalization with this reference genes. Mann-Whitney U test was used to evaluate significant difference between the groups, the degree of correlation (r) was assessed using Spearman test.
Results
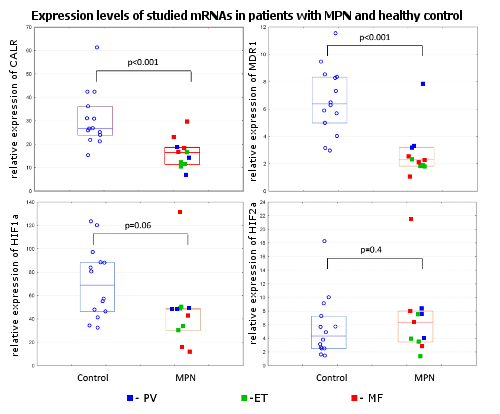
Conclusion
Session topic: 15. Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Biology
Keyword(s): Myeloproliferative disorder, MDR1, Gene expression
Abstract: PB2028
Type: Publication Only
Background
Aims
Investigate the mRNA expression levels of HIF-1a and HIF-2a, MDR1 and CALR genes in whole blood samples from patients with JAK2 V617F positive MPN.
Methods
Real-time PCR was performed to detect of HIF1a, HIF2a, MDR1 and CALR mRNA transcripts levels in white blood cells 14 healthy volunteers (median age 22 years, range 21-58 years, 57% males) and 11 (median age 44 years, range 20-77 years, 45% males) patients with JAK2 V617F-positive MPN, median of allelic burden is 36%, range 9-87%. Venous blood were collected in tube with RNAse inhibitor. Total RNA was isolated using “RIBO-zol-D” (Aplisens) and were transcribed using “Reverta-L” (Aplisens). PCR was optimized for the thermocycler CFX96 (Bio-Rad). The results were calculated utilizing the delta Ct method in the software package of “R”. The threshold cycles (Ct) genes and housekeeping genes (TBP, GUS, ABL) determined using Cy0 method. The results was normalization with this reference genes. Mann-Whitney U test was used to evaluate significant difference between the groups, the degree of correlation (r) was assessed using Spearman test.
Results

Conclusion
Session topic: 15. Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Biology
Keyword(s): Myeloproliferative disorder, MDR1, Gene expression


