
Contributions
Abstract: PB1999
Type: Publication Only
Background
Lenalidomide (Len) and dexamethasone (DEX) combination therapy (Ld) is now the standard treatment of multiple myeloma (MM). Len has both a direct effect on MM cells and an immunomodulatory effect and recently many drugs are combined with Ld therapy to expect the synergistic anti-tumor immune response. However, adverse events (AEs) make continuation of Ld therapy difficult for some patients especially for elderly patients.
Aims
To investigate the safe and effective plasma concentration of Len and the anti-tumor immune response change in MM patients treated by Ld therapy.
Methods
Forty patients (18 men and 22 women) were enrolled in this study. Median age was 75.5 years old (range 61-86). Len was administered on days 1–21 of a 28-day cycle; and DEX, on days 1, 8, 15, and 22. The plasma concentrations of Len just before oral administration and 1, 2, and 4 hr thereafter were analyzed by using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Before and after Ld therapy, Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of MM patients were isolated from whole blood by Ficoll-Hypaque density-gradient centrifugation. PBMCs were stained with the fluorescent dye-conjugated antibodies against surface and intracellular antigens and evaluated by multicolor flow cytometry. Intracellular cytokine production of IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-2 and CD107a molecule was detected after stimulation with PMA/ionomycin for 5 hours in the presence of protein transport inhibitor Golgi stop (BD Bioscience). Analysis was performed using LSR Fortessa (BD Bioscience) and Flowjo version 10.2 software (TreeStar). This study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Akita University Hospital, and all recipients gave written informed consent.
Results
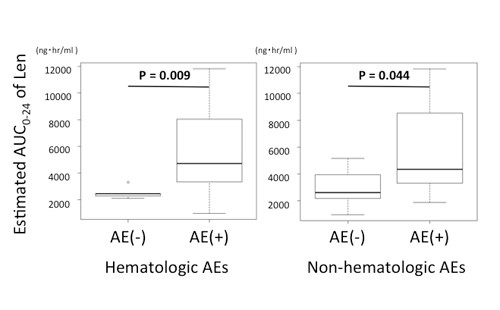
21 patients showed renal impairment (RI) necessary to adjust initial Len dosage. Adverse cytogenetics of del17p and t(4;14), detected by using fluorescence in situ hybridization, were found in 2 and 4 patients, respectively. The median initial dosage of Len was 15 mg and DEX 20 mg. The overall response rates were 68.6 % and the 2-year progression-free survival was 70.8% at a median follow-up of 26.5 month. Grade 3 to 4 nonhematologic AEs were observed only in 8 patients. We estimated the AUC0-24 of Len by using formula as we previously reported (Ther Drug Monit 2014) and the cut-off value of the hematologic AEs was 2613.5ng・hr/ml (sensitivity 81.8%, specificity 80%) and non-hematologic AEs 3023.6ng・ hr/ml (sensitivity 78.9%, specificity 62.5%). After Ld therapy, naïve subset of CD4 and CD8 T cells and monocytic MDSC reduced significantly. On the other hand, effector memory subset and intracellular cytokine productions of IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-2, and CD107a of CD4 and CD8 T cells increased significantly.
Conclusion
Len can be administered safely even in elderly patients with RI by using the estimated AUC0-24 of Len as a prediction marker of AEs. Enhanced cytokine production and increased memory subset of T cells were observed after Ld treatment.
Session topic: 14. Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Keyword(s): Pharmacokinetic, Multiple Myeloma, Immunomodulatory thalidomide analog, Immune response
Abstract: PB1999
Type: Publication Only
Background
Lenalidomide (Len) and dexamethasone (DEX) combination therapy (Ld) is now the standard treatment of multiple myeloma (MM). Len has both a direct effect on MM cells and an immunomodulatory effect and recently many drugs are combined with Ld therapy to expect the synergistic anti-tumor immune response. However, adverse events (AEs) make continuation of Ld therapy difficult for some patients especially for elderly patients.
Aims
To investigate the safe and effective plasma concentration of Len and the anti-tumor immune response change in MM patients treated by Ld therapy.
Methods
Forty patients (18 men and 22 women) were enrolled in this study. Median age was 75.5 years old (range 61-86). Len was administered on days 1–21 of a 28-day cycle; and DEX, on days 1, 8, 15, and 22. The plasma concentrations of Len just before oral administration and 1, 2, and 4 hr thereafter were analyzed by using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Before and after Ld therapy, Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of MM patients were isolated from whole blood by Ficoll-Hypaque density-gradient centrifugation. PBMCs were stained with the fluorescent dye-conjugated antibodies against surface and intracellular antigens and evaluated by multicolor flow cytometry. Intracellular cytokine production of IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-2 and CD107a molecule was detected after stimulation with PMA/ionomycin for 5 hours in the presence of protein transport inhibitor Golgi stop (BD Bioscience). Analysis was performed using LSR Fortessa (BD Bioscience) and Flowjo version 10.2 software (TreeStar). This study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Akita University Hospital, and all recipients gave written informed consent.
Results
21 patients showed renal impairment (RI) necessary to adjust initial Len dosage. Adverse cytogenetics of del17p and t(4;14), detected by using fluorescence in situ hybridization, were found in 2 and 4 patients, respectively. The median initial dosage of Len was 15 mg and DEX 20 mg. The overall response rates were 68.6 % and the 2-year progression-free survival was 70.8% at a median follow-up of 26.5 month. Grade 3 to 4 nonhematologic AEs were observed only in 8 patients. We estimated the AUC0-24 of Len by using formula as we previously reported (Ther Drug Monit 2014) and the cut-off value of the hematologic AEs was 2613.5ng・hr/ml (sensitivity 81.8%, specificity 80%) and non-hematologic AEs 3023.6ng・ hr/ml (sensitivity 78.9%, specificity 62.5%). After Ld therapy, naïve subset of CD4 and CD8 T cells and monocytic MDSC reduced significantly. On the other hand, effector memory subset and intracellular cytokine productions of IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-2, and CD107a of CD4 and CD8 T cells increased significantly.

Conclusion
Len can be administered safely even in elderly patients with RI by using the estimated AUC0-24 of Len as a prediction marker of AEs. Enhanced cytokine production and increased memory subset of T cells were observed after Ld treatment.
Session topic: 14. Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Keyword(s): Pharmacokinetic, Multiple Myeloma, Immunomodulatory thalidomide analog, Immune response


