Abstract: PB1980
Type: Publication Only
Background
Multipe myeloma (MM) and HIV infection in AIDS stage until now its considered not to be associated. Recently new ideas appear in the literature such as influence of HAART on the treatment outcomes of MM in HIV negative patiens.
Aims
To find literature sources on multiple myeloma in HIV positive patients and elucidate the problem of this association. evaluate the impact of HAART in multiple myeloma.
Methods
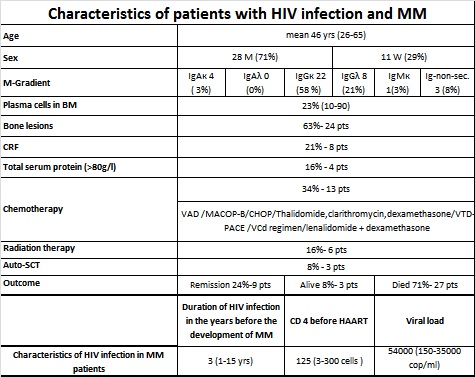
Patients were retrospectively identified out of 39 cases of MM and HIV from Pubmed/Medline from 1983 to 2017, and own case reported.
Results
Patients with MM and HIV infection did not differ significantly from the MM in HIV-negative with respect to age, gender, stages and renal function. Effects of HAART on levels of serum M-protein HAART itself has been reported to decrease M-protein in an HIV+ patient with MM. We determined whether HAART alone, in the absence of MM treatment, had any effects on the level of serum M-protein in HIV+MM patients. Depending on the interval between the discovery of the HIV infection HAART treatment initiation, and the diagnosis of MM and initiation of its treatment. The overall and progression-free survival of HIV+ MM patients on HAART appeared to be superior to that of HIV-negative MM patients. The survival of the HIV+ MM patients were also superior to that of non-HIV MM patients reported in the literature. The majority of HIV+ MM patients who had long-term follow-up in our study did not show clinical symptoms of MM and were free of serum-M protein after primary MM therapy in the presence or absence of HAART and maintained treatment with HAART alone. Although MM is not an AIDS-defining illness, meta-analyses of large population studies reveal an increased risk of MM in HIV/AIDS patients. HIV infection is commonly associated with B cell hyperproliferation, as indicated by polyclonal hyperglobulinemia and the development of various autoantibodies. This is presumed to be usually due to these CD4 deficient patients’ inability to control Epstein-Barr virus infections, which immortalize B cells. This may help to explain the increased incidence of MM in HIV+ patients. However, HIV can neither infect B lymphocytes or plasma cells, nor drive their malignant transformation. Some authors are going to treat multiple myeloma in HIV seronegative patients with HAART in combination with chemotherapy (Geling Lia and co-authors, Leukemia Research,2014). A 38 year-old Russian male presented at the Moscow clinical Center in 2015 with pronounced ossalgya and inability to move. Total protein 135 g/l with 81.7 g/l of IgG-k M-protein and no presence of Bence Jones protein. Bone skeletal survey showed multiple generalized lytic lesions. Bone marrow aspirate and biopsy showed 46% plasma cells. Serum creatinine – 104 mkmol/l. HIV and hepatitis C (genotype 1a) screening test were positive, confirmed with Western blot analysis. The CD4 count was 290 cells, HIV viral load 1500 copies/ml, hepatitis C viral load 14,2 mln copies. He was started on HAART, combined with chemotherapy 5 courses of СР+CVP+МР and 7 V-MP. In 2017 total serum protein– 97,3 g/l, M-protein 31,2 g/l, serum creatinine 63,0 mkmol/l. Now he is active without any bone pain receives Pegasis and lamivudine.
Conclusion
Patients with MM and HIV infection did not differ significantly from the MM in HIV-negative with respect to age, gender, stages and renal function, and treatment with addition of HAART.Recently was reported that HAART itself may reduce and even remove m-gradient in HIV positive patients. It is considered to include HAART in HIV negative patients with MM.The problem of MM and HIV/AIDS association remains unclear and needs to be elucidated.
Session topic: 14. Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Keyword(s): Multiple Myeloma, HIV





