BCR-ABL DEL. C.1086-1270 (P.R362FS*21) AND TKI RESISTANCE IN CML PATIENTS FROM RUSSIAN FEDERATION
(Abstract release date: 05/18/17)
EHA Library. Abdullaev A. 05/18/17; 182521; PB1807

Adhamjon Abdullaev
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: PB1807
Type: Publication Only
Background
Data concerning the impact of BCR-ABL del. c.1086-1270 on TKI resistance in CML is still controversial. This mutation was first described by Curvo et al. (2008) and was thought to confer TKI resistance. However computer modeling performed by Meggyesi N. et al. (2012) revealed disruption of ATP binding site in mutated tyrosine kinase therefore abrogating enzymatic activity. Nevertheless pathogenic effect of BCR-ABL p.R362fs*21 could be attributed to the formation of heterodimer with “wild type” Bcr-Abl р210 as described by Poulikakos P.I. et al. (2011).
Aims
To assess the impact of BCR-ABL del. c.1086-1270 (p.R362fs*21) on TKI resistance in CML patients from Russian Federation.
Methods
33 male and 49 female CML patients (age 24-80) with BCR-ABL transcript level > 0.1% were included in the study. BCR-ABL del. c.1086-1270 was estimated by nested PCR followed by Sanger sequencing. Initial screening for deletions was performed by means of fragment analysis (Applied Biosystems 3130).
Results
92 RNA (cDNA) samples isolated from peripheral blood of 82 CML patients were tested. BCR-ABL del. c.1086-1270 (p.R362fs*21) was found in 32 patients (39%). 15 out of 32 (47%) patients with deletion were TKI sensitive while 17 (55%) were TKI resistant. In one TKI resistant case BCR-ABL del. c.1086-1270 was accompanied by BCR-ABL c.844G˃C p.E282Q point mutation not described so far (Figure 1). This mutation was found in BCR-ABL del. c.1086-1270 transcript only and was absent in “wild type” Bcr-Abl р210 transcript amplified from the same patient.
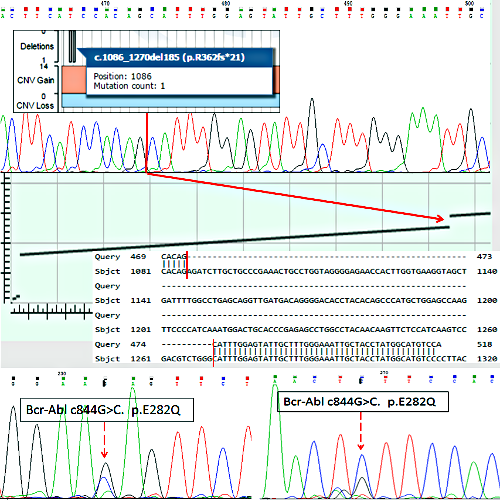
Conclusion
BCR-ABL del. c.1086-1270 could be found in almost half of CML patients and have no evident impact on the induction of big molecular response in TKI sensitive cases. Our observation that independent c.844G˃C p.E282Q point mutation expressed on the same BCR-ABL transcript with deletion c.1086-1270 (p.R362fs*21) being absent in “wild type” transcript strongly contradicts the hypothesis, that del. c.1086-1270 could be generated by alternative splicing of “wild type” BCR-ABL transcript.
Session topic: 7. Chronic myeloid leukemia - Biology
Keyword(s): Mutation, Chronic myeloid leukemia, BCR-ABL
Abstract: PB1807
Type: Publication Only
Background
Data concerning the impact of BCR-ABL del. c.1086-1270 on TKI resistance in CML is still controversial. This mutation was first described by Curvo et al. (2008) and was thought to confer TKI resistance. However computer modeling performed by Meggyesi N. et al. (2012) revealed disruption of ATP binding site in mutated tyrosine kinase therefore abrogating enzymatic activity. Nevertheless pathogenic effect of BCR-ABL p.R362fs*21 could be attributed to the formation of heterodimer with “wild type” Bcr-Abl р210 as described by Poulikakos P.I. et al. (2011).
Aims
To assess the impact of BCR-ABL del. c.1086-1270 (p.R362fs*21) on TKI resistance in CML patients from Russian Federation.
Methods
33 male and 49 female CML patients (age 24-80) with BCR-ABL transcript level > 0.1% were included in the study. BCR-ABL del. c.1086-1270 was estimated by nested PCR followed by Sanger sequencing. Initial screening for deletions was performed by means of fragment analysis (Applied Biosystems 3130).
Results
92 RNA (cDNA) samples isolated from peripheral blood of 82 CML patients were tested. BCR-ABL del. c.1086-1270 (p.R362fs*21) was found in 32 patients (39%). 15 out of 32 (47%) patients with deletion were TKI sensitive while 17 (55%) were TKI resistant. In one TKI resistant case BCR-ABL del. c.1086-1270 was accompanied by BCR-ABL c.844G˃C p.E282Q point mutation not described so far (Figure 1). This mutation was found in BCR-ABL del. c.1086-1270 transcript only and was absent in “wild type” Bcr-Abl р210 transcript amplified from the same patient.

Conclusion
BCR-ABL del. c.1086-1270 could be found in almost half of CML patients and have no evident impact on the induction of big molecular response in TKI sensitive cases. Our observation that independent c.844G˃C p.E282Q point mutation expressed on the same BCR-ABL transcript with deletion c.1086-1270 (p.R362fs*21) being absent in “wild type” transcript strongly contradicts the hypothesis, that del. c.1086-1270 could be generated by alternative splicing of “wild type” BCR-ABL transcript.
Session topic: 7. Chronic myeloid leukemia - Biology
Keyword(s): Mutation, Chronic myeloid leukemia, BCR-ABL
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


