
Contributions
Abstract: PB1683
Type: Publication Only
Background
Cardiotoxicity of chemotherapeutic drugs, in particular anthracycline antibiotics (AA), is one of the biggest problems in treatment of patients with acute leukemia (AL). Chemotherapy with AA is accompanied by systemic endothelial dysfunction, increasing the cardiovascular toxicity risk and promoting vascular complications. Patients with co-morbid ischemic heart disease (IHD) are at extremely high risk of myocardial injury and in need of anthracycline cardiotoxicity (AC) prevention.
Aims
To assess the effectiveness of L-arginine in the prevention of endothelial dysfunction as a predictor of acute AC in patients with AL and co-morbid ischemic heart disease.
Methods
Results
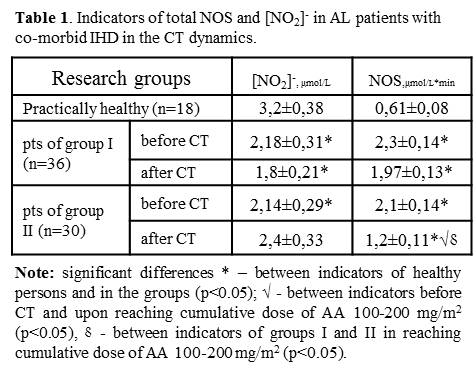
Conclusion
Thus, during the CT with the inclusion of AA without L-arginine in patients with AL and co-morbid IHD we observed the depletion of NO substrate production, accompanied by endothelial dysfunction impairment. The additional appointment of L-arginine on the background of CT can restore synthesis of NO and, respectively, the mechanism of NO-dependent vasodilation, thus reducing the risk of early anthracycline cardiotoxicity development.
Session topic: 4. Acute myeloid leukemia - Clinical
Keyword(s): Prevention, Endothelial dysfunction, Anthracycline, acute leukemia
Abstract: PB1683
Type: Publication Only
Background
Cardiotoxicity of chemotherapeutic drugs, in particular anthracycline antibiotics (AA), is one of the biggest problems in treatment of patients with acute leukemia (AL). Chemotherapy with AA is accompanied by systemic endothelial dysfunction, increasing the cardiovascular toxicity risk and promoting vascular complications. Patients with co-morbid ischemic heart disease (IHD) are at extremely high risk of myocardial injury and in need of anthracycline cardiotoxicity (AC) prevention.
Aims
To assess the effectiveness of L-arginine in the prevention of endothelial dysfunction as a predictor of acute AC in patients with AL and co-morbid ischemic heart disease.
Methods
Results

Conclusion
Thus, during the CT with the inclusion of AA without L-arginine in patients with AL and co-morbid IHD we observed the depletion of NO substrate production, accompanied by endothelial dysfunction impairment. The additional appointment of L-arginine on the background of CT can restore synthesis of NO and, respectively, the mechanism of NO-dependent vasodilation, thus reducing the risk of early anthracycline cardiotoxicity development.
Session topic: 4. Acute myeloid leukemia - Clinical
Keyword(s): Prevention, Endothelial dysfunction, Anthracycline, acute leukemia


