
Contributions
Abstract: PB1665
Type: Publication Only
Background
Aims
We would like to explore a potential synergic effect between JQ1 and Curcumin molecules in the attempt to develop a novel therapeutic alternative to standard chemotherapy and to deeply investigate features underlying the molecular pathogenesis in pediatric MLL-rearranged pediatric AML.
Methods
Results
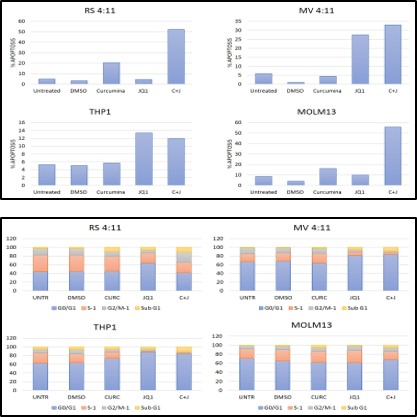
In apoptosis analysis, a synergic effect was detected for all 4 cell lines, similarly cell cycle evaluation showed a significant accumulation of cells at SubG1 phase (2-8 fold) (Figure). XTT metabolic assay showed a reduction in proliferation percentage: 65±5 for curcumin and JQ1 single treatment and 59±5 for combination of drugs in both MLL-AF4 cell lines, meanwhile in MOLM13 cells it was 64±2 and 87±2 for curcumin and JQ1, respectively and 76±2 for their combination (P<0.005). The THP1 cells did not shown any significant modulation in the proliferation. We decided to focus our study on t(4:11) translocated cells, considering the more intense effect of the combined drugs on previous analysis. qRT-PCR and western blot experiments revealed a synergic effect of the 2 experimental drugs on both apoptosis and proliferation gene related (bcl2, caspase3, Parp, cdkn1a) as well as on the direct targets of the drugs (cMyc, AcH3K14). Finally, in MLL-AF4 cell lines, curcumin and JQ1 together induced a significant decrease in mir-99a expression.
Conclusion
Our data demonstrated that curcumin and JQ1, inhibiting HATs and BRD4 respectively, exert a more intense synergic effect on MLL-AF4 than in MLL-AF9 cells. Increased apoptosis together with a reduced proliferation rate, prompted us to investigate on molecular pathway in which targets of these drugs are involved. Intriguingly, we found a significant decrease in cMyc, bcl2 and AcH3K14 expression, confirming that both curcumin and JQ1 have a synergic effect. Additionally, we revealed a significant reduced expression of mir-99a, a well know oncomiR reported to act as negative regulator of differentiation and involved in drug-resistance, typically up-regulated in pediatric AML and ALL.
Session topic: 3. Acute myeloid leukemia - Biology
Keyword(s): Pediatric, MYC, Leukemia cell line, 11q23
Abstract: PB1665
Type: Publication Only
Background
Aims
We would like to explore a potential synergic effect between JQ1 and Curcumin molecules in the attempt to develop a novel therapeutic alternative to standard chemotherapy and to deeply investigate features underlying the molecular pathogenesis in pediatric MLL-rearranged pediatric AML.
Methods
Results
In apoptosis analysis, a synergic effect was detected for all 4 cell lines, similarly cell cycle evaluation showed a significant accumulation of cells at SubG1 phase (2-8 fold) (Figure). XTT metabolic assay showed a reduction in proliferation percentage: 65±5 for curcumin and JQ1 single treatment and 59±5 for combination of drugs in both MLL-AF4 cell lines, meanwhile in MOLM13 cells it was 64±2 and 87±2 for curcumin and JQ1, respectively and 76±2 for their combination (P<0.005). The THP1 cells did not shown any significant modulation in the proliferation. We decided to focus our study on t(4:11) translocated cells, considering the more intense effect of the combined drugs on previous analysis. qRT-PCR and western blot experiments revealed a synergic effect of the 2 experimental drugs on both apoptosis and proliferation gene related (bcl2, caspase3, Parp, cdkn1a) as well as on the direct targets of the drugs (cMyc, AcH3K14). Finally, in MLL-AF4 cell lines, curcumin and JQ1 together induced a significant decrease in mir-99a expression.

Conclusion
Our data demonstrated that curcumin and JQ1, inhibiting HATs and BRD4 respectively, exert a more intense synergic effect on MLL-AF4 than in MLL-AF9 cells. Increased apoptosis together with a reduced proliferation rate, prompted us to investigate on molecular pathway in which targets of these drugs are involved. Intriguingly, we found a significant decrease in cMyc, bcl2 and AcH3K14 expression, confirming that both curcumin and JQ1 have a synergic effect. Additionally, we revealed a significant reduced expression of mir-99a, a well know oncomiR reported to act as negative regulator of differentiation and involved in drug-resistance, typically up-regulated in pediatric AML and ALL.
Session topic: 3. Acute myeloid leukemia - Biology
Keyword(s): Pediatric, MYC, Leukemia cell line, 11q23


