T-CELL RECEPTOR Β (TRB) REPERTOIRE CHARACTERISTICS IN RELAPSED/REFRACTORY (R/R) B-CELL PRECURSOR ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA (BCP-ALL) ON BLINATUMOMAB TREATMENT.
(Abstract release date: 05/18/17)
EHA Library. Knecht H. 06/25/17; 182090; S803

Henrik Knecht
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: S803
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA22: On Sunday, June 25, 2017 from 09:00 - 09:15
Location: Room N103
Background
Blinatumomab (Blin) is a bispecific monoclonal antibody, activating autologous effector T-cells and redirecting them against CD19-positive malignant cells. This leads to polyclonal effector T‑cell expansion which is the necessary component of its antitumour mechanism. Recent reports indicated promising antitumour activity of Blin in relapsed/refractory (r/r) B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL). However, approximately half of these patients do not achieve minimal residual disease (MRD) response.
Thanks to recent advances in next generation sequencing (NGS) of immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene rearrangements the deep and comprehensive evaluation of expanded T-cell repertoire on Blin treatment is now possible.
Aims
To compare the differrences in TRB repertoire diversity and composition between two groups of patients with r/r ALL:
1) responders: reaching MRD negativity at the latest at day 29 of 1. Blin cycle (C1D29), and
2) persisters: with quantifiable MRD positivity (>0.01%) at C1D29, or with MRD > 1% at cycle 1 day 15 (C1D15) if C1D29 sample is not available.
Methods
We used NGS to investigate TRB repertoire in bone marrow samples (114× at time of screening (scr), 74× C1D15, 98× C1D29) of 114 r/r Ph-negative BCP-ALL patients (median age: persisters 47; responders 42; p-value = 0.81). Patients received Blinatumomab within the phase II trial (MT103‑211). Sequencing libraries were prepared using 100ng of DNA via 2-step PCR and sequenced on the Illumina MiSeq (2 x 250bp) with a median coverage of 117,563 reads (range 59.512 - 447.767 reads) per sample. In the first PCR virtually all TRB rearrangements present in the investigated sample were amplified using universal V(D)- and J-regions primers. In the second step, sequencing adaptors and sample-specific barcodes were added.
Annotation of V (D)- and J-regions of TRB sequences was performed using ARResT/Interrogate (Bystry, Bioinformatics, 2016). Diversity of TRB repertoire within patient groups and time points was expressed as the Shannon index, using the R-package vegan. Analysis of variance was employed to assess statistically significant differences in diversity between groups and time.
Results
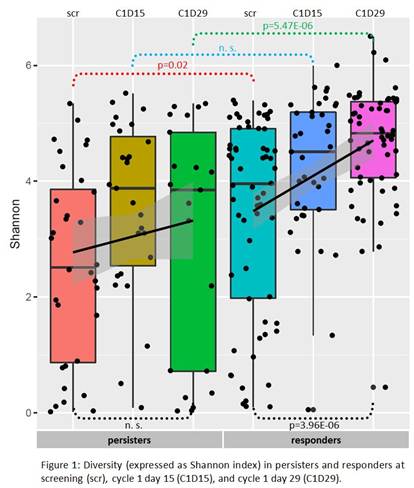
Diversity of TRB repertoire (Fig. 1) was significantly higher in responders at time of scr (p=0.02) and at C1D29 (p=5.47E-6). Patients in the persisters group had significantly higher blast counts, which is in accordance with previously published data (Topp, The Lancet Oncology, 2015). The increase of diversity between scr and C1D29 of Blinatumomab treatment was sharp and highly significant in responders (p=3.96E-6), but not statistically significant in persisters (p=0.4).
Conclusion
We showed that Blin responders have significantly higher TRB repertoire diversity at scr compared to persisters and that the repertoire expansion during Blin treatment is sharper in responders. Other repertoire characteristics did not differ significantly between groups. Further studies on larger patient cohorts are necessary in order to elucidate whether the response to treatment can be predicted by repertoire diversity at scr.
Amplicon NGS is a useful tool for monitoring of T-cell repertoire. Development, standardization, and validation of TRB primer sets is in progress within EuroClonality-NGS Consortium.
Research Support: Amgen
Session topic: 2. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia - Clinical
Abstract: S803
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA22: On Sunday, June 25, 2017 from 09:00 - 09:15
Location: Room N103
Background
Blinatumomab (Blin) is a bispecific monoclonal antibody, activating autologous effector T-cells and redirecting them against CD19-positive malignant cells. This leads to polyclonal effector T‑cell expansion which is the necessary component of its antitumour mechanism. Recent reports indicated promising antitumour activity of Blin in relapsed/refractory (r/r) B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL). However, approximately half of these patients do not achieve minimal residual disease (MRD) response.
Thanks to recent advances in next generation sequencing (NGS) of immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene rearrangements the deep and comprehensive evaluation of expanded T-cell repertoire on Blin treatment is now possible.
Aims
To compare the differrences in TRB repertoire diversity and composition between two groups of patients with r/r ALL:
1) responders: reaching MRD negativity at the latest at day 29 of 1. Blin cycle (C1D29), and
2) persisters: with quantifiable MRD positivity (>0.01%) at C1D29, or with MRD > 1% at cycle 1 day 15 (C1D15) if C1D29 sample is not available.
Methods
We used NGS to investigate TRB repertoire in bone marrow samples (114× at time of screening (scr), 74× C1D15, 98× C1D29) of 114 r/r Ph-negative BCP-ALL patients (median age: persisters 47; responders 42; p-value = 0.81). Patients received Blinatumomab within the phase II trial (MT103‑211). Sequencing libraries were prepared using 100ng of DNA via 2-step PCR and sequenced on the Illumina MiSeq (2 x 250bp) with a median coverage of 117,563 reads (range 59.512 - 447.767 reads) per sample. In the first PCR virtually all TRB rearrangements present in the investigated sample were amplified using universal V(D)- and J-regions primers. In the second step, sequencing adaptors and sample-specific barcodes were added.
Annotation of V (D)- and J-regions of TRB sequences was performed using ARResT/Interrogate (Bystry, Bioinformatics, 2016). Diversity of TRB repertoire within patient groups and time points was expressed as the Shannon index, using the R-package vegan. Analysis of variance was employed to assess statistically significant differences in diversity between groups and time.
Results
Diversity of TRB repertoire (Fig. 1) was significantly higher in responders at time of scr (p=0.02) and at C1D29 (p=5.47E-6). Patients in the persisters group had significantly higher blast counts, which is in accordance with previously published data (Topp, The Lancet Oncology, 2015). The increase of diversity between scr and C1D29 of Blinatumomab treatment was sharp and highly significant in responders (p=3.96E-6), but not statistically significant in persisters (p=0.4).

Conclusion
We showed that Blin responders have significantly higher TRB repertoire diversity at scr compared to persisters and that the repertoire expansion during Blin treatment is sharper in responders. Other repertoire characteristics did not differ significantly between groups. Further studies on larger patient cohorts are necessary in order to elucidate whether the response to treatment can be predicted by repertoire diversity at scr.
Amplicon NGS is a useful tool for monitoring of T-cell repertoire. Development, standardization, and validation of TRB primer sets is in progress within EuroClonality-NGS Consortium.
Research Support: Amgen
Session topic: 2. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia - Clinical
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


