
Contributions
Abstract: S775
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA22: On Sunday, June 25, 2017 from 08:15 - 08:30
Location: Hall C
Background
The Phase III GALLIUM study (NCT01332968) showed that obinutuzumab (GA101; G) significantly prolonged PFS in previously untreated FL pts relative to rituximab (R) when combined with chemotherapy (chemo; CHOP, CVP or bendamustine [B]). Grade 3–5 and serious AEs were more common with G-chemo.
Aims
To explore outcomes by immunochemotherapy regimen.
Methods
Pts were aged ≥18 yrs with documented, previously untreated FL (grades 1–3a), advanced disease (stage III/IV or stage II with tumor diameter ≥7cm), ECOG PS 0–2, and requiring treatment according to GELF criteria. Chemo regimen was allocated by center. Pts were randomized 1:1 (stratified by chemo, FLIPI-1 group and geographic region) to R 375mg/m2 on day (D) 1 of each cycle (C) or G 1000mg on D1, 8 and 15 of C1 and D1 of C2–8, for 6 or 8 cycles depending on chemo. Pts with CR or PR at EOI (per Cheson 2007) continued to receive R or G every 2 months for 2 yrs or until progression. The cut-off date for this analysis was September 10 2016. All pts gave informed consent.
Results
Table. Safety summary (number (%) of FL pts* with ≥1 AE) | ||||||||
G-B(n=338) | R-B(n=338) | G-CHOP(n=193) | R-CHOP(n=203) | G-CVP(n=61) | R-CVP(n=56) | G-chemo(n=595) | R-chemo(n=597) | |
AEs | 338(100) | 331(97.9) | 191(99.0) | 201(99.0) | 61(100) | 56(100) | 593(99.7) | 585(98.0) |
Grade 3–5 AEs | 233(68.9) | 228(67.5) | 171(88.6) | 151(74.4) | 42(68.9) | 30(53.6) | 449(75.5) | 409(68.5) |
Neutropenia† | 100(29.6) | 102(30.2) | 137(71.0) | 111(54.7) | 28(45.9) | 13(23.2) | 265(44.5) | 226(37.9) |
Leucopenia† | 11(3.3) | 15(4.4) | 39(20.2) | 34(16.7) | 1(1.6) | 1(1.8) | 51(8.6) | 50(8.4) |
Febrile neutropenia† | 18(5.3) | 13(3.8) | 22(11.4) | 14(6.9) | 2(3.3) | 2(3.6) | 42(7.1) | 29(4.9) |
AEs of special interest by category | ||||||||
Grade 3–5 Infections‡ | 89(26.3) | 66(19.5) | 23(11.9) | 24(12.4) | 8(13.1) | 7(12.5) | 121(20.3) | 98(16.4) |
Second neoplasms§ | 37(10.9) | 23(6.8) | 9(4.7) | 11(5.4) | 1(1.6) | 2(3.6) | 47(7.9) | 36(6.0) |
SAEs | 176(52.1) | 160(47.3) | 76(39.4) | 67(33.0) | 26(42.6) | 19(33.9) | 281(47.2) | 246(41.2) |
Fatal AEs | 20(5.9) | 16(4.7) | 3(1.6) | 4(2.0) | 1(1.6) | 1(1.8) | 24(4.0) | 21(3.5) |
AEs causing Tx discontinuation | 52(15.4) | 48(14.2) | 32(16.6) | 31(15.3) | 11(18.0) | 9(16.1) | 98(16.5) | 88(14.7) |
*Pts who received ≥1 dose of study drug. Three pts received G but no chemo; †Occurring in >10% of pts in any group; ‡MedDRA SOC ‘Infections and Infestations’; §Malignant or unspecified tumors occurring >6 mo after first study drug intake | ||||||||
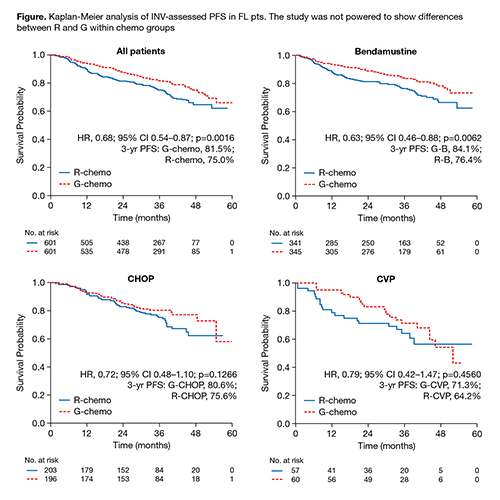
Conclusion
In treatment-naive FL pts, PFS was superior with G-chemo relative to R-chemo with consistent effects across chemo regimens. Some differences were seen in safety profiles between chemo regimens, but comparisons may be confounded by the lack of randomization.
Session topic: 19. Indolent Non-Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Keyword(s): Obinutuzumab, Follicular lymphoma, Rituximab
Abstract: S775
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA22: On Sunday, June 25, 2017 from 08:15 - 08:30
Location: Hall C
Background
The Phase III GALLIUM study (NCT01332968) showed that obinutuzumab (GA101; G) significantly prolonged PFS in previously untreated FL pts relative to rituximab (R) when combined with chemotherapy (chemo; CHOP, CVP or bendamustine [B]). Grade 3–5 and serious AEs were more common with G-chemo.
Aims
To explore outcomes by immunochemotherapy regimen.
Methods
Pts were aged ≥18 yrs with documented, previously untreated FL (grades 1–3a), advanced disease (stage III/IV or stage II with tumor diameter ≥7cm), ECOG PS 0–2, and requiring treatment according to GELF criteria. Chemo regimen was allocated by center. Pts were randomized 1:1 (stratified by chemo, FLIPI-1 group and geographic region) to R 375mg/m2 on day (D) 1 of each cycle (C) or G 1000mg on D1, 8 and 15 of C1 and D1 of C2–8, for 6 or 8 cycles depending on chemo. Pts with CR or PR at EOI (per Cheson 2007) continued to receive R or G every 2 months for 2 yrs or until progression. The cut-off date for this analysis was September 10 2016. All pts gave informed consent.
Results
Table. Safety summary (number (%) of FL pts* with ≥1 AE) | ||||||||
G-B(n=338) | R-B(n=338) | G-CHOP(n=193) | R-CHOP(n=203) | G-CVP(n=61) | R-CVP(n=56) | G-chemo(n=595) | R-chemo(n=597) | |
AEs | 338(100) | 331(97.9) | 191(99.0) | 201(99.0) | 61(100) | 56(100) | 593(99.7) | 585(98.0) |
Grade 3–5 AEs | 233(68.9) | 228(67.5) | 171(88.6) | 151(74.4) | 42(68.9) | 30(53.6) | 449(75.5) | 409(68.5) |
Neutropenia† | 100(29.6) | 102(30.2) | 137(71.0) | 111(54.7) | 28(45.9) | 13(23.2) | 265(44.5) | 226(37.9) |
Leucopenia† | 11(3.3) | 15(4.4) | 39(20.2) | 34(16.7) | 1(1.6) | 1(1.8) | 51(8.6) | 50(8.4) |
Febrile neutropenia† | 18(5.3) | 13(3.8) | 22(11.4) | 14(6.9) | 2(3.3) | 2(3.6) | 42(7.1) | 29(4.9) |
AEs of special interest by category | ||||||||
Grade 3–5 Infections‡ | 89(26.3) | 66(19.5) | 23(11.9) | 24(12.4) | 8(13.1) | 7(12.5) | 121(20.3) | 98(16.4) |
Second neoplasms§ | 37(10.9) | 23(6.8) | 9(4.7) | 11(5.4) | 1(1.6) | 2(3.6) | 47(7.9) | 36(6.0) |
SAEs | 176(52.1) | 160(47.3) | 76(39.4) | 67(33.0) | 26(42.6) | 19(33.9) | 281(47.2) | 246(41.2) |
Fatal AEs | 20(5.9) | 16(4.7) | 3(1.6) | 4(2.0) | 1(1.6) | 1(1.8) | 24(4.0) | 21(3.5) |
AEs causing Tx discontinuation | 52(15.4) | 48(14.2) | 32(16.6) | 31(15.3) | 11(18.0) | 9(16.1) | 98(16.5) | 88(14.7) |
*Pts who received ≥1 dose of study drug. Three pts received G but no chemo; †Occurring in >10% of pts in any group; ‡MedDRA SOC ‘Infections and Infestations’; §Malignant or unspecified tumors occurring >6 mo after first study drug intake | ||||||||

Conclusion
In treatment-naive FL pts, PFS was superior with G-chemo relative to R-chemo with consistent effects across chemo regimens. Some differences were seen in safety profiles between chemo regimens, but comparisons may be confounded by the lack of randomization.
Session topic: 19. Indolent Non-Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Keyword(s): Obinutuzumab, Follicular lymphoma, Rituximab


