
Contributions
Abstract: S501
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA22: On Saturday, June 24, 2017 from 16:00 - 16:15
Location: Room N109
Background
We recently reported the results of the phase III randomized HOVON87/NMSG18 study showing comparable efficacy of treatment with melphalan, prednisolone and thalidomide following by thalidomide maintenance (MPT-T) versus melphalan, prednisolone and lenalidomide followed by lenalidomide maintenance (MPR-R) (Zweegman S et al. Blood 2016;127(9):1109-1116). As not only efficacy but also potential toxicity affecting quality of life (QoL) guides the choice of treatment, health-related (HR) QoL is important.
Aims
Methods
Results
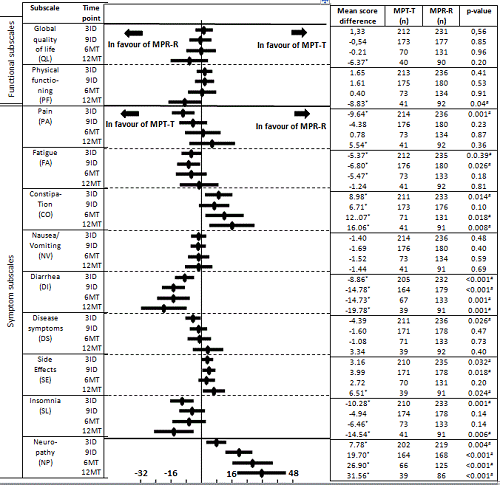
Change in HRQoL per arm: In MPT-T MID was reached for the following subscales; global QoL increased after 9ID until 12MT (MID range 7-13), pain decreased at every time point (MID range -21 to -23), disease symptoms deceased after 9ID (MID -12), fatigue decreased during MT (MID 12) and insomnia decreased at each time point (MID range -11 to -21). In MPR-R the MID was reached for the following subscales; global QoL increased after 9ID until 12MT (MID range 8-14), physical functioning increased at 12MT (MID 13), pain decreased at every time point (MID range -14 to -26) and insomnia decreased at 6MT (MID -10).
Difference between MPT-T and MPR-R: In the MPT-T arm significantly (p<0.05) and/or clinically (mean score difference (MSD) ≥5 points) less pain and disease symptoms at 3ID, less fatigue at 3ID and 9ID, less diarrhea and less insomnia at all time points were observed. In contrast, patients on MPR-R reported better global QoL, better physical functioning and less pain at 12MT, in general less side effects of treatment, and less constipation and neuropathy separately, at all time points than patients treated with MPT-T.
Conclusion
Session topic: 35. Quality of life, palliative care, ethics and health economics
Keyword(s): Thalidomide, Quality of Life, Multiple Myeloma
Abstract: S501
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA22: On Saturday, June 24, 2017 from 16:00 - 16:15
Location: Room N109
Background
We recently reported the results of the phase III randomized HOVON87/NMSG18 study showing comparable efficacy of treatment with melphalan, prednisolone and thalidomide following by thalidomide maintenance (MPT-T) versus melphalan, prednisolone and lenalidomide followed by lenalidomide maintenance (MPR-R) (Zweegman S et al. Blood 2016;127(9):1109-1116). As not only efficacy but also potential toxicity affecting quality of life (QoL) guides the choice of treatment, health-related (HR) QoL is important.
Aims
Methods
Results
Change in HRQoL per arm: In MPT-T MID was reached for the following subscales; global QoL increased after 9ID until 12MT (MID range 7-13), pain decreased at every time point (MID range -21 to -23), disease symptoms deceased after 9ID (MID -12), fatigue decreased during MT (MID 12) and insomnia decreased at each time point (MID range -11 to -21). In MPR-R the MID was reached for the following subscales; global QoL increased after 9ID until 12MT (MID range 8-14), physical functioning increased at 12MT (MID 13), pain decreased at every time point (MID range -14 to -26) and insomnia decreased at 6MT (MID -10).
Difference between MPT-T and MPR-R: In the MPT-T arm significantly (p<0.05) and/or clinically (mean score difference (MSD) ≥5 points) less pain and disease symptoms at 3ID, less fatigue at 3ID and 9ID, less diarrhea and less insomnia at all time points were observed. In contrast, patients on MPR-R reported better global QoL, better physical functioning and less pain at 12MT, in general less side effects of treatment, and less constipation and neuropathy separately, at all time points than patients treated with MPT-T.

Conclusion
Session topic: 35. Quality of life, palliative care, ethics and health economics
Keyword(s): Thalidomide, Quality of Life, Multiple Myeloma


