
Contributions
Abstract: S490
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA22: On Saturday, June 24, 2017 from 17:00 - 17:15
Location: Room N105
Background
As key factors in gene post-transcriptional regulation, microRNAs(miRNAs) have been identified to play important roles in carcinogenesis in various tumors. Myelodysplastic syndrome(MDS) is a group of clonal myeloid disorders characterized by refractory quantitative and qualitative abnormalities of hemocytes and its pathogenesis is poorly understood. Some studies have showed that abnormal expressions of some miRNAs have close relationship with the pathogenesis of MDS. Recently, low RPS14 expression is found common in all kinds of myelodysplastic syndromes including patients without 5q deletion, but its mechanism remains unclear.
Aims
To determine the cause of RPS14 reduction in MDS except 5q- syndrome, influence of miRNAs on RPS14 expression was analyzed, and the role of specific miRNA on proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis of hematopoietic stem cells were evaluated. This research will help reveal the pathogenesis of MDS from a new angle and provide new ideas for the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis evaluation of MDS.
Methods
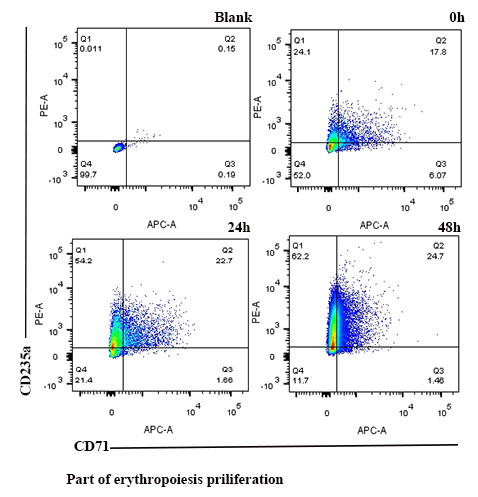
Firstly, we predicted that miR-223 may target 3’UTR of RPS14 by bioinformatics software, then verified if the special miRNA could target RPS14 by assay of luciferase activity. Secondly, the mRNA expression level of miR223 were detected in the bone marrow(BM)selected from 28 MDS patients including ten RCUD patients, ten RCMD patients, four RAEB-1 patients and four RAEB-2 patients, meanwhile, the miR223 expression status were tested in four kinds cell lines including SKM-1, HL-60,K562 and THP-1 cell lines through qRT-PCR and RPS14 expression was detected by means of immunofluorescence(IF). Thirdly, constructing lentivirus which carried miR223 overexpression vector and inhibitor were infected to the SKM-1 cell line and k562 cell line which had the highest level of RPS14, then apoptotic analysis was detected by flow cytometry method and proliferation was tested by CCK-8 assay. Fourthly, hemin (50 μM,) was used to induce erythroid differentiation of K562 cells which carried miR223 overexpression We used flow cytometry method(CD71 and CD235a makers)and qRT-PCR(CD235 and r-globin) to detect the erythroid proliferation
Results
1.We verified miR223 could target RPS14 by assay of luciferase activity.
Conclusion
MDS patients had higher miR-223 expression compared with health controls. We demonstrated that miR223 could promote cell proliferation, inhibit cell apoptosis and suppress terminal erythropoiesis through target RPS14
Session topic: 10. Myelodysplastic syndromes - Clinical
Keyword(s): MDS
Abstract: S490
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA22: On Saturday, June 24, 2017 from 17:00 - 17:15
Location: Room N105
Background
As key factors in gene post-transcriptional regulation, microRNAs(miRNAs) have been identified to play important roles in carcinogenesis in various tumors. Myelodysplastic syndrome(MDS) is a group of clonal myeloid disorders characterized by refractory quantitative and qualitative abnormalities of hemocytes and its pathogenesis is poorly understood. Some studies have showed that abnormal expressions of some miRNAs have close relationship with the pathogenesis of MDS. Recently, low RPS14 expression is found common in all kinds of myelodysplastic syndromes including patients without 5q deletion, but its mechanism remains unclear.
Aims
To determine the cause of RPS14 reduction in MDS except 5q- syndrome, influence of miRNAs on RPS14 expression was analyzed, and the role of specific miRNA on proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis of hematopoietic stem cells were evaluated. This research will help reveal the pathogenesis of MDS from a new angle and provide new ideas for the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis evaluation of MDS.
Methods
Firstly, we predicted that miR-223 may target 3’UTR of RPS14 by bioinformatics software, then verified if the special miRNA could target RPS14 by assay of luciferase activity. Secondly, the mRNA expression level of miR223 were detected in the bone marrow(BM)selected from 28 MDS patients including ten RCUD patients, ten RCMD patients, four RAEB-1 patients and four RAEB-2 patients, meanwhile, the miR223 expression status were tested in four kinds cell lines including SKM-1, HL-60,K562 and THP-1 cell lines through qRT-PCR and RPS14 expression was detected by means of immunofluorescence(IF). Thirdly, constructing lentivirus which carried miR223 overexpression vector and inhibitor were infected to the SKM-1 cell line and k562 cell line which had the highest level of RPS14, then apoptotic analysis was detected by flow cytometry method and proliferation was tested by CCK-8 assay. Fourthly, hemin (50 μM,) was used to induce erythroid differentiation of K562 cells which carried miR223 overexpression We used flow cytometry method(CD71 and CD235a makers)and qRT-PCR(CD235 and r-globin) to detect the erythroid proliferation
Results
1.We verified miR223 could target RPS14 by assay of luciferase activity.

Conclusion
MDS patients had higher miR-223 expression compared with health controls. We demonstrated that miR223 could promote cell proliferation, inhibit cell apoptosis and suppress terminal erythropoiesis through target RPS14
Session topic: 10. Myelodysplastic syndromes - Clinical
Keyword(s): MDS


