
Contributions
Abstract: S478
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA22: On Saturday, June 24, 2017 from 16:30 - 16:45
Location: Hall E
Background
Adults with B-cell precursor (BCP) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) often relapse following standard induction/consolidation chemotherapy (CTX). Prognosis following second and successive CTX salvage regimens (S2+) is poor compared with first salvage (S1) or frontline therapy, with less favorable outcomes among patients with shorter CR duration. Blinatumomab links cytotoxic CD3-positive T cells and CD19-positive B cells to induce tumor cell lysis. In a randomized phase 3 trial of blinatumomab vs investigator’s choice of 4 standard of care CTX (SOC) regimens, median OS was 7.7 months in the blinatumomab group vs 4.0 months with SOC (Kantarjian H, et al., NEJM 2017). Here, we evaluate outcomes by salvage status for patients in this study (NCT02013167).
Aims
To evaluate responses to blinatumomab vs SOC in patients with relapsed/refractory ALL by prior salvage therapy status.
Methods
Patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) BCP-ALL in this international multicenter trial were randomized 2:1 to blinatumomab (n=271) or SOC (n=134). For this analysis, salvage status was adjudicated separately from prior randomization strata. Blinatumomab was given by continuous IV infusion (9 µg/d in week 1 of cycle 1, then 28 µg/d) in cycles of 4 weeks on, 2 weeks off. The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS), determined from time of randomization until death due to any cause. Adverse events (AE) of interest were coded according to MedDRA version 16.0.
Results
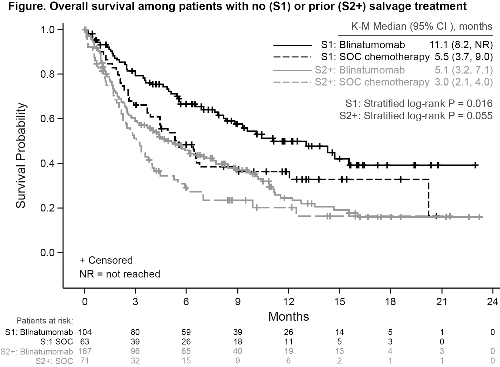
At baseline, patient characteristics were balanced between groups within salvage designations. The rate of complete remission, with or without full hematologic recovery (CR/CRh/CRi) in both the S1 and S2+ groups was higher in the blinatumomab arm compared with the SOC arm (Table).
No prior salvage (S1) | Any prior salvage (S2+) | |||
Blinatumomab (n=104) | SOC (n=63) | Blinatumomab (n=167) | SOC (n=71) | |
Age ≥35 years, n (%) | 65 (62.5) | 37 (58.7) | 82 (49.1) | 37 (52.1) |
Prior HSCT, n (%) | 29 (27.9) | 20 (31.7) | 65 (38.9) | 26 (36.6) |
First relapse with remission duration <12 mo, n (%) | 58 (55.8) | 30 (47.6) | 51 (30.5) | 19 (26.8) |
Maximum blasts ≥50% by central/local lab, n (%) | 78 (75.0) | 45 (71.4) | 123 (73.7) | 59 (83.1) |
K-M Median OS, mo (95% CI) | 11.1 (8.2, NR)* | 5.5 (3.7, 9.0) | 5.1 (3.2, 7.1) | 3.0 (2.1, 4.0) |
HR 0.59 (95% CI 0.38, 0.91) P=0.016 | HR 0.72 (95% CI 0.51, 1.01) P=0.055 | |||
Best response (CR/CR/CRi), n (%) [95% CI] | 53 (51.0) [41.0, 60.9] | 23 (36.5) [24.7, 49.6] | 66 (39.5) [32.1, 47.4] | 10 (14.1) [7.0, 24.4] |
P=0.07 | P<0.001 | |||
Conclusion
Patients in this trial receiving blinatumomab for R/R ALL achieved improved OS and remission rates compared with SOC regardless of prior salvage therapy. Improved OS compared with SOC in S1 patients supports earlier use of blinatumomab.
Session topic: 2. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia - Clinical
Keyword(s): Immunotherapy, Salvage therapy, Relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract: S478
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA22: On Saturday, June 24, 2017 from 16:30 - 16:45
Location: Hall E
Background
Adults with B-cell precursor (BCP) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) often relapse following standard induction/consolidation chemotherapy (CTX). Prognosis following second and successive CTX salvage regimens (S2+) is poor compared with first salvage (S1) or frontline therapy, with less favorable outcomes among patients with shorter CR duration. Blinatumomab links cytotoxic CD3-positive T cells and CD19-positive B cells to induce tumor cell lysis. In a randomized phase 3 trial of blinatumomab vs investigator’s choice of 4 standard of care CTX (SOC) regimens, median OS was 7.7 months in the blinatumomab group vs 4.0 months with SOC (Kantarjian H, et al., NEJM 2017). Here, we evaluate outcomes by salvage status for patients in this study (NCT02013167).
Aims
To evaluate responses to blinatumomab vs SOC in patients with relapsed/refractory ALL by prior salvage therapy status.
Methods
Patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) BCP-ALL in this international multicenter trial were randomized 2:1 to blinatumomab (n=271) or SOC (n=134). For this analysis, salvage status was adjudicated separately from prior randomization strata. Blinatumomab was given by continuous IV infusion (9 µg/d in week 1 of cycle 1, then 28 µg/d) in cycles of 4 weeks on, 2 weeks off. The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS), determined from time of randomization until death due to any cause. Adverse events (AE) of interest were coded according to MedDRA version 16.0.
Results
At baseline, patient characteristics were balanced between groups within salvage designations. The rate of complete remission, with or without full hematologic recovery (CR/CRh/CRi) in both the S1 and S2+ groups was higher in the blinatumomab arm compared with the SOC arm (Table).
No prior salvage (S1) | Any prior salvage (S2+) | |||
Blinatumomab (n=104) | SOC (n=63) | Blinatumomab (n=167) | SOC (n=71) | |
Age ≥35 years, n (%) | 65 (62.5) | 37 (58.7) | 82 (49.1) | 37 (52.1) |
Prior HSCT, n (%) | 29 (27.9) | 20 (31.7) | 65 (38.9) | 26 (36.6) |
First relapse with remission duration <12 mo, n (%) | 58 (55.8) | 30 (47.6) | 51 (30.5) | 19 (26.8) |
Maximum blasts ≥50% by central/local lab, n (%) | 78 (75.0) | 45 (71.4) | 123 (73.7) | 59 (83.1) |
K-M Median OS, mo (95% CI) | 11.1 (8.2, NR)* | 5.5 (3.7, 9.0) | 5.1 (3.2, 7.1) | 3.0 (2.1, 4.0) |
HR 0.59 (95% CI 0.38, 0.91) P=0.016 | HR 0.72 (95% CI 0.51, 1.01) P=0.055 | |||
Best response (CR/CR/CRi), n (%) [95% CI] | 53 (51.0) [41.0, 60.9] | 23 (36.5) [24.7, 49.6] | 66 (39.5) [32.1, 47.4] | 10 (14.1) [7.0, 24.4] |
P=0.07 | P<0.001 | |||

Conclusion
Patients in this trial receiving blinatumomab for R/R ALL achieved improved OS and remission rates compared with SOC regardless of prior salvage therapy. Improved OS compared with SOC in S1 patients supports earlier use of blinatumomab.
Session topic: 2. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia - Clinical
Keyword(s): Immunotherapy, Salvage therapy, Relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia


