INDUCTION OF NA
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Chiou T. 06/10/16; 135160; S127

Prof. Dr. Tzeon-Jye Chiou
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: S127
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA21: On Friday, June 10, 2016 from 12:30 - 12:45
Location: Hall C13
Background
Allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) has been used to treat some of haematological malignancies and inherited or acquired non-malignant diseases. Unfortunately, graft-versus-host disease (GVDH) occurred approximately 15% in transplant recipients and decreases the success of allogeneic HSCT. At present, no effective treatment can completely prevent the GVHD from allogeneic HSCT patients. CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) have been shown to be important in maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing autoimmunity. However, 5% to 10% Tregs could be measured in human CD4+ T cells and few Tregs would convert to conventional activated T cells because of losing FoxP3 expression. It had been reported to correlate with the occurrence and severity of GVHD in some study.
Aims
In order to study the potential use of Treg cells for GVHD prevention, we attempt to evaluate the better method to increase the number of induced Treg cells (iTregs) in donor’s PB and stabilize the FoxP3 in iTreg cells. To isolate the effective CD4+CD25+Foxp3+CD127-iTreg cells for clinical application and to establish a quick method to identify the functional iTreg cells is the study goal. Therefore, naïve T cells isolation for regulatory T cell induction is an important issue.
Methods
Mouse splenocytes were prepared from mouse spleen. Human PBSC were prepared from peripheral blood (PB) of healthy donors by Ficoll-Hypaque density gradient centrifugation. All T cells were isolated by negative selection; then CD4+naïve T cells were harvested. After that, the CD4+naïve T cells were activated by anti-CD3/CD28 beads in the presence of IL-2, TGF-β and retinoic acid (RA) containing RPMI1640 medium. The cells cultured with 3-day-nutrient-deprived medium (only 5% FBS), then refreshed the cells into the full nutrient supplement (10% FBS) for another 5 days. The harvested cells were analyzed by flow cytometry method with fluorescence-conjugated CD-antibodies, including CD4, CD25, CD127 and FoxP3. After trypanblue staining, the number of iTreg cell was counted by hemacytometer. The iTreg cells also harvested and the expression of functional marker genes in iTreg cells were analyzed via qPCR.
Results
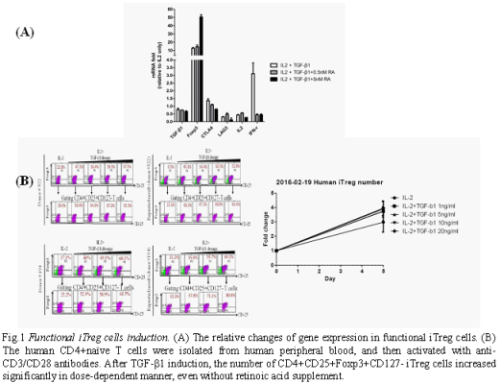
In nutrient-deprived (5% FBS for 3 days in advance) culture system, we found the TGF-β triggered the mouse iTreg cells formation in a dose-dependent manner and increased iTreg cells formation efficiency under retinoic acid condition. Our data showed that we could induce the CD4+CD25+Foxp3+CD127-iTreg cells more than 90%. The supplement of retinoic acid (0.1 and 0.5 nM) stabilized the FoxP3+ gene expression in iTregs during this incubation period; and the stability of FoxP3 expression and iTreg cell number could be maintained at least 12 days in vitro. The stability of iTreg cells is an important criterion for clinical use. Furthermore, we have analyzed the FoxP3 gene and the bio-functional marker genes expression in iTreg cells to confirm the functional cells (Fig.1A). Based on these results, we consider the human T cells should be used. Therefore, we have investigated the human regulatory T cell induction. Human CD4+ naïve T cells were isolated from PB and activated via antibodies. The CD4+CD25+Foxp3+CD127-iTreg cells were induced to around 60~80% under IL-2 and TGF-β1 containing media, even without retinoic acid supplement (Fig.1B). It indicated we could harvest more iTreg cells under such condition. As we know, nTreg could suppress the induction of iTreg in vivo; further, we should remove the nTreg for improving the iTreg formation under cytokines supplement condition.
Conclusion
Our study showed that the combination of IL-2, TGF-β1 and RA in 3-day-nutrient-deprived medium could convert CD4+naïve T cells to CD4+CD25+FoxP3+CD127- iTreg cells and stabilize FoxP3 expression in the iTreg cells markedly. Further, we use the marker genes to clarify the biological function of iTregs in vitro. It may be to identify the functional iTreg cells quickly, after iTreg cells induction. Based on this method, we could harvest more and effective iTreg cells ready for use. It should be helpful for clinical application. GVHD mouse model will be established by using allogeneic HSCT to verify iTreg’s function in vivo.
Session topic: Stem cell transplantation - Experimental
Keyword(s): Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), T cell activation, T regulatory cells
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA21: On Friday, June 10, 2016 from 12:30 - 12:45
Location: Hall C13
Background
Allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) has been used to treat some of haematological malignancies and inherited or acquired non-malignant diseases. Unfortunately, graft-versus-host disease (GVDH) occurred approximately 15% in transplant recipients and decreases the success of allogeneic HSCT. At present, no effective treatment can completely prevent the GVHD from allogeneic HSCT patients. CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) have been shown to be important in maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing autoimmunity. However, 5% to 10% Tregs could be measured in human CD4+ T cells and few Tregs would convert to conventional activated T cells because of losing FoxP3 expression. It had been reported to correlate with the occurrence and severity of GVHD in some study.
Aims
In order to study the potential use of Treg cells for GVHD prevention, we attempt to evaluate the better method to increase the number of induced Treg cells (iTregs) in donor’s PB and stabilize the FoxP3 in iTreg cells. To isolate the effective CD4+CD25+Foxp3+CD127-iTreg cells for clinical application and to establish a quick method to identify the functional iTreg cells is the study goal. Therefore, naïve T cells isolation for regulatory T cell induction is an important issue.
Methods
Mouse splenocytes were prepared from mouse spleen. Human PBSC were prepared from peripheral blood (PB) of healthy donors by Ficoll-Hypaque density gradient centrifugation. All T cells were isolated by negative selection; then CD4+naïve T cells were harvested. After that, the CD4+naïve T cells were activated by anti-CD3/CD28 beads in the presence of IL-2, TGF-β and retinoic acid (RA) containing RPMI1640 medium. The cells cultured with 3-day-nutrient-deprived medium (only 5% FBS), then refreshed the cells into the full nutrient supplement (10% FBS) for another 5 days. The harvested cells were analyzed by flow cytometry method with fluorescence-conjugated CD-antibodies, including CD4, CD25, CD127 and FoxP3. After trypanblue staining, the number of iTreg cell was counted by hemacytometer. The iTreg cells also harvested and the expression of functional marker genes in iTreg cells were analyzed via qPCR.
Results
In nutrient-deprived (5% FBS for 3 days in advance) culture system, we found the TGF-β triggered the mouse iTreg cells formation in a dose-dependent manner and increased iTreg cells formation efficiency under retinoic acid condition. Our data showed that we could induce the CD4+CD25+Foxp3+CD127-iTreg cells more than 90%. The supplement of retinoic acid (0.1 and 0.5 nM) stabilized the FoxP3+ gene expression in iTregs during this incubation period; and the stability of FoxP3 expression and iTreg cell number could be maintained at least 12 days in vitro. The stability of iTreg cells is an important criterion for clinical use. Furthermore, we have analyzed the FoxP3 gene and the bio-functional marker genes expression in iTreg cells to confirm the functional cells (Fig.1A). Based on these results, we consider the human T cells should be used. Therefore, we have investigated the human regulatory T cell induction. Human CD4+ naïve T cells were isolated from PB and activated via antibodies. The CD4+CD25+Foxp3+CD127-iTreg cells were induced to around 60~80% under IL-2 and TGF-β1 containing media, even without retinoic acid supplement (Fig.1B). It indicated we could harvest more iTreg cells under such condition. As we know, nTreg could suppress the induction of iTreg in vivo; further, we should remove the nTreg for improving the iTreg formation under cytokines supplement condition.
Conclusion
Our study showed that the combination of IL-2, TGF-β1 and RA in 3-day-nutrient-deprived medium could convert CD4+naïve T cells to CD4+CD25+FoxP3+CD127- iTreg cells and stabilize FoxP3 expression in the iTreg cells markedly. Further, we use the marker genes to clarify the biological function of iTregs in vitro. It may be to identify the functional iTreg cells quickly, after iTreg cells induction. Based on this method, we could harvest more and effective iTreg cells ready for use. It should be helpful for clinical application. GVHD mouse model will be established by using allogeneic HSCT to verify iTreg’s function in vivo.

Session topic: Stem cell transplantation - Experimental
Keyword(s): Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), T cell activation, T regulatory cells
Abstract: S127
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA21: On Friday, June 10, 2016 from 12:30 - 12:45
Location: Hall C13
Background
Allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) has been used to treat some of haematological malignancies and inherited or acquired non-malignant diseases. Unfortunately, graft-versus-host disease (GVDH) occurred approximately 15% in transplant recipients and decreases the success of allogeneic HSCT. At present, no effective treatment can completely prevent the GVHD from allogeneic HSCT patients. CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) have been shown to be important in maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing autoimmunity. However, 5% to 10% Tregs could be measured in human CD4+ T cells and few Tregs would convert to conventional activated T cells because of losing FoxP3 expression. It had been reported to correlate with the occurrence and severity of GVHD in some study.
Aims
In order to study the potential use of Treg cells for GVHD prevention, we attempt to evaluate the better method to increase the number of induced Treg cells (iTregs) in donor’s PB and stabilize the FoxP3 in iTreg cells. To isolate the effective CD4+CD25+Foxp3+CD127-iTreg cells for clinical application and to establish a quick method to identify the functional iTreg cells is the study goal. Therefore, naïve T cells isolation for regulatory T cell induction is an important issue.
Methods
Mouse splenocytes were prepared from mouse spleen. Human PBSC were prepared from peripheral blood (PB) of healthy donors by Ficoll-Hypaque density gradient centrifugation. All T cells were isolated by negative selection; then CD4+naïve T cells were harvested. After that, the CD4+naïve T cells were activated by anti-CD3/CD28 beads in the presence of IL-2, TGF-β and retinoic acid (RA) containing RPMI1640 medium. The cells cultured with 3-day-nutrient-deprived medium (only 5% FBS), then refreshed the cells into the full nutrient supplement (10% FBS) for another 5 days. The harvested cells were analyzed by flow cytometry method with fluorescence-conjugated CD-antibodies, including CD4, CD25, CD127 and FoxP3. After trypanblue staining, the number of iTreg cell was counted by hemacytometer. The iTreg cells also harvested and the expression of functional marker genes in iTreg cells were analyzed via qPCR.
Results
In nutrient-deprived (5% FBS for 3 days in advance) culture system, we found the TGF-β triggered the mouse iTreg cells formation in a dose-dependent manner and increased iTreg cells formation efficiency under retinoic acid condition. Our data showed that we could induce the CD4+CD25+Foxp3+CD127-iTreg cells more than 90%. The supplement of retinoic acid (0.1 and 0.5 nM) stabilized the FoxP3+ gene expression in iTregs during this incubation period; and the stability of FoxP3 expression and iTreg cell number could be maintained at least 12 days in vitro. The stability of iTreg cells is an important criterion for clinical use. Furthermore, we have analyzed the FoxP3 gene and the bio-functional marker genes expression in iTreg cells to confirm the functional cells (Fig.1A). Based on these results, we consider the human T cells should be used. Therefore, we have investigated the human regulatory T cell induction. Human CD4+ naïve T cells were isolated from PB and activated via antibodies. The CD4+CD25+Foxp3+CD127-iTreg cells were induced to around 60~80% under IL-2 and TGF-β1 containing media, even without retinoic acid supplement (Fig.1B). It indicated we could harvest more iTreg cells under such condition. As we know, nTreg could suppress the induction of iTreg in vivo; further, we should remove the nTreg for improving the iTreg formation under cytokines supplement condition.
Conclusion
Our study showed that the combination of IL-2, TGF-β1 and RA in 3-day-nutrient-deprived medium could convert CD4+naïve T cells to CD4+CD25+FoxP3+CD127- iTreg cells and stabilize FoxP3 expression in the iTreg cells markedly. Further, we use the marker genes to clarify the biological function of iTregs in vitro. It may be to identify the functional iTreg cells quickly, after iTreg cells induction. Based on this method, we could harvest more and effective iTreg cells ready for use. It should be helpful for clinical application. GVHD mouse model will be established by using allogeneic HSCT to verify iTreg’s function in vivo.

Session topic: Stem cell transplantation - Experimental
Keyword(s): Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), T cell activation, T regulatory cells
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA21: On Friday, June 10, 2016 from 12:30 - 12:45
Location: Hall C13
Background
Allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) has been used to treat some of haematological malignancies and inherited or acquired non-malignant diseases. Unfortunately, graft-versus-host disease (GVDH) occurred approximately 15% in transplant recipients and decreases the success of allogeneic HSCT. At present, no effective treatment can completely prevent the GVHD from allogeneic HSCT patients. CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) have been shown to be important in maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing autoimmunity. However, 5% to 10% Tregs could be measured in human CD4+ T cells and few Tregs would convert to conventional activated T cells because of losing FoxP3 expression. It had been reported to correlate with the occurrence and severity of GVHD in some study.
Aims
In order to study the potential use of Treg cells for GVHD prevention, we attempt to evaluate the better method to increase the number of induced Treg cells (iTregs) in donor’s PB and stabilize the FoxP3 in iTreg cells. To isolate the effective CD4+CD25+Foxp3+CD127-iTreg cells for clinical application and to establish a quick method to identify the functional iTreg cells is the study goal. Therefore, naïve T cells isolation for regulatory T cell induction is an important issue.
Methods
Mouse splenocytes were prepared from mouse spleen. Human PBSC were prepared from peripheral blood (PB) of healthy donors by Ficoll-Hypaque density gradient centrifugation. All T cells were isolated by negative selection; then CD4+naïve T cells were harvested. After that, the CD4+naïve T cells were activated by anti-CD3/CD28 beads in the presence of IL-2, TGF-β and retinoic acid (RA) containing RPMI1640 medium. The cells cultured with 3-day-nutrient-deprived medium (only 5% FBS), then refreshed the cells into the full nutrient supplement (10% FBS) for another 5 days. The harvested cells were analyzed by flow cytometry method with fluorescence-conjugated CD-antibodies, including CD4, CD25, CD127 and FoxP3. After trypanblue staining, the number of iTreg cell was counted by hemacytometer. The iTreg cells also harvested and the expression of functional marker genes in iTreg cells were analyzed via qPCR.
Results
In nutrient-deprived (5% FBS for 3 days in advance) culture system, we found the TGF-β triggered the mouse iTreg cells formation in a dose-dependent manner and increased iTreg cells formation efficiency under retinoic acid condition. Our data showed that we could induce the CD4+CD25+Foxp3+CD127-iTreg cells more than 90%. The supplement of retinoic acid (0.1 and 0.5 nM) stabilized the FoxP3+ gene expression in iTregs during this incubation period; and the stability of FoxP3 expression and iTreg cell number could be maintained at least 12 days in vitro. The stability of iTreg cells is an important criterion for clinical use. Furthermore, we have analyzed the FoxP3 gene and the bio-functional marker genes expression in iTreg cells to confirm the functional cells (Fig.1A). Based on these results, we consider the human T cells should be used. Therefore, we have investigated the human regulatory T cell induction. Human CD4+ naïve T cells were isolated from PB and activated via antibodies. The CD4+CD25+Foxp3+CD127-iTreg cells were induced to around 60~80% under IL-2 and TGF-β1 containing media, even without retinoic acid supplement (Fig.1B). It indicated we could harvest more iTreg cells under such condition. As we know, nTreg could suppress the induction of iTreg in vivo; further, we should remove the nTreg for improving the iTreg formation under cytokines supplement condition.
Conclusion
Our study showed that the combination of IL-2, TGF-β1 and RA in 3-day-nutrient-deprived medium could convert CD4+naïve T cells to CD4+CD25+FoxP3+CD127- iTreg cells and stabilize FoxP3 expression in the iTreg cells markedly. Further, we use the marker genes to clarify the biological function of iTregs in vitro. It may be to identify the functional iTreg cells quickly, after iTreg cells induction. Based on this method, we could harvest more and effective iTreg cells ready for use. It should be helpful for clinical application. GVHD mouse model will be established by using allogeneic HSCT to verify iTreg’s function in vivo.

Session topic: Stem cell transplantation - Experimental
Keyword(s): Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), T cell activation, T regulatory cells
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


