TO PROMOTE THE MEDICAL QUALITY OF HEMATOPOIETIC MALIGNANCIES BY INTERGRATION OF QUALITY CONTROL CIRCLE AND PHS WIN-WIN CONCEPT
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Jiang Q. 06/09/16; 135006; PB2106

Prof. Qian-Li Jiang
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: PB2106
Type: Publication Only
Background
Infection and bleeding contribute to about 2/3 and 1/3 of mortality associated with hematopoietic malignancies in Nanfang Hospital, China. Patients, hospital staff, medical students and social groups were involved in this QCC.
Aims
To promote the medical quality, two rounds of Quality Control Circle (QCC) were carried out, with the aim to solve the above mentioned complications.
Methods
1 The perianal infection is the most common infection for hematopoietic malignancies (up to 60%—100%, Ann Hematol. 2003; 82:S167). With severe immunodeficiency, the perianal infection rate was 17.2% in the bone marrow transplantation center (2013Apr.-Sep.). Then QCC1 was carried out following the 10 steps of Plan-Do-Check-Action. Bacterial colony culture experiments from perianal skin before and after sanitization were performed. Since warm aqueous solution of potassium permanganate are recommended for sanitization, such bacterial colony culture is also used to find a proper drug concentration, water temperature and soaking time etc. Eventually a tool kit was developed (CN patent No.201520820954.7) to ensure the standardization of procedures. 2 With the team of QCC1, we started QCC2 for decreasing mortality due to bleeding, the shortfall being the insufficient supply of platelets. Tackling of this condition is more complicated and demanding, which also exists in many developing countries. We integrated the functioning of PHS, which stands for patients (P); hospital staff (H); students and social workers (S); in accordance with the complementary advantages (Table 1) for co-operation. Four strategies were incorporated as: Establishing a professional team, systematic education, setting up a platelet donor bank and a new platelet harvest station.
Results
1 The perianal infection rate gradually decreased from 17.2% to 5.25% and subsequently declined in the following year. Apparently each case of perianal infection could detrimentally prolong hospitalization by ≥2w and approximately 28,000 Yuan of expenditure for treatment, as well as witnessing >4,000/year such hospitalized cases in Nanfang Hospital and from amongst 40,000 new findings of leukemia in China, this QCC1 was awarded the first Prize of Chinese QCC in 2014.2 Comparing 9 months(m) before QCC2 (2014Feb.-Oct.) and 9 m later (2014Nov.-2015July), we found that the number of platelet transfusions in the department of Hematology increased from 2815U to 3674U (130.5%) and the success rate of applications increased from 58.67% to 75.77%. Within 9 m, QCC2 helped to establish a professional team named as Blood and Bone marrow China (BBCn) which have conducted 19 public lectures, a proficient platelet donors Bank with 448 volunteers and donated 135U of platelet directly. Interestingly, a new platelet harvest station is under construction in Nanfang Hospital, which will harvest thousands of new blood platelets each year. Mortality due to bleeding will significantly decrease thereafter. Tab. 1 Analysis of patient, hospital stuff, student and society (PHS)
Conclusion
QCC and PHS win-win concept could promote the medical quality of hematopoietic malignancies. Most beneficially, they will also alleviate the social conflicts between doctors and patients tremendously in China.
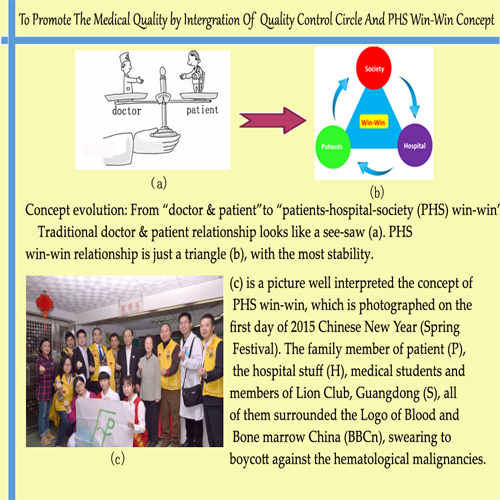
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Infection, Medical patients, Platelet transfusion, Quality control
Type: Publication Only
Background
Infection and bleeding contribute to about 2/3 and 1/3 of mortality associated with hematopoietic malignancies in Nanfang Hospital, China. Patients, hospital staff, medical students and social groups were involved in this QCC.
Aims
To promote the medical quality, two rounds of Quality Control Circle (QCC) were carried out, with the aim to solve the above mentioned complications.
Methods
1 The perianal infection is the most common infection for hematopoietic malignancies (up to 60%—100%, Ann Hematol. 2003; 82:S167). With severe immunodeficiency, the perianal infection rate was 17.2% in the bone marrow transplantation center (2013Apr.-Sep.). Then QCC1 was carried out following the 10 steps of Plan-Do-Check-Action. Bacterial colony culture experiments from perianal skin before and after sanitization were performed. Since warm aqueous solution of potassium permanganate are recommended for sanitization, such bacterial colony culture is also used to find a proper drug concentration, water temperature and soaking time etc. Eventually a tool kit was developed (CN patent No.201520820954.7) to ensure the standardization of procedures. 2 With the team of QCC1, we started QCC2 for decreasing mortality due to bleeding, the shortfall being the insufficient supply of platelets. Tackling of this condition is more complicated and demanding, which also exists in many developing countries. We integrated the functioning of PHS, which stands for patients (P); hospital staff (H); students and social workers (S); in accordance with the complementary advantages (Table 1) for co-operation. Four strategies were incorporated as: Establishing a professional team, systematic education, setting up a platelet donor bank and a new platelet harvest station.
Results
1 The perianal infection rate gradually decreased from 17.2% to 5.25% and subsequently declined in the following year. Apparently each case of perianal infection could detrimentally prolong hospitalization by ≥2w and approximately 28,000 Yuan of expenditure for treatment, as well as witnessing >4,000/year such hospitalized cases in Nanfang Hospital and from amongst 40,000 new findings of leukemia in China, this QCC1 was awarded the first Prize of Chinese QCC in 2014.2 Comparing 9 months(m) before QCC2 (2014Feb.-Oct.) and 9 m later (2014Nov.-2015July), we found that the number of platelet transfusions in the department of Hematology increased from 2815U to 3674U (130.5%) and the success rate of applications increased from 58.67% to 75.77%. Within 9 m, QCC2 helped to establish a professional team named as Blood and Bone marrow China (BBCn) which have conducted 19 public lectures, a proficient platelet donors Bank with 448 volunteers and donated 135U of platelet directly. Interestingly, a new platelet harvest station is under construction in Nanfang Hospital, which will harvest thousands of new blood platelets each year. Mortality due to bleeding will significantly decrease thereafter. Tab. 1 Analysis of patient, hospital stuff, student and society (PHS)
| Presence of | Absence of | |
| Patient | DiseasesSocial relationshipsOption to select a hospital | KnowledgePsychological comfortBlood/PlateletMoney |
| Hospital stuff | KnowledgeExperience | TimeEnthusiasm |
| Student &Society | TimeMoneyEnthusiasmBlood/Platelet, etc.) | InformationTrainingTrust |
Conclusion
QCC and PHS win-win concept could promote the medical quality of hematopoietic malignancies. Most beneficially, they will also alleviate the social conflicts between doctors and patients tremendously in China.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Infection, Medical patients, Platelet transfusion, Quality control
Abstract: PB2106
Type: Publication Only
Background
Infection and bleeding contribute to about 2/3 and 1/3 of mortality associated with hematopoietic malignancies in Nanfang Hospital, China. Patients, hospital staff, medical students and social groups were involved in this QCC.
Aims
To promote the medical quality, two rounds of Quality Control Circle (QCC) were carried out, with the aim to solve the above mentioned complications.
Methods
1 The perianal infection is the most common infection for hematopoietic malignancies (up to 60%—100%, Ann Hematol. 2003; 82:S167). With severe immunodeficiency, the perianal infection rate was 17.2% in the bone marrow transplantation center (2013Apr.-Sep.). Then QCC1 was carried out following the 10 steps of Plan-Do-Check-Action. Bacterial colony culture experiments from perianal skin before and after sanitization were performed. Since warm aqueous solution of potassium permanganate are recommended for sanitization, such bacterial colony culture is also used to find a proper drug concentration, water temperature and soaking time etc. Eventually a tool kit was developed (CN patent No.201520820954.7) to ensure the standardization of procedures. 2 With the team of QCC1, we started QCC2 for decreasing mortality due to bleeding, the shortfall being the insufficient supply of platelets. Tackling of this condition is more complicated and demanding, which also exists in many developing countries. We integrated the functioning of PHS, which stands for patients (P); hospital staff (H); students and social workers (S); in accordance with the complementary advantages (Table 1) for co-operation. Four strategies were incorporated as: Establishing a professional team, systematic education, setting up a platelet donor bank and a new platelet harvest station.
Results
1 The perianal infection rate gradually decreased from 17.2% to 5.25% and subsequently declined in the following year. Apparently each case of perianal infection could detrimentally prolong hospitalization by ≥2w and approximately 28,000 Yuan of expenditure for treatment, as well as witnessing >4,000/year such hospitalized cases in Nanfang Hospital and from amongst 40,000 new findings of leukemia in China, this QCC1 was awarded the first Prize of Chinese QCC in 2014.2 Comparing 9 months(m) before QCC2 (2014Feb.-Oct.) and 9 m later (2014Nov.-2015July), we found that the number of platelet transfusions in the department of Hematology increased from 2815U to 3674U (130.5%) and the success rate of applications increased from 58.67% to 75.77%. Within 9 m, QCC2 helped to establish a professional team named as Blood and Bone marrow China (BBCn) which have conducted 19 public lectures, a proficient platelet donors Bank with 448 volunteers and donated 135U of platelet directly. Interestingly, a new platelet harvest station is under construction in Nanfang Hospital, which will harvest thousands of new blood platelets each year. Mortality due to bleeding will significantly decrease thereafter. Tab. 1 Analysis of patient, hospital stuff, student and society (PHS)
Conclusion
QCC and PHS win-win concept could promote the medical quality of hematopoietic malignancies. Most beneficially, they will also alleviate the social conflicts between doctors and patients tremendously in China.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Infection, Medical patients, Platelet transfusion, Quality control
Type: Publication Only
Background
Infection and bleeding contribute to about 2/3 and 1/3 of mortality associated with hematopoietic malignancies in Nanfang Hospital, China. Patients, hospital staff, medical students and social groups were involved in this QCC.
Aims
To promote the medical quality, two rounds of Quality Control Circle (QCC) were carried out, with the aim to solve the above mentioned complications.
Methods
1 The perianal infection is the most common infection for hematopoietic malignancies (up to 60%—100%, Ann Hematol. 2003; 82:S167). With severe immunodeficiency, the perianal infection rate was 17.2% in the bone marrow transplantation center (2013Apr.-Sep.). Then QCC1 was carried out following the 10 steps of Plan-Do-Check-Action. Bacterial colony culture experiments from perianal skin before and after sanitization were performed. Since warm aqueous solution of potassium permanganate are recommended for sanitization, such bacterial colony culture is also used to find a proper drug concentration, water temperature and soaking time etc. Eventually a tool kit was developed (CN patent No.201520820954.7) to ensure the standardization of procedures. 2 With the team of QCC1, we started QCC2 for decreasing mortality due to bleeding, the shortfall being the insufficient supply of platelets. Tackling of this condition is more complicated and demanding, which also exists in many developing countries. We integrated the functioning of PHS, which stands for patients (P); hospital staff (H); students and social workers (S); in accordance with the complementary advantages (Table 1) for co-operation. Four strategies were incorporated as: Establishing a professional team, systematic education, setting up a platelet donor bank and a new platelet harvest station.
Results
1 The perianal infection rate gradually decreased from 17.2% to 5.25% and subsequently declined in the following year. Apparently each case of perianal infection could detrimentally prolong hospitalization by ≥2w and approximately 28,000 Yuan of expenditure for treatment, as well as witnessing >4,000/year such hospitalized cases in Nanfang Hospital and from amongst 40,000 new findings of leukemia in China, this QCC1 was awarded the first Prize of Chinese QCC in 2014.2 Comparing 9 months(m) before QCC2 (2014Feb.-Oct.) and 9 m later (2014Nov.-2015July), we found that the number of platelet transfusions in the department of Hematology increased from 2815U to 3674U (130.5%) and the success rate of applications increased from 58.67% to 75.77%. Within 9 m, QCC2 helped to establish a professional team named as Blood and Bone marrow China (BBCn) which have conducted 19 public lectures, a proficient platelet donors Bank with 448 volunteers and donated 135U of platelet directly. Interestingly, a new platelet harvest station is under construction in Nanfang Hospital, which will harvest thousands of new blood platelets each year. Mortality due to bleeding will significantly decrease thereafter. Tab. 1 Analysis of patient, hospital stuff, student and society (PHS)
| Presence of | Absence of | |
| Patient | DiseasesSocial relationshipsOption to select a hospital | KnowledgePsychological comfortBlood/PlateletMoney |
| Hospital stuff | KnowledgeExperience | TimeEnthusiasm |
| Student &Society | TimeMoneyEnthusiasmBlood/Platelet, etc.) | InformationTrainingTrust |
Conclusion
QCC and PHS win-win concept could promote the medical quality of hematopoietic malignancies. Most beneficially, they will also alleviate the social conflicts between doctors and patients tremendously in China.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Infection, Medical patients, Platelet transfusion, Quality control
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


