QUINACRINE SYNERGIZES WITH DOXORUBICIN IN INHIBITING THE SURVIVAL OF DLBCL CELL BY SUPPRESSING NF-KB AND ALTERING CELL-CYCLE PROGRESSION
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Shujun Y. 06/09/16; 134942; PB2042

Mr. Yang Shujun
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: PB2042
Type: Publication Only
Background
Diffuse large B‑cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is an aggressive B‑cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma that affects patients of all ages with a wide range of clinical presentations. Although DLBCL is curable even in advanced stages, up to one-third of patients will not achieve cure with initial therapy. To test drug combinations that could improve the efficacy of chemotherapeutics used currently. We combined doxorubicin (dox) with quinacrine (qc), which inhibits the FACT complex that is required for NF- κB transcriptional activity.
Aims
The aim of this study was to test drug combinations that could improve the efficacy of chemotherapeutics currently used, such as dox, to Provide new and better drugs for clinical treatment of DLBCL.
Methods
Cells were maintained in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% FBS. All cells were kept at 37 ℃ in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. Cell viability was determined by the MTT assay. The combination index (CI) was assessed by using Calcusyn software. Cells stained with propidium iodide (PI), the cell-cycle distribution was assessed by FACScan (BD) Biosciences analysis. Cells were infected with the NF-κB-luciferase Lentiviral construct and stably selected with puromycin. The influence of Qc on the activity of NF-κB was tested using luciferase assay system.
Results
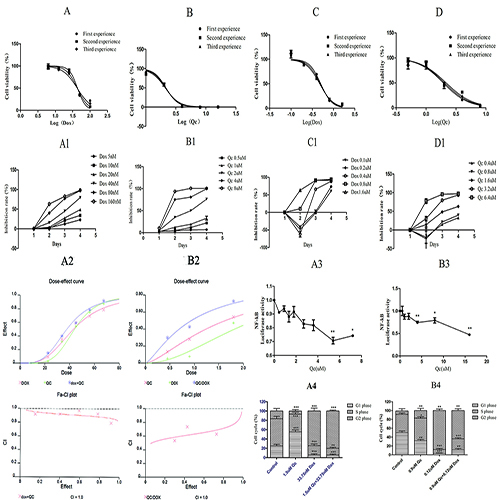
Qc synergizes with dox in inhibiting the proliferation of DLBCL cell lines; Qc has the ability to suppressing NF-κB-dependent luciferase activity, which means qc inhibits the activity of NF-κB, as well as alrer the cell cycle of DLBCL cell lines.
Conclusion
Qc can inhibit the growth of DLBCL tumor cells, enhance the curative effect of chemotherapy drugs such as dox, its possible mechanism is qc could inhibit the NF-kB activity which plays key roles in DLBCL cell survival and chemotheraputic resistance, as well as alter the cell cycle progression.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Type: Publication Only
Background
Diffuse large B‑cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is an aggressive B‑cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma that affects patients of all ages with a wide range of clinical presentations. Although DLBCL is curable even in advanced stages, up to one-third of patients will not achieve cure with initial therapy. To test drug combinations that could improve the efficacy of chemotherapeutics used currently. We combined doxorubicin (dox) with quinacrine (qc), which inhibits the FACT complex that is required for NF- κB transcriptional activity.
Aims
The aim of this study was to test drug combinations that could improve the efficacy of chemotherapeutics currently used, such as dox, to Provide new and better drugs for clinical treatment of DLBCL.
Methods
Cells were maintained in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% FBS. All cells were kept at 37 ℃ in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. Cell viability was determined by the MTT assay. The combination index (CI) was assessed by using Calcusyn software. Cells stained with propidium iodide (PI), the cell-cycle distribution was assessed by FACScan (BD) Biosciences analysis. Cells were infected with the NF-κB-luciferase Lentiviral construct and stably selected with puromycin. The influence of Qc on the activity of NF-κB was tested using luciferase assay system.
Results
Qc synergizes with dox in inhibiting the proliferation of DLBCL cell lines; Qc has the ability to suppressing NF-κB-dependent luciferase activity, which means qc inhibits the activity of NF-κB, as well as alrer the cell cycle of DLBCL cell lines.
Conclusion
Qc can inhibit the growth of DLBCL tumor cells, enhance the curative effect of chemotherapy drugs such as dox, its possible mechanism is qc could inhibit the NF-kB activity which plays key roles in DLBCL cell survival and chemotheraputic resistance, as well as alter the cell cycle progression.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Abstract: PB2042
Type: Publication Only
Background
Diffuse large B‑cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is an aggressive B‑cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma that affects patients of all ages with a wide range of clinical presentations. Although DLBCL is curable even in advanced stages, up to one-third of patients will not achieve cure with initial therapy. To test drug combinations that could improve the efficacy of chemotherapeutics used currently. We combined doxorubicin (dox) with quinacrine (qc), which inhibits the FACT complex that is required for NF- κB transcriptional activity.
Aims
The aim of this study was to test drug combinations that could improve the efficacy of chemotherapeutics currently used, such as dox, to Provide new and better drugs for clinical treatment of DLBCL.
Methods
Cells were maintained in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% FBS. All cells were kept at 37 ℃ in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. Cell viability was determined by the MTT assay. The combination index (CI) was assessed by using Calcusyn software. Cells stained with propidium iodide (PI), the cell-cycle distribution was assessed by FACScan (BD) Biosciences analysis. Cells were infected with the NF-κB-luciferase Lentiviral construct and stably selected with puromycin. The influence of Qc on the activity of NF-κB was tested using luciferase assay system.
Results
Qc synergizes with dox in inhibiting the proliferation of DLBCL cell lines; Qc has the ability to suppressing NF-κB-dependent luciferase activity, which means qc inhibits the activity of NF-κB, as well as alrer the cell cycle of DLBCL cell lines.
Conclusion
Qc can inhibit the growth of DLBCL tumor cells, enhance the curative effect of chemotherapy drugs such as dox, its possible mechanism is qc could inhibit the NF-kB activity which plays key roles in DLBCL cell survival and chemotheraputic resistance, as well as alter the cell cycle progression.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Type: Publication Only
Background
Diffuse large B‑cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is an aggressive B‑cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma that affects patients of all ages with a wide range of clinical presentations. Although DLBCL is curable even in advanced stages, up to one-third of patients will not achieve cure with initial therapy. To test drug combinations that could improve the efficacy of chemotherapeutics used currently. We combined doxorubicin (dox) with quinacrine (qc), which inhibits the FACT complex that is required for NF- κB transcriptional activity.
Aims
The aim of this study was to test drug combinations that could improve the efficacy of chemotherapeutics currently used, such as dox, to Provide new and better drugs for clinical treatment of DLBCL.
Methods
Cells were maintained in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% FBS. All cells were kept at 37 ℃ in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. Cell viability was determined by the MTT assay. The combination index (CI) was assessed by using Calcusyn software. Cells stained with propidium iodide (PI), the cell-cycle distribution was assessed by FACScan (BD) Biosciences analysis. Cells were infected with the NF-κB-luciferase Lentiviral construct and stably selected with puromycin. The influence of Qc on the activity of NF-κB was tested using luciferase assay system.
Results
Qc synergizes with dox in inhibiting the proliferation of DLBCL cell lines; Qc has the ability to suppressing NF-κB-dependent luciferase activity, which means qc inhibits the activity of NF-κB, as well as alrer the cell cycle of DLBCL cell lines.
Conclusion
Qc can inhibit the growth of DLBCL tumor cells, enhance the curative effect of chemotherapy drugs such as dox, its possible mechanism is qc could inhibit the NF-kB activity which plays key roles in DLBCL cell survival and chemotheraputic resistance, as well as alter the cell cycle progression.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


