CYR61/CCN1 STIMULATED THE PROLIFERATION AND DIFFERENTIATION OF OSTEOBLASTS IN MYELOMA BONE DISEASE IN VITRO
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Fu R. 06/09/16; 134836; PB1936

Dr. Rong Fu
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: PB1936
Type: Publication Only
Background
Myeloma bone disease (MBD) is a most common complication of multiple myeloma, which can cause high mortality. Cysteine-rich 61 (Cyr61 or CCN1), one secreted protein in bone marrow(BM) microenvironment, has diverse effects on many cellular activities like growth and differentiation. However, the effect of CCN1 on osteoblasts (OBs) in MBD is unclear.
Aims
To explore the effect of CCN1 on osteroblasts in MBD.
Methods
The levels of CCN1 in MBD patients were detected by ELISA and RT-PCR. The OBs from MBD patients were cultured with CCN1 in vitro, and proliferation and differentiation of OBs were observed. The transcription factors, runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2), β-Catenin and bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP2), were investigated by RT-PCR.
Results
The results showed that CCN1 level elevated in BM supernatant and CYR61 overexpressed in OBs in newly diagnosed MBD patients. After 30ng/L CCN1 stimulation for 24 hours in vitro, the OBs quantity increased to (3.39 ± 1.21) × 105/mL, significantly higher than the blank (P = 0.046). Meanwhile, the amount of mineralized nodules (14.33± 5.72/HPF) was also significantly increased than the blank group (9.11 ± 0.97/HPF) (P = 0.048). Futhermore, Runx2 and β-Catenin upregulated in OBs after CCN1 stimulation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, CCN1 can stimulate the proliferation and differentiation of OBs via Wnt pathway in MBD.
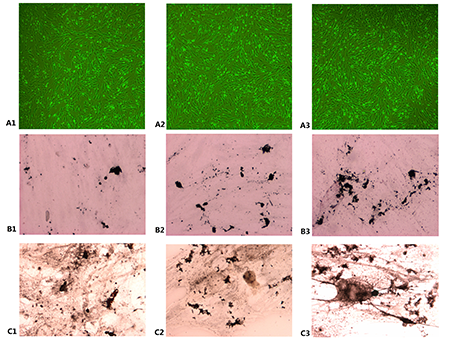
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Myeloma, Osteoblast
Type: Publication Only
Background
Myeloma bone disease (MBD) is a most common complication of multiple myeloma, which can cause high mortality. Cysteine-rich 61 (Cyr61 or CCN1), one secreted protein in bone marrow(BM) microenvironment, has diverse effects on many cellular activities like growth and differentiation. However, the effect of CCN1 on osteoblasts (OBs) in MBD is unclear.
Aims
To explore the effect of CCN1 on osteroblasts in MBD.
Methods
The levels of CCN1 in MBD patients were detected by ELISA and RT-PCR. The OBs from MBD patients were cultured with CCN1 in vitro, and proliferation and differentiation of OBs were observed. The transcription factors, runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2), β-Catenin and bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP2), were investigated by RT-PCR.
Results
The results showed that CCN1 level elevated in BM supernatant and CYR61 overexpressed in OBs in newly diagnosed MBD patients. After 30ng/L CCN1 stimulation for 24 hours in vitro, the OBs quantity increased to (3.39 ± 1.21) × 105/mL, significantly higher than the blank (P = 0.046). Meanwhile, the amount of mineralized nodules (14.33± 5.72/HPF) was also significantly increased than the blank group (9.11 ± 0.97/HPF) (P = 0.048). Futhermore, Runx2 and β-Catenin upregulated in OBs after CCN1 stimulation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, CCN1 can stimulate the proliferation and differentiation of OBs via Wnt pathway in MBD.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Myeloma, Osteoblast
Abstract: PB1936
Type: Publication Only
Background
Myeloma bone disease (MBD) is a most common complication of multiple myeloma, which can cause high mortality. Cysteine-rich 61 (Cyr61 or CCN1), one secreted protein in bone marrow(BM) microenvironment, has diverse effects on many cellular activities like growth and differentiation. However, the effect of CCN1 on osteoblasts (OBs) in MBD is unclear.
Aims
To explore the effect of CCN1 on osteroblasts in MBD.
Methods
The levels of CCN1 in MBD patients were detected by ELISA and RT-PCR. The OBs from MBD patients were cultured with CCN1 in vitro, and proliferation and differentiation of OBs were observed. The transcription factors, runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2), β-Catenin and bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP2), were investigated by RT-PCR.
Results
The results showed that CCN1 level elevated in BM supernatant and CYR61 overexpressed in OBs in newly diagnosed MBD patients. After 30ng/L CCN1 stimulation for 24 hours in vitro, the OBs quantity increased to (3.39 ± 1.21) × 105/mL, significantly higher than the blank (P = 0.046). Meanwhile, the amount of mineralized nodules (14.33± 5.72/HPF) was also significantly increased than the blank group (9.11 ± 0.97/HPF) (P = 0.048). Futhermore, Runx2 and β-Catenin upregulated in OBs after CCN1 stimulation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, CCN1 can stimulate the proliferation and differentiation of OBs via Wnt pathway in MBD.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Myeloma, Osteoblast
Type: Publication Only
Background
Myeloma bone disease (MBD) is a most common complication of multiple myeloma, which can cause high mortality. Cysteine-rich 61 (Cyr61 or CCN1), one secreted protein in bone marrow(BM) microenvironment, has diverse effects on many cellular activities like growth and differentiation. However, the effect of CCN1 on osteoblasts (OBs) in MBD is unclear.
Aims
To explore the effect of CCN1 on osteroblasts in MBD.
Methods
The levels of CCN1 in MBD patients were detected by ELISA and RT-PCR. The OBs from MBD patients were cultured with CCN1 in vitro, and proliferation and differentiation of OBs were observed. The transcription factors, runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2), β-Catenin and bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP2), were investigated by RT-PCR.
Results
The results showed that CCN1 level elevated in BM supernatant and CYR61 overexpressed in OBs in newly diagnosed MBD patients. After 30ng/L CCN1 stimulation for 24 hours in vitro, the OBs quantity increased to (3.39 ± 1.21) × 105/mL, significantly higher than the blank (P = 0.046). Meanwhile, the amount of mineralized nodules (14.33± 5.72/HPF) was also significantly increased than the blank group (9.11 ± 0.97/HPF) (P = 0.048). Futhermore, Runx2 and β-Catenin upregulated in OBs after CCN1 stimulation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, CCN1 can stimulate the proliferation and differentiation of OBs via Wnt pathway in MBD.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Myeloma, Osteoblast
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


