REAL-WORLD DATA FROM 54 BELGIAN PATIENTS FROM THE PONATINIB NAMED PATIENT PROGRAMME (NPP)
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Devos T. 06/09/16; 134722; PB1822

Prof. Timothy Devos
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: PB1822
Type: Publication Only
Background
Ponatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) indicated for adult patients with refractory chronic- (CP), accelerated- (AP), or blast-phase (BP) chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ALL), or those with the T315I mutation. Fifty-four patients from 17 Belgian centres entered the ponatinib Named Patient Programme (NPP) from August 2012 through September 2015.
Aims
To provide evidence of the efficacy and safety of ponatinib in real-world Belgian patients.
Methods
Limited patient data were collected prospectively for patients enrolled in the NPP, based on a questionnaire approved by the Ethics Committee of the Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc. Demographic data are presented for all patients, and efficacy and safety data for patients recruited from August 2012 through June 2015 with at least 3 months of follow-up. All patients provided informed consent.
Results
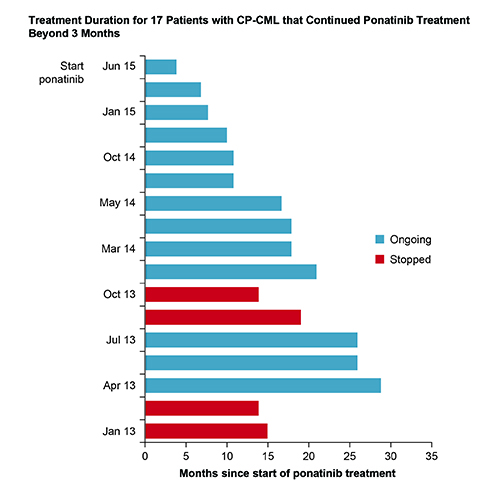
Patients with CP-CML (N=35), AP/BP CML (N=5) or Ph+ALL (N=14) had a median age of 62 years; 89% were in ≥3rd-line of TKI therapy. Mutation analysis revealed baseline mutations in 43% of CP-CML and 83% of Ph+ALL patients; 42% and 40% of mutations were T315I. Of CP-CML patients 63% received a starting dose of 45mg/day, 29% 30mg/day and 8% 15mg/day. Dose reductions occurred in 42% of CP-CML patients: 29% due to adverse events and 13% to prevent cardiovascular complications after achieving response. For Ph+ALL patients, starting doses were 45 mg/day (69%), 30 mg/day (23%), and 15 mg/day (8%). Among 27 CP-CML patients with outcome data, 10 patients stopped ponatinib within 3 months due to: disease progression (n=2), thrombocytopenia (n=2), gastrointestinal complaints (n=2), cutaneous lesions, uncontrolled hypertension, ischemic CVA and planned allotransplant (n=1 each). Best responses in CP-CML patients treated beyond 3 months were: major molecular response (MMR; n=10), complete cytogenetic response (CCyR; n=3), partial cytogenetic response (PCyR; n=2), and complete hematologic response (CHR; n=2). Four of 17 CP-CML patients discontinued due to disease progression (n=2) and vascular occlusive events (toe necrosis after 19 months [n=1]; cardiac death after 14 months [n=1]). Thirteen CP-CML patients remain on treatment (median: 17 months; Figure). Among 10 evaluable Ph+ALL patients, 4 achieved MMR, 3 of whom remain in remission after 15, 24 and 33 months.
Conclusion
Despite limited data, ponatinib appears efficacious in the Belgian NPP; results appear comparable to the PACE clinical trial, which included resistant or intolerant CML and Ph+ALL patients.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Chronic myeloid leukemia, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Type: Publication Only
Background
Ponatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) indicated for adult patients with refractory chronic- (CP), accelerated- (AP), or blast-phase (BP) chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ALL), or those with the T315I mutation. Fifty-four patients from 17 Belgian centres entered the ponatinib Named Patient Programme (NPP) from August 2012 through September 2015.
Aims
To provide evidence of the efficacy and safety of ponatinib in real-world Belgian patients.
Methods
Limited patient data were collected prospectively for patients enrolled in the NPP, based on a questionnaire approved by the Ethics Committee of the Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc. Demographic data are presented for all patients, and efficacy and safety data for patients recruited from August 2012 through June 2015 with at least 3 months of follow-up. All patients provided informed consent.
Results
Patients with CP-CML (N=35), AP/BP CML (N=5) or Ph+ALL (N=14) had a median age of 62 years; 89% were in ≥3rd-line of TKI therapy. Mutation analysis revealed baseline mutations in 43% of CP-CML and 83% of Ph+ALL patients; 42% and 40% of mutations were T315I. Of CP-CML patients 63% received a starting dose of 45mg/day, 29% 30mg/day and 8% 15mg/day. Dose reductions occurred in 42% of CP-CML patients: 29% due to adverse events and 13% to prevent cardiovascular complications after achieving response. For Ph+ALL patients, starting doses were 45 mg/day (69%), 30 mg/day (23%), and 15 mg/day (8%). Among 27 CP-CML patients with outcome data, 10 patients stopped ponatinib within 3 months due to: disease progression (n=2), thrombocytopenia (n=2), gastrointestinal complaints (n=2), cutaneous lesions, uncontrolled hypertension, ischemic CVA and planned allotransplant (n=1 each). Best responses in CP-CML patients treated beyond 3 months were: major molecular response (MMR; n=10), complete cytogenetic response (CCyR; n=3), partial cytogenetic response (PCyR; n=2), and complete hematologic response (CHR; n=2). Four of 17 CP-CML patients discontinued due to disease progression (n=2) and vascular occlusive events (toe necrosis after 19 months [n=1]; cardiac death after 14 months [n=1]). Thirteen CP-CML patients remain on treatment (median: 17 months; Figure). Among 10 evaluable Ph+ALL patients, 4 achieved MMR, 3 of whom remain in remission after 15, 24 and 33 months.
Conclusion
Despite limited data, ponatinib appears efficacious in the Belgian NPP; results appear comparable to the PACE clinical trial, which included resistant or intolerant CML and Ph+ALL patients.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Chronic myeloid leukemia, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Abstract: PB1822
Type: Publication Only
Background
Ponatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) indicated for adult patients with refractory chronic- (CP), accelerated- (AP), or blast-phase (BP) chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ALL), or those with the T315I mutation. Fifty-four patients from 17 Belgian centres entered the ponatinib Named Patient Programme (NPP) from August 2012 through September 2015.
Aims
To provide evidence of the efficacy and safety of ponatinib in real-world Belgian patients.
Methods
Limited patient data were collected prospectively for patients enrolled in the NPP, based on a questionnaire approved by the Ethics Committee of the Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc. Demographic data are presented for all patients, and efficacy and safety data for patients recruited from August 2012 through June 2015 with at least 3 months of follow-up. All patients provided informed consent.
Results
Patients with CP-CML (N=35), AP/BP CML (N=5) or Ph+ALL (N=14) had a median age of 62 years; 89% were in ≥3rd-line of TKI therapy. Mutation analysis revealed baseline mutations in 43% of CP-CML and 83% of Ph+ALL patients; 42% and 40% of mutations were T315I. Of CP-CML patients 63% received a starting dose of 45mg/day, 29% 30mg/day and 8% 15mg/day. Dose reductions occurred in 42% of CP-CML patients: 29% due to adverse events and 13% to prevent cardiovascular complications after achieving response. For Ph+ALL patients, starting doses were 45 mg/day (69%), 30 mg/day (23%), and 15 mg/day (8%). Among 27 CP-CML patients with outcome data, 10 patients stopped ponatinib within 3 months due to: disease progression (n=2), thrombocytopenia (n=2), gastrointestinal complaints (n=2), cutaneous lesions, uncontrolled hypertension, ischemic CVA and planned allotransplant (n=1 each). Best responses in CP-CML patients treated beyond 3 months were: major molecular response (MMR; n=10), complete cytogenetic response (CCyR; n=3), partial cytogenetic response (PCyR; n=2), and complete hematologic response (CHR; n=2). Four of 17 CP-CML patients discontinued due to disease progression (n=2) and vascular occlusive events (toe necrosis after 19 months [n=1]; cardiac death after 14 months [n=1]). Thirteen CP-CML patients remain on treatment (median: 17 months; Figure). Among 10 evaluable Ph+ALL patients, 4 achieved MMR, 3 of whom remain in remission after 15, 24 and 33 months.
Conclusion
Despite limited data, ponatinib appears efficacious in the Belgian NPP; results appear comparable to the PACE clinical trial, which included resistant or intolerant CML and Ph+ALL patients.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Chronic myeloid leukemia, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Type: Publication Only
Background
Ponatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) indicated for adult patients with refractory chronic- (CP), accelerated- (AP), or blast-phase (BP) chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ALL), or those with the T315I mutation. Fifty-four patients from 17 Belgian centres entered the ponatinib Named Patient Programme (NPP) from August 2012 through September 2015.
Aims
To provide evidence of the efficacy and safety of ponatinib in real-world Belgian patients.
Methods
Limited patient data were collected prospectively for patients enrolled in the NPP, based on a questionnaire approved by the Ethics Committee of the Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc. Demographic data are presented for all patients, and efficacy and safety data for patients recruited from August 2012 through June 2015 with at least 3 months of follow-up. All patients provided informed consent.
Results
Patients with CP-CML (N=35), AP/BP CML (N=5) or Ph+ALL (N=14) had a median age of 62 years; 89% were in ≥3rd-line of TKI therapy. Mutation analysis revealed baseline mutations in 43% of CP-CML and 83% of Ph+ALL patients; 42% and 40% of mutations were T315I. Of CP-CML patients 63% received a starting dose of 45mg/day, 29% 30mg/day and 8% 15mg/day. Dose reductions occurred in 42% of CP-CML patients: 29% due to adverse events and 13% to prevent cardiovascular complications after achieving response. For Ph+ALL patients, starting doses were 45 mg/day (69%), 30 mg/day (23%), and 15 mg/day (8%). Among 27 CP-CML patients with outcome data, 10 patients stopped ponatinib within 3 months due to: disease progression (n=2), thrombocytopenia (n=2), gastrointestinal complaints (n=2), cutaneous lesions, uncontrolled hypertension, ischemic CVA and planned allotransplant (n=1 each). Best responses in CP-CML patients treated beyond 3 months were: major molecular response (MMR; n=10), complete cytogenetic response (CCyR; n=3), partial cytogenetic response (PCyR; n=2), and complete hematologic response (CHR; n=2). Four of 17 CP-CML patients discontinued due to disease progression (n=2) and vascular occlusive events (toe necrosis after 19 months [n=1]; cardiac death after 14 months [n=1]). Thirteen CP-CML patients remain on treatment (median: 17 months; Figure). Among 10 evaluable Ph+ALL patients, 4 achieved MMR, 3 of whom remain in remission after 15, 24 and 33 months.
Conclusion
Despite limited data, ponatinib appears efficacious in the Belgian NPP; results appear comparable to the PACE clinical trial, which included resistant or intolerant CML and Ph+ALL patients.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Chronic myeloid leukemia, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


