IMPACT OF IGVH MUTATIONAL STATUS IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA WITH ISOLATED GOOD AND INTERMEDIATE RISK GENETIC ABERRATIONS
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Miguel Juárez-Salcedo L. 06/09/16; 134687; PB1787

Dr. Luis Miguel Juárez-Salcedo
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: PB1787
Type: Publication Only
Background
Genetic abnormalities in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) have prognostic impact. The presence of trisomy 12 (T12) and normal karyotype (NK), and 13q deletion (del13q) are associated with an intermediate and good risk profile in CLL, respectively (Dohner et al. NEJM, 2000). The unmutated status of the immunoglobulin variable heavy chain gene (IgVH) correlates with survival in sole del13q CLL (Gladstone et al, Leukemia 2011). The prognostic relevance of IgVH mutational status in isolated intermediate risk genetic variants (T12 and NK) has not been described. We investigated the impact of the IgVH mutational status in CLL patients with isolated del13q, T12 or NK in a large single institution cohort.
Aims
To assess the prognostic impact of the IGVH mutational status in CLL patients with isolated del13q, T12 and NK.
Methods
From January 2000 to January 2013 we identified 1267 CLL patients using the Moffitt Cancer Center and Total Cancer Care databases. Descriptive data was reported in patients with both unmutated (<2% from the germline sequence) and mutated IgVH (>2% from the germline sequence). Time to first treatment (TFT) and overall survival (OS) were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and the log-rank test. A significant difference was considered at p≤0.05. All analyses were done using SPSS version 19.0.
Results
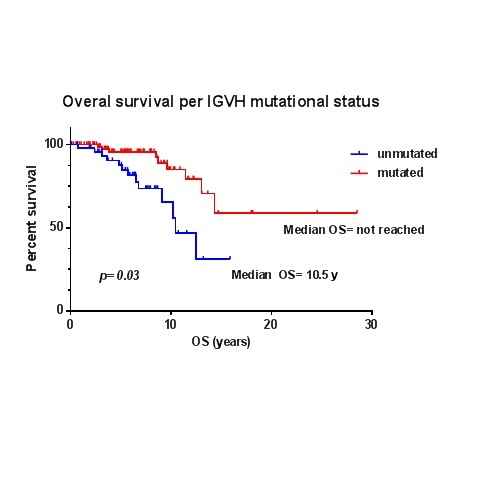
We identified 145 CLL patients (median age: 59 years) with isolated del13q (mutated IgHV = 96, 66.2%; unmutated IgVH = 49, 33.8%), 49 patients (median age: 64 years) with isolated T12 (mutated IgVH = 17, 34.7%; unmutated IgVH = 32, 65.3%), and 79 patients (median age: 57 years) with NK (mutated IgVH = 41, 51.9%; unmutated IgVH = 38, 48.1%), respectively. Unmutated IgVH was associated with shorter TFT in patients with sole del13q (unmutated 2.1 years vs. mutated 6.0 years, p < 0.001) and isolated NK (unmutated 1.9 years vs. mutated 3.3 year, p = 0.05). IgVH mutational status had no impact in the TFT of patients with sole T12. Patients with isolated del13q and mutated IgVH had a longer median OS compared to unmutated patients (not reached vs. 10.5 years, p=0.03). Nonetheless, the IgVH mutational status did not significantly impact the OS of sole T12 patients (p=0.29) and NK (p=0.14).
Conclusion
Our results confirm the negative impact of the unmutated IgVH status in CLL patients with isolated del13q. The mutational IgVH status did not impact the OS of T12 and NK CLL patients.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Immunoglobulin gene, Mutation status
Type: Publication Only
Background
Genetic abnormalities in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) have prognostic impact. The presence of trisomy 12 (T12) and normal karyotype (NK), and 13q deletion (del13q) are associated with an intermediate and good risk profile in CLL, respectively (Dohner et al. NEJM, 2000). The unmutated status of the immunoglobulin variable heavy chain gene (IgVH) correlates with survival in sole del13q CLL (Gladstone et al, Leukemia 2011). The prognostic relevance of IgVH mutational status in isolated intermediate risk genetic variants (T12 and NK) has not been described. We investigated the impact of the IgVH mutational status in CLL patients with isolated del13q, T12 or NK in a large single institution cohort.
Aims
To assess the prognostic impact of the IGVH mutational status in CLL patients with isolated del13q, T12 and NK.
Methods
From January 2000 to January 2013 we identified 1267 CLL patients using the Moffitt Cancer Center and Total Cancer Care databases. Descriptive data was reported in patients with both unmutated (<2% from the germline sequence) and mutated IgVH (>2% from the germline sequence). Time to first treatment (TFT) and overall survival (OS) were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and the log-rank test. A significant difference was considered at p≤0.05. All analyses were done using SPSS version 19.0.
Results
We identified 145 CLL patients (median age: 59 years) with isolated del13q (mutated IgHV = 96, 66.2%; unmutated IgVH = 49, 33.8%), 49 patients (median age: 64 years) with isolated T12 (mutated IgVH = 17, 34.7%; unmutated IgVH = 32, 65.3%), and 79 patients (median age: 57 years) with NK (mutated IgVH = 41, 51.9%; unmutated IgVH = 38, 48.1%), respectively. Unmutated IgVH was associated with shorter TFT in patients with sole del13q (unmutated 2.1 years vs. mutated 6.0 years, p < 0.001) and isolated NK (unmutated 1.9 years vs. mutated 3.3 year, p = 0.05). IgVH mutational status had no impact in the TFT of patients with sole T12. Patients with isolated del13q and mutated IgVH had a longer median OS compared to unmutated patients (not reached vs. 10.5 years, p=0.03). Nonetheless, the IgVH mutational status did not significantly impact the OS of sole T12 patients (p=0.29) and NK (p=0.14).
Conclusion
Our results confirm the negative impact of the unmutated IgVH status in CLL patients with isolated del13q. The mutational IgVH status did not impact the OS of T12 and NK CLL patients.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Immunoglobulin gene, Mutation status
Abstract: PB1787
Type: Publication Only
Background
Genetic abnormalities in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) have prognostic impact. The presence of trisomy 12 (T12) and normal karyotype (NK), and 13q deletion (del13q) are associated with an intermediate and good risk profile in CLL, respectively (Dohner et al. NEJM, 2000). The unmutated status of the immunoglobulin variable heavy chain gene (IgVH) correlates with survival in sole del13q CLL (Gladstone et al, Leukemia 2011). The prognostic relevance of IgVH mutational status in isolated intermediate risk genetic variants (T12 and NK) has not been described. We investigated the impact of the IgVH mutational status in CLL patients with isolated del13q, T12 or NK in a large single institution cohort.
Aims
To assess the prognostic impact of the IGVH mutational status in CLL patients with isolated del13q, T12 and NK.
Methods
From January 2000 to January 2013 we identified 1267 CLL patients using the Moffitt Cancer Center and Total Cancer Care databases. Descriptive data was reported in patients with both unmutated (<2% from the germline sequence) and mutated IgVH (>2% from the germline sequence). Time to first treatment (TFT) and overall survival (OS) were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and the log-rank test. A significant difference was considered at p≤0.05. All analyses were done using SPSS version 19.0.
Results
We identified 145 CLL patients (median age: 59 years) with isolated del13q (mutated IgHV = 96, 66.2%; unmutated IgVH = 49, 33.8%), 49 patients (median age: 64 years) with isolated T12 (mutated IgVH = 17, 34.7%; unmutated IgVH = 32, 65.3%), and 79 patients (median age: 57 years) with NK (mutated IgVH = 41, 51.9%; unmutated IgVH = 38, 48.1%), respectively. Unmutated IgVH was associated with shorter TFT in patients with sole del13q (unmutated 2.1 years vs. mutated 6.0 years, p < 0.001) and isolated NK (unmutated 1.9 years vs. mutated 3.3 year, p = 0.05). IgVH mutational status had no impact in the TFT of patients with sole T12. Patients with isolated del13q and mutated IgVH had a longer median OS compared to unmutated patients (not reached vs. 10.5 years, p=0.03). Nonetheless, the IgVH mutational status did not significantly impact the OS of sole T12 patients (p=0.29) and NK (p=0.14).
Conclusion
Our results confirm the negative impact of the unmutated IgVH status in CLL patients with isolated del13q. The mutational IgVH status did not impact the OS of T12 and NK CLL patients.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Immunoglobulin gene, Mutation status
Type: Publication Only
Background
Genetic abnormalities in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) have prognostic impact. The presence of trisomy 12 (T12) and normal karyotype (NK), and 13q deletion (del13q) are associated with an intermediate and good risk profile in CLL, respectively (Dohner et al. NEJM, 2000). The unmutated status of the immunoglobulin variable heavy chain gene (IgVH) correlates with survival in sole del13q CLL (Gladstone et al, Leukemia 2011). The prognostic relevance of IgVH mutational status in isolated intermediate risk genetic variants (T12 and NK) has not been described. We investigated the impact of the IgVH mutational status in CLL patients with isolated del13q, T12 or NK in a large single institution cohort.
Aims
To assess the prognostic impact of the IGVH mutational status in CLL patients with isolated del13q, T12 and NK.
Methods
From January 2000 to January 2013 we identified 1267 CLL patients using the Moffitt Cancer Center and Total Cancer Care databases. Descriptive data was reported in patients with both unmutated (<2% from the germline sequence) and mutated IgVH (>2% from the germline sequence). Time to first treatment (TFT) and overall survival (OS) were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and the log-rank test. A significant difference was considered at p≤0.05. All analyses were done using SPSS version 19.0.
Results
We identified 145 CLL patients (median age: 59 years) with isolated del13q (mutated IgHV = 96, 66.2%; unmutated IgVH = 49, 33.8%), 49 patients (median age: 64 years) with isolated T12 (mutated IgVH = 17, 34.7%; unmutated IgVH = 32, 65.3%), and 79 patients (median age: 57 years) with NK (mutated IgVH = 41, 51.9%; unmutated IgVH = 38, 48.1%), respectively. Unmutated IgVH was associated with shorter TFT in patients with sole del13q (unmutated 2.1 years vs. mutated 6.0 years, p < 0.001) and isolated NK (unmutated 1.9 years vs. mutated 3.3 year, p = 0.05). IgVH mutational status had no impact in the TFT of patients with sole T12. Patients with isolated del13q and mutated IgVH had a longer median OS compared to unmutated patients (not reached vs. 10.5 years, p=0.03). Nonetheless, the IgVH mutational status did not significantly impact the OS of sole T12 patients (p=0.29) and NK (p=0.14).
Conclusion
Our results confirm the negative impact of the unmutated IgVH status in CLL patients with isolated del13q. The mutational IgVH status did not impact the OS of T12 and NK CLL patients.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Immunoglobulin gene, Mutation status
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


