TREATMENT OUTCOME OF DIFFUSE LARGE B CELL LYMPHOMA IN RITUXIMAB ERA AND THE PROGNOSTIC VALUE OF R-IPI SCORE AT A CANCER CENTER IN TAIWAN: SINGLE INSTITUTION EXPERIENCE
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Sung M. 06/09/16; 134613; PB1713

Mr. Meng-Ta Sung
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: PB1713
Type: Publication Only
Background
The treatment outcome of diffuse large B cell lymphoma showed major improvement in rituximab era. The predictor of outcome is still under investigation.
Aims
To review and analyze the treatment experience of newly diagnosed diffuse large B cell lymphoma in rituximab era in our institution.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed medical records from Jan 2005 to Dec 2014 from our institution. We figured out patients with newly diagnosed diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Clinical characteristics, treatment response, treatment modality, and survival were analyzed.
Results
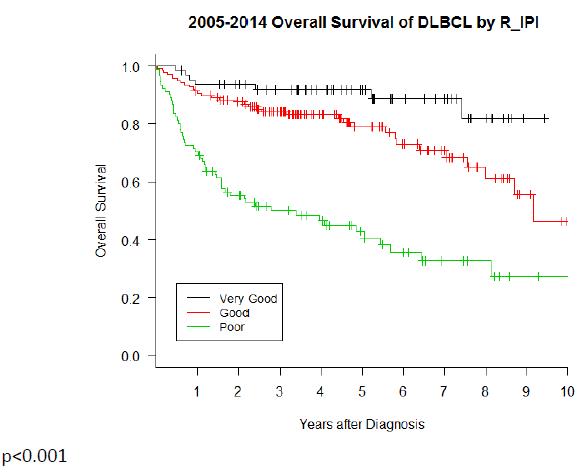
From Jan 2005 to Dec 2014, there were 292 newly diagnosed diffuse large B cell lymphoma in our institution. Median age was 57 years old. 50.7% of patients had advanced stage (stage III&IV), and 7.9% had poor performance status(ECOG2-4). According to revised International Prognostic Index score(R-IPI score), 21.6% had very good prognosis (score 0), 47.2% had good prognosis (score 1 or 2), and 31.2% had poor prognosis(score 3,4 or 5). According to primary site,62.3% had lymphadenopathy, 8.2% had mediastinum disease, 16.1% had gastrointestinal disease. Ki67 was available in 59.9% of patients. According to cell origin, germinal center B-cell-like(GCB) was 11.7% and non-GCB was 9.9%.78.4% of patients did not perform the test. HBsAg was positive in 25.3% of patients. 81.3% of patients were treated with RCHOP-like regimen. Complete remission(CR) was achieved in 79.4% of patients. 3-year event free survival(EFS) and overall survival(OS) were 70% and 75.3%, respectively. 5-year event free survival(EFS) and overall survival(OS) were 64.9% and 70%, respectively. The 5-year OS was 92.7%,77.5%,66%,47.3% in stageI/II/III/IV, respectively(p<0.001). The 5-year OS was 91.8%, 78.9%,42.8% in R-IPI very good group, good group and poor group, respectively(p<0.001). CR, treated with R-CHOP-like regimen, R-IPI score predicted the outcome of the patient. Primary site, Ki67, GCB were not associated with outcome in our cohort. Though Taiwan is in HBV endemic area, HsAg was not associated with outcome in our cohort.
Conclusion
Diffuse large B cell lymphoma has good prognosis for majority of patients in rituximab era. R-IPI score has significant prognostic value in Asian population. However, for patients with higher stage and higher IPI score, further investigation to improve outcome is still required.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, Rituximab, Survival, Treatment
Type: Publication Only
Background
The treatment outcome of diffuse large B cell lymphoma showed major improvement in rituximab era. The predictor of outcome is still under investigation.
Aims
To review and analyze the treatment experience of newly diagnosed diffuse large B cell lymphoma in rituximab era in our institution.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed medical records from Jan 2005 to Dec 2014 from our institution. We figured out patients with newly diagnosed diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Clinical characteristics, treatment response, treatment modality, and survival were analyzed.
Results
From Jan 2005 to Dec 2014, there were 292 newly diagnosed diffuse large B cell lymphoma in our institution. Median age was 57 years old. 50.7% of patients had advanced stage (stage III&IV), and 7.9% had poor performance status(ECOG2-4). According to revised International Prognostic Index score(R-IPI score), 21.6% had very good prognosis (score 0), 47.2% had good prognosis (score 1 or 2), and 31.2% had poor prognosis(score 3,4 or 5). According to primary site,62.3% had lymphadenopathy, 8.2% had mediastinum disease, 16.1% had gastrointestinal disease. Ki67 was available in 59.9% of patients. According to cell origin, germinal center B-cell-like(GCB) was 11.7% and non-GCB was 9.9%.78.4% of patients did not perform the test. HBsAg was positive in 25.3% of patients. 81.3% of patients were treated with RCHOP-like regimen. Complete remission(CR) was achieved in 79.4% of patients. 3-year event free survival(EFS) and overall survival(OS) were 70% and 75.3%, respectively. 5-year event free survival(EFS) and overall survival(OS) were 64.9% and 70%, respectively. The 5-year OS was 92.7%,77.5%,66%,47.3% in stageI/II/III/IV, respectively(p<0.001). The 5-year OS was 91.8%, 78.9%,42.8% in R-IPI very good group, good group and poor group, respectively(p<0.001). CR, treated with R-CHOP-like regimen, R-IPI score predicted the outcome of the patient. Primary site, Ki67, GCB were not associated with outcome in our cohort. Though Taiwan is in HBV endemic area, HsAg was not associated with outcome in our cohort.
Conclusion
Diffuse large B cell lymphoma has good prognosis for majority of patients in rituximab era. R-IPI score has significant prognostic value in Asian population. However, for patients with higher stage and higher IPI score, further investigation to improve outcome is still required.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, Rituximab, Survival, Treatment
Abstract: PB1713
Type: Publication Only
Background
The treatment outcome of diffuse large B cell lymphoma showed major improvement in rituximab era. The predictor of outcome is still under investigation.
Aims
To review and analyze the treatment experience of newly diagnosed diffuse large B cell lymphoma in rituximab era in our institution.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed medical records from Jan 2005 to Dec 2014 from our institution. We figured out patients with newly diagnosed diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Clinical characteristics, treatment response, treatment modality, and survival were analyzed.
Results
From Jan 2005 to Dec 2014, there were 292 newly diagnosed diffuse large B cell lymphoma in our institution. Median age was 57 years old. 50.7% of patients had advanced stage (stage III&IV), and 7.9% had poor performance status(ECOG2-4). According to revised International Prognostic Index score(R-IPI score), 21.6% had very good prognosis (score 0), 47.2% had good prognosis (score 1 or 2), and 31.2% had poor prognosis(score 3,4 or 5). According to primary site,62.3% had lymphadenopathy, 8.2% had mediastinum disease, 16.1% had gastrointestinal disease. Ki67 was available in 59.9% of patients. According to cell origin, germinal center B-cell-like(GCB) was 11.7% and non-GCB was 9.9%.78.4% of patients did not perform the test. HBsAg was positive in 25.3% of patients. 81.3% of patients were treated with RCHOP-like regimen. Complete remission(CR) was achieved in 79.4% of patients. 3-year event free survival(EFS) and overall survival(OS) were 70% and 75.3%, respectively. 5-year event free survival(EFS) and overall survival(OS) were 64.9% and 70%, respectively. The 5-year OS was 92.7%,77.5%,66%,47.3% in stageI/II/III/IV, respectively(p<0.001). The 5-year OS was 91.8%, 78.9%,42.8% in R-IPI very good group, good group and poor group, respectively(p<0.001). CR, treated with R-CHOP-like regimen, R-IPI score predicted the outcome of the patient. Primary site, Ki67, GCB were not associated with outcome in our cohort. Though Taiwan is in HBV endemic area, HsAg was not associated with outcome in our cohort.
Conclusion
Diffuse large B cell lymphoma has good prognosis for majority of patients in rituximab era. R-IPI score has significant prognostic value in Asian population. However, for patients with higher stage and higher IPI score, further investigation to improve outcome is still required.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, Rituximab, Survival, Treatment
Type: Publication Only
Background
The treatment outcome of diffuse large B cell lymphoma showed major improvement in rituximab era. The predictor of outcome is still under investigation.
Aims
To review and analyze the treatment experience of newly diagnosed diffuse large B cell lymphoma in rituximab era in our institution.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed medical records from Jan 2005 to Dec 2014 from our institution. We figured out patients with newly diagnosed diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Clinical characteristics, treatment response, treatment modality, and survival were analyzed.
Results
From Jan 2005 to Dec 2014, there were 292 newly diagnosed diffuse large B cell lymphoma in our institution. Median age was 57 years old. 50.7% of patients had advanced stage (stage III&IV), and 7.9% had poor performance status(ECOG2-4). According to revised International Prognostic Index score(R-IPI score), 21.6% had very good prognosis (score 0), 47.2% had good prognosis (score 1 or 2), and 31.2% had poor prognosis(score 3,4 or 5). According to primary site,62.3% had lymphadenopathy, 8.2% had mediastinum disease, 16.1% had gastrointestinal disease. Ki67 was available in 59.9% of patients. According to cell origin, germinal center B-cell-like(GCB) was 11.7% and non-GCB was 9.9%.78.4% of patients did not perform the test. HBsAg was positive in 25.3% of patients. 81.3% of patients were treated with RCHOP-like regimen. Complete remission(CR) was achieved in 79.4% of patients. 3-year event free survival(EFS) and overall survival(OS) were 70% and 75.3%, respectively. 5-year event free survival(EFS) and overall survival(OS) were 64.9% and 70%, respectively. The 5-year OS was 92.7%,77.5%,66%,47.3% in stageI/II/III/IV, respectively(p<0.001). The 5-year OS was 91.8%, 78.9%,42.8% in R-IPI very good group, good group and poor group, respectively(p<0.001). CR, treated with R-CHOP-like regimen, R-IPI score predicted the outcome of the patient. Primary site, Ki67, GCB were not associated with outcome in our cohort. Though Taiwan is in HBV endemic area, HsAg was not associated with outcome in our cohort.
Conclusion
Diffuse large B cell lymphoma has good prognosis for majority of patients in rituximab era. R-IPI score has significant prognostic value in Asian population. However, for patients with higher stage and higher IPI score, further investigation to improve outcome is still required.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, Rituximab, Survival, Treatment
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


