A TWO-CENTER RETROSPECTIVE COMPARISON OF BEAM VS. BUCYVP16 CONDITIONING PRIOR TO AUTOLOGOUS HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION IN PATIENTS WITH NON-HODGKIN’S LYMPHOMA.
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Singer S. 06/09/16; 133063; E1514

Dr. Sara Singer
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: E1514
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
High dose chemotherapy followed by autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (AHSCT) has become the standard of care for patients with relapsed chemo-sensitive Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (NHL). Various conditioning regimens have been developed to improve outcome, but no regimen has proven superior. We compare the outcomes of Carmustine, Etoposide, Cytarabine, Melphalan (BEAM) used at the Ohio State University to that of Busulfan, Cyclophosphamide, Etoposide (BUCYVP16) used at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation.
Aims
To compare the efficacy and toxicity of BEAM and BUCYVP16 conditioning regimens in patients with relapsed NHL undergoing AHSCT.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed patients treated with BEAM (n=269) or BUCYVP16 (n=409) followed by AHSCT between 2006 and 2014. Kaplan-Meier estimates were used to analyze progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). Cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) was measured from transplant date until relapse, treating deaths as competing risks using Pepe and Mori test.
Results
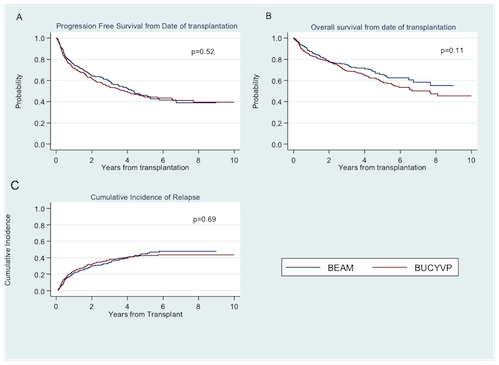
Patient characteristics were similar for age (median 60 (20-77) vs. 58 (27-78)), disease stage at diagnosis (p=0.29), prior radiation exposure (p=0.68), and response status at transplant (94.7% CR/PR vs. 93.2%) for BEAM vs. BUCYVP16 respectively. Differences were number of prior treatments (median 2 (1-8) vs. 2 (1-13), p<0.01), comorbidity index (74.0% 0-3 vs. 80.9%, p=0.03), and median CD34 dose infused (4.3 vs. 6.02, p<0.01) for BEAM vs. BUCYVP16. Median follow-up from diagnosis and transplant was 6.6 years and 4.0 years respectively for BEAM and 7.0 years and 4.3 years for BUCYVP16. Median day to neutrophil engraftment was 10 (8-19) vs. 10 (9-15) (p<0.01) and median time to platelet engraftment was 18 (11-69) vs. 16 (3-129) (p<0.01) for BEAM vs. BUCYVP16. There were no statistical differences in CIR, PFS or OS. At 1, 3 and 5 years from AHSCT, PFS was 75%, 59%, and 46% vs. 72%, 54%, and 44% (p=0.52); OS 88%, 75%, and 66% vs. 83%, 69% and 59% (p=0.11) in the BEAM vs. BUCYVP16 groups respectively (Figure 1). Veno-occlusive disease (VOD) was higher in the BEAM group (7 pts (2.6%) compared to none in BYCYVP16 (p<0.01)) but grade 3 or 4 mucositis was lower in BEAM (24.2%) compared to 56.1% in BUCYVP16 (p<0.01). There were no differences in hemorrhagic cystitis or second primary malignancy.
Conclusion
This large retrospective study showed no statistical difference in PFS, OS, or CIR between BEAM and BUCVP16 conditioning regimens for AHSCT in relapsed NHL. Veno-occlusive disease occurred more frequently in the BEAM group, while grade 3 or 4 mucositis occurred more frequently in the BUCYVP16 group.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, Busulfan, Melphalan, Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
High dose chemotherapy followed by autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (AHSCT) has become the standard of care for patients with relapsed chemo-sensitive Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (NHL). Various conditioning regimens have been developed to improve outcome, but no regimen has proven superior. We compare the outcomes of Carmustine, Etoposide, Cytarabine, Melphalan (BEAM) used at the Ohio State University to that of Busulfan, Cyclophosphamide, Etoposide (BUCYVP16) used at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation.
Aims
To compare the efficacy and toxicity of BEAM and BUCYVP16 conditioning regimens in patients with relapsed NHL undergoing AHSCT.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed patients treated with BEAM (n=269) or BUCYVP16 (n=409) followed by AHSCT between 2006 and 2014. Kaplan-Meier estimates were used to analyze progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). Cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) was measured from transplant date until relapse, treating deaths as competing risks using Pepe and Mori test.
Results
Patient characteristics were similar for age (median 60 (20-77) vs. 58 (27-78)), disease stage at diagnosis (p=0.29), prior radiation exposure (p=0.68), and response status at transplant (94.7% CR/PR vs. 93.2%) for BEAM vs. BUCYVP16 respectively. Differences were number of prior treatments (median 2 (1-8) vs. 2 (1-13), p<0.01), comorbidity index (74.0% 0-3 vs. 80.9%, p=0.03), and median CD34 dose infused (4.3 vs. 6.02, p<0.01) for BEAM vs. BUCYVP16. Median follow-up from diagnosis and transplant was 6.6 years and 4.0 years respectively for BEAM and 7.0 years and 4.3 years for BUCYVP16. Median day to neutrophil engraftment was 10 (8-19) vs. 10 (9-15) (p<0.01) and median time to platelet engraftment was 18 (11-69) vs. 16 (3-129) (p<0.01) for BEAM vs. BUCYVP16. There were no statistical differences in CIR, PFS or OS. At 1, 3 and 5 years from AHSCT, PFS was 75%, 59%, and 46% vs. 72%, 54%, and 44% (p=0.52); OS 88%, 75%, and 66% vs. 83%, 69% and 59% (p=0.11) in the BEAM vs. BUCYVP16 groups respectively (Figure 1). Veno-occlusive disease (VOD) was higher in the BEAM group (7 pts (2.6%) compared to none in BYCYVP16 (p<0.01)) but grade 3 or 4 mucositis was lower in BEAM (24.2%) compared to 56.1% in BUCYVP16 (p<0.01). There were no differences in hemorrhagic cystitis or second primary malignancy.
Conclusion
This large retrospective study showed no statistical difference in PFS, OS, or CIR between BEAM and BUCVP16 conditioning regimens for AHSCT in relapsed NHL. Veno-occlusive disease occurred more frequently in the BEAM group, while grade 3 or 4 mucositis occurred more frequently in the BUCYVP16 group.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, Busulfan, Melphalan, Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Abstract: E1514
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
High dose chemotherapy followed by autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (AHSCT) has become the standard of care for patients with relapsed chemo-sensitive Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (NHL). Various conditioning regimens have been developed to improve outcome, but no regimen has proven superior. We compare the outcomes of Carmustine, Etoposide, Cytarabine, Melphalan (BEAM) used at the Ohio State University to that of Busulfan, Cyclophosphamide, Etoposide (BUCYVP16) used at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation.
Aims
To compare the efficacy and toxicity of BEAM and BUCYVP16 conditioning regimens in patients with relapsed NHL undergoing AHSCT.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed patients treated with BEAM (n=269) or BUCYVP16 (n=409) followed by AHSCT between 2006 and 2014. Kaplan-Meier estimates were used to analyze progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). Cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) was measured from transplant date until relapse, treating deaths as competing risks using Pepe and Mori test.
Results
Patient characteristics were similar for age (median 60 (20-77) vs. 58 (27-78)), disease stage at diagnosis (p=0.29), prior radiation exposure (p=0.68), and response status at transplant (94.7% CR/PR vs. 93.2%) for BEAM vs. BUCYVP16 respectively. Differences were number of prior treatments (median 2 (1-8) vs. 2 (1-13), p<0.01), comorbidity index (74.0% 0-3 vs. 80.9%, p=0.03), and median CD34 dose infused (4.3 vs. 6.02, p<0.01) for BEAM vs. BUCYVP16. Median follow-up from diagnosis and transplant was 6.6 years and 4.0 years respectively for BEAM and 7.0 years and 4.3 years for BUCYVP16. Median day to neutrophil engraftment was 10 (8-19) vs. 10 (9-15) (p<0.01) and median time to platelet engraftment was 18 (11-69) vs. 16 (3-129) (p<0.01) for BEAM vs. BUCYVP16. There were no statistical differences in CIR, PFS or OS. At 1, 3 and 5 years from AHSCT, PFS was 75%, 59%, and 46% vs. 72%, 54%, and 44% (p=0.52); OS 88%, 75%, and 66% vs. 83%, 69% and 59% (p=0.11) in the BEAM vs. BUCYVP16 groups respectively (Figure 1). Veno-occlusive disease (VOD) was higher in the BEAM group (7 pts (2.6%) compared to none in BYCYVP16 (p<0.01)) but grade 3 or 4 mucositis was lower in BEAM (24.2%) compared to 56.1% in BUCYVP16 (p<0.01). There were no differences in hemorrhagic cystitis or second primary malignancy.
Conclusion
This large retrospective study showed no statistical difference in PFS, OS, or CIR between BEAM and BUCVP16 conditioning regimens for AHSCT in relapsed NHL. Veno-occlusive disease occurred more frequently in the BEAM group, while grade 3 or 4 mucositis occurred more frequently in the BUCYVP16 group.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, Busulfan, Melphalan, Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
High dose chemotherapy followed by autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (AHSCT) has become the standard of care for patients with relapsed chemo-sensitive Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (NHL). Various conditioning regimens have been developed to improve outcome, but no regimen has proven superior. We compare the outcomes of Carmustine, Etoposide, Cytarabine, Melphalan (BEAM) used at the Ohio State University to that of Busulfan, Cyclophosphamide, Etoposide (BUCYVP16) used at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation.
Aims
To compare the efficacy and toxicity of BEAM and BUCYVP16 conditioning regimens in patients with relapsed NHL undergoing AHSCT.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed patients treated with BEAM (n=269) or BUCYVP16 (n=409) followed by AHSCT between 2006 and 2014. Kaplan-Meier estimates were used to analyze progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). Cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) was measured from transplant date until relapse, treating deaths as competing risks using Pepe and Mori test.
Results
Patient characteristics were similar for age (median 60 (20-77) vs. 58 (27-78)), disease stage at diagnosis (p=0.29), prior radiation exposure (p=0.68), and response status at transplant (94.7% CR/PR vs. 93.2%) for BEAM vs. BUCYVP16 respectively. Differences were number of prior treatments (median 2 (1-8) vs. 2 (1-13), p<0.01), comorbidity index (74.0% 0-3 vs. 80.9%, p=0.03), and median CD34 dose infused (4.3 vs. 6.02, p<0.01) for BEAM vs. BUCYVP16. Median follow-up from diagnosis and transplant was 6.6 years and 4.0 years respectively for BEAM and 7.0 years and 4.3 years for BUCYVP16. Median day to neutrophil engraftment was 10 (8-19) vs. 10 (9-15) (p<0.01) and median time to platelet engraftment was 18 (11-69) vs. 16 (3-129) (p<0.01) for BEAM vs. BUCYVP16. There were no statistical differences in CIR, PFS or OS. At 1, 3 and 5 years from AHSCT, PFS was 75%, 59%, and 46% vs. 72%, 54%, and 44% (p=0.52); OS 88%, 75%, and 66% vs. 83%, 69% and 59% (p=0.11) in the BEAM vs. BUCYVP16 groups respectively (Figure 1). Veno-occlusive disease (VOD) was higher in the BEAM group (7 pts (2.6%) compared to none in BYCYVP16 (p<0.01)) but grade 3 or 4 mucositis was lower in BEAM (24.2%) compared to 56.1% in BUCYVP16 (p<0.01). There were no differences in hemorrhagic cystitis or second primary malignancy.
Conclusion
This large retrospective study showed no statistical difference in PFS, OS, or CIR between BEAM and BUCVP16 conditioning regimens for AHSCT in relapsed NHL. Veno-occlusive disease occurred more frequently in the BEAM group, while grade 3 or 4 mucositis occurred more frequently in the BUCYVP16 group.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, Busulfan, Melphalan, Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


