ASSESSING NPM1 MUTATIONS TYPE A AS MINIMAL RESIDUAL DISEASE MARKER BY DIGITAL DROPLET PCR BEFORE STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION IS A STRONG PROGNOSTIC FACTOR IN PATIENTS WITH AML
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Bill M. 06/09/16; 133046; E1497

Mr. Marius Bill
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: E1497
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients (pts) who relapse after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HCT) have a dismal prognosis. Identifying AML pts with high risk of hematological relapse after HCT is crucial for treatment guidance. Mutations in the NPM1 gene (NPM1mut) occur early in leukemogenesis & are relatively stable during disease course, representing suitable Minimal residual disease (MRD) markers. Recently, MRD assessment, based e.g. on the quantitative detection of NPM1mut, has been shown to be of clinical relevance. However, data in pts receiving HCT is limited.
Aims
We tested the feasibility of NPM1mut type A (NPM1mutA) - representing up to 80% of all NPM1mut – as pre-HCT MRD marker using digital droplet PCR (ddPCR) for sensitive & specific absolute quantification without the use of standard curves.
Methods
We identified 46 AML pts with available bone marrow (BM) pre-HCT (within 30 days before HCT) & NPM1mutA who were in complete remission with (CR; n=42; 91.3%) or without complete hematological recovery (CRi; n=4; 8.7%). Median age was 64.5 (range 33.1-74.1) years (y). Pts received HCT after myeloablative (Cyclophosphamide 2x60mg/kg + 12Gy total body irradiation [TBI], n=11) or non-myeloablative (Fludarabine 3x30mg/m² + 2Gy TBI, n=35) conditioning at our institution between 2000 & 2015. Median follow-up was 2.1y. NPM1mutA & CEBPA mutation status were assessed by Sanger sequencing & presence of an internal tandem duplication in FLT3 by fragment analysis in diagnostic BM. NPM1mutA copy numbers were assessed by ddPCR in pre-HCT BM. Results were normalized to ABL1 copy numbers. Samples were measured in triplicates & those with mutation burden ≤0.01% or <3 positive droplets were defined as negative according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Results
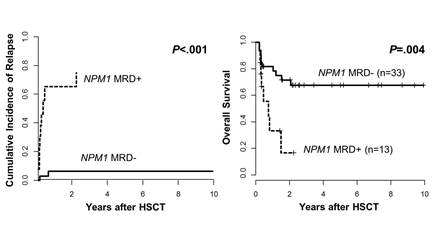
At diagnosis 40 pts (87.0%) had a normal karyotype. According to European LeukemiaNet (ELN) classification 26 (56.5%) had favorable, 14 (30.4%) intermediate-I, 5 (10.9%) intermediate-II & 1 (2.2%) adverse genetic risk. 18 pts harbored a FLT3-ITD & 4 were CEBPA mut.We found 13 (28.3%) of the 46 pts to be MRD+ pre-HCT (NPM1mutA/ABL1 range 0.014% - 612.88%). Except for a trend for lower peripheral blast count at diagnosis (dx) in the MRD+ group (P=.07) no differences were detected between MRD+ & MRD- pts in other clinical or molecular characteristics (i.e. agedx, sex, ELN group distribution, Hbdx, Plateletsdx, white blood countdx, BM blastsdx, CR1 vs. CR2 vs. CRi, CEBPAmut, FLT3-ITD). The number of chemotherapy cycles pre-HCT was not different between the MRD+ & MRD- group.Eleven pts relapsed of which 9 (81.8%) were MRD+ pre-HCT. Four patients did not experience relapse but were MRD+, 2 of them died within 100 days after HCT due to treatment-related complications. With respect to the remission status, only 2 (50%) of the 4 pts transplanted in CRi suffered relapse & both were MRD+.MRD+ pre-HCT was associated with a significantly higher cumulative incidence of relapse (P<0.001, Figure 1A) & shorter overall survival (OS, P=0.004, Figure 1B).
Conclusion
Our study demonstrated that the novel ddPCR is a feasible method to determine NPM1mutA MRD burden by absolute quantification. Pre-HCT MRD+ identified pts with a significantly higher relapse rate & subsequently shorter OS independently of the clinical, cytogenetical & molecular context. MRD monitoring by NPM1mut detection before HCT should be incorporated in clinical trials to validate these data & guide therapeutic decisions for AML pts.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant, AML, MRD
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients (pts) who relapse after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HCT) have a dismal prognosis. Identifying AML pts with high risk of hematological relapse after HCT is crucial for treatment guidance. Mutations in the NPM1 gene (NPM1mut) occur early in leukemogenesis & are relatively stable during disease course, representing suitable Minimal residual disease (MRD) markers. Recently, MRD assessment, based e.g. on the quantitative detection of NPM1mut, has been shown to be of clinical relevance. However, data in pts receiving HCT is limited.
Aims
We tested the feasibility of NPM1mut type A (NPM1mutA) - representing up to 80% of all NPM1mut – as pre-HCT MRD marker using digital droplet PCR (ddPCR) for sensitive & specific absolute quantification without the use of standard curves.
Methods
We identified 46 AML pts with available bone marrow (BM) pre-HCT (within 30 days before HCT) & NPM1mutA who were in complete remission with (CR; n=42; 91.3%) or without complete hematological recovery (CRi; n=4; 8.7%). Median age was 64.5 (range 33.1-74.1) years (y). Pts received HCT after myeloablative (Cyclophosphamide 2x60mg/kg + 12Gy total body irradiation [TBI], n=11) or non-myeloablative (Fludarabine 3x30mg/m² + 2Gy TBI, n=35) conditioning at our institution between 2000 & 2015. Median follow-up was 2.1y. NPM1mutA & CEBPA mutation status were assessed by Sanger sequencing & presence of an internal tandem duplication in FLT3 by fragment analysis in diagnostic BM. NPM1mutA copy numbers were assessed by ddPCR in pre-HCT BM. Results were normalized to ABL1 copy numbers. Samples were measured in triplicates & those with mutation burden ≤0.01% or <3 positive droplets were defined as negative according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Results
At diagnosis 40 pts (87.0%) had a normal karyotype. According to European LeukemiaNet (ELN) classification 26 (56.5%) had favorable, 14 (30.4%) intermediate-I, 5 (10.9%) intermediate-II & 1 (2.2%) adverse genetic risk. 18 pts harbored a FLT3-ITD & 4 were CEBPA mut.We found 13 (28.3%) of the 46 pts to be MRD+ pre-HCT (NPM1mutA/ABL1 range 0.014% - 612.88%). Except for a trend for lower peripheral blast count at diagnosis (dx) in the MRD+ group (P=.07) no differences were detected between MRD+ & MRD- pts in other clinical or molecular characteristics (i.e. agedx, sex, ELN group distribution, Hbdx, Plateletsdx, white blood countdx, BM blastsdx, CR1 vs. CR2 vs. CRi, CEBPAmut, FLT3-ITD). The number of chemotherapy cycles pre-HCT was not different between the MRD+ & MRD- group.Eleven pts relapsed of which 9 (81.8%) were MRD+ pre-HCT. Four patients did not experience relapse but were MRD+, 2 of them died within 100 days after HCT due to treatment-related complications. With respect to the remission status, only 2 (50%) of the 4 pts transplanted in CRi suffered relapse & both were MRD+.MRD+ pre-HCT was associated with a significantly higher cumulative incidence of relapse (P<0.001, Figure 1A) & shorter overall survival (OS, P=0.004, Figure 1B).
Conclusion
Our study demonstrated that the novel ddPCR is a feasible method to determine NPM1mutA MRD burden by absolute quantification. Pre-HCT MRD+ identified pts with a significantly higher relapse rate & subsequently shorter OS independently of the clinical, cytogenetical & molecular context. MRD monitoring by NPM1mut detection before HCT should be incorporated in clinical trials to validate these data & guide therapeutic decisions for AML pts.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant, AML, MRD
Abstract: E1497
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients (pts) who relapse after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HCT) have a dismal prognosis. Identifying AML pts with high risk of hematological relapse after HCT is crucial for treatment guidance. Mutations in the NPM1 gene (NPM1mut) occur early in leukemogenesis & are relatively stable during disease course, representing suitable Minimal residual disease (MRD) markers. Recently, MRD assessment, based e.g. on the quantitative detection of NPM1mut, has been shown to be of clinical relevance. However, data in pts receiving HCT is limited.
Aims
We tested the feasibility of NPM1mut type A (NPM1mutA) - representing up to 80% of all NPM1mut – as pre-HCT MRD marker using digital droplet PCR (ddPCR) for sensitive & specific absolute quantification without the use of standard curves.
Methods
We identified 46 AML pts with available bone marrow (BM) pre-HCT (within 30 days before HCT) & NPM1mutA who were in complete remission with (CR; n=42; 91.3%) or without complete hematological recovery (CRi; n=4; 8.7%). Median age was 64.5 (range 33.1-74.1) years (y). Pts received HCT after myeloablative (Cyclophosphamide 2x60mg/kg + 12Gy total body irradiation [TBI], n=11) or non-myeloablative (Fludarabine 3x30mg/m² + 2Gy TBI, n=35) conditioning at our institution between 2000 & 2015. Median follow-up was 2.1y. NPM1mutA & CEBPA mutation status were assessed by Sanger sequencing & presence of an internal tandem duplication in FLT3 by fragment analysis in diagnostic BM. NPM1mutA copy numbers were assessed by ddPCR in pre-HCT BM. Results were normalized to ABL1 copy numbers. Samples were measured in triplicates & those with mutation burden ≤0.01% or <3 positive droplets were defined as negative according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Results
At diagnosis 40 pts (87.0%) had a normal karyotype. According to European LeukemiaNet (ELN) classification 26 (56.5%) had favorable, 14 (30.4%) intermediate-I, 5 (10.9%) intermediate-II & 1 (2.2%) adverse genetic risk. 18 pts harbored a FLT3-ITD & 4 were CEBPA mut.We found 13 (28.3%) of the 46 pts to be MRD+ pre-HCT (NPM1mutA/ABL1 range 0.014% - 612.88%). Except for a trend for lower peripheral blast count at diagnosis (dx) in the MRD+ group (P=.07) no differences were detected between MRD+ & MRD- pts in other clinical or molecular characteristics (i.e. agedx, sex, ELN group distribution, Hbdx, Plateletsdx, white blood countdx, BM blastsdx, CR1 vs. CR2 vs. CRi, CEBPAmut, FLT3-ITD). The number of chemotherapy cycles pre-HCT was not different between the MRD+ & MRD- group.Eleven pts relapsed of which 9 (81.8%) were MRD+ pre-HCT. Four patients did not experience relapse but were MRD+, 2 of them died within 100 days after HCT due to treatment-related complications. With respect to the remission status, only 2 (50%) of the 4 pts transplanted in CRi suffered relapse & both were MRD+.MRD+ pre-HCT was associated with a significantly higher cumulative incidence of relapse (P<0.001, Figure 1A) & shorter overall survival (OS, P=0.004, Figure 1B).
Conclusion
Our study demonstrated that the novel ddPCR is a feasible method to determine NPM1mutA MRD burden by absolute quantification. Pre-HCT MRD+ identified pts with a significantly higher relapse rate & subsequently shorter OS independently of the clinical, cytogenetical & molecular context. MRD monitoring by NPM1mut detection before HCT should be incorporated in clinical trials to validate these data & guide therapeutic decisions for AML pts.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant, AML, MRD
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients (pts) who relapse after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HCT) have a dismal prognosis. Identifying AML pts with high risk of hematological relapse after HCT is crucial for treatment guidance. Mutations in the NPM1 gene (NPM1mut) occur early in leukemogenesis & are relatively stable during disease course, representing suitable Minimal residual disease (MRD) markers. Recently, MRD assessment, based e.g. on the quantitative detection of NPM1mut, has been shown to be of clinical relevance. However, data in pts receiving HCT is limited.
Aims
We tested the feasibility of NPM1mut type A (NPM1mutA) - representing up to 80% of all NPM1mut – as pre-HCT MRD marker using digital droplet PCR (ddPCR) for sensitive & specific absolute quantification without the use of standard curves.
Methods
We identified 46 AML pts with available bone marrow (BM) pre-HCT (within 30 days before HCT) & NPM1mutA who were in complete remission with (CR; n=42; 91.3%) or without complete hematological recovery (CRi; n=4; 8.7%). Median age was 64.5 (range 33.1-74.1) years (y). Pts received HCT after myeloablative (Cyclophosphamide 2x60mg/kg + 12Gy total body irradiation [TBI], n=11) or non-myeloablative (Fludarabine 3x30mg/m² + 2Gy TBI, n=35) conditioning at our institution between 2000 & 2015. Median follow-up was 2.1y. NPM1mutA & CEBPA mutation status were assessed by Sanger sequencing & presence of an internal tandem duplication in FLT3 by fragment analysis in diagnostic BM. NPM1mutA copy numbers were assessed by ddPCR in pre-HCT BM. Results were normalized to ABL1 copy numbers. Samples were measured in triplicates & those with mutation burden ≤0.01% or <3 positive droplets were defined as negative according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Results
At diagnosis 40 pts (87.0%) had a normal karyotype. According to European LeukemiaNet (ELN) classification 26 (56.5%) had favorable, 14 (30.4%) intermediate-I, 5 (10.9%) intermediate-II & 1 (2.2%) adverse genetic risk. 18 pts harbored a FLT3-ITD & 4 were CEBPA mut.We found 13 (28.3%) of the 46 pts to be MRD+ pre-HCT (NPM1mutA/ABL1 range 0.014% - 612.88%). Except for a trend for lower peripheral blast count at diagnosis (dx) in the MRD+ group (P=.07) no differences were detected between MRD+ & MRD- pts in other clinical or molecular characteristics (i.e. agedx, sex, ELN group distribution, Hbdx, Plateletsdx, white blood countdx, BM blastsdx, CR1 vs. CR2 vs. CRi, CEBPAmut, FLT3-ITD). The number of chemotherapy cycles pre-HCT was not different between the MRD+ & MRD- group.Eleven pts relapsed of which 9 (81.8%) were MRD+ pre-HCT. Four patients did not experience relapse but were MRD+, 2 of them died within 100 days after HCT due to treatment-related complications. With respect to the remission status, only 2 (50%) of the 4 pts transplanted in CRi suffered relapse & both were MRD+.MRD+ pre-HCT was associated with a significantly higher cumulative incidence of relapse (P<0.001, Figure 1A) & shorter overall survival (OS, P=0.004, Figure 1B).
Conclusion
Our study demonstrated that the novel ddPCR is a feasible method to determine NPM1mutA MRD burden by absolute quantification. Pre-HCT MRD+ identified pts with a significantly higher relapse rate & subsequently shorter OS independently of the clinical, cytogenetical & molecular context. MRD monitoring by NPM1mut detection before HCT should be incorporated in clinical trials to validate these data & guide therapeutic decisions for AML pts.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant, AML, MRD
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


