PROGNOSIS FACTORS CONDITIONING THE RISK OF MIELOFIBROTIC TRANSFORMATION IN ESSENTIAL THROMBOCYTHEMIA: SIGNIFICANCE OF ALLELIC BURDEN AND THE NUMBER OF LEUCOCYTES AT DIAGNOSIS IN YOUNG PATIENTS.
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Montero M. 06/09/16; 132916; E1367

Mrs. Maria Isabel Montero
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: E1367
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Even though there are predictive prognostic scores of thrombotic risk in patients with Essential Thrombocythemia (ET), there is no agreement established on the factors influencing the evolution of myelofibrosis in these patients, this is a factor that adversely affects their life expectancy, which is initially similar to that of the healthy population of the same age.
Aims
To analyse in a group of patients with ET the impact of parameters such as age, platelet count at diagnosis, number of leucocytes, time until cytoreductive therapy was needed, time under observation, presence of JAK2 V617F mutation and allelic burden on the risk of myelofibrotic transformation.
Methods
We analysed a total of 100 patients diagnosed in our centre between 1996 and 2013 based on bone marrow study. All patients received anti- platelet agregation and began cytoreductive therapy with hydroxyurea and / or anagrelide according to IPSET criteria. JAK2 V617F mutation was detected by allele - specific real- time quantitative in peripheral blood samples. Homozygous patients for the mutation occurred when the load allelic was > 50%, being the rest considered heterozygous. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 15.0 software, considering a statistical significant difference if p < 0.05.
Results
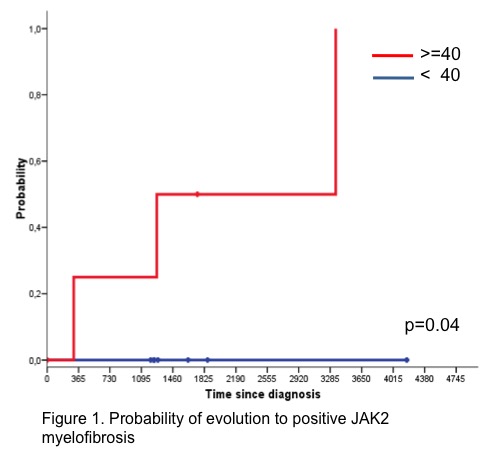
Average age of the study population was 63 years. 73% of patients had JAK2 V617F mutation, being homozygous for the same 7% of patients. 11% of patients progressed to myelofibrosis, with a median follow-up of 5 years from diagnosis to transformation. The transformed and untransformed groups were similar in platelet count at diagnosis, time under observation, time to need for cytoreductive treatment and presence of the mutation JAK2 V617F, although there is a tendency to older (74 vs. 63) and more number of leukocytes (15,1x10e9 /L vs. 9,6x10e9 /L) in the transformed versus non-transformed group. Patients with JAK2 V617F mutation and allelic burden above 40% had a higher risk of myelofibrotic transformation in the multivariate analysis, with an accumulated incidence at 5 years of 57.1 % (Figure 1), p = 0.04.
Conclusion
Patients with ET and JAK2 V617F mutation have an increased risk of myelofibrotic transformation when allelic burden is above 40 %, which is why specific therapeutic strategies will be needed aimed at reducing allelic burden to maintain an adequate life expectancy in young patients with this condition. Leucocytes cell count at diagnosis would be a variant to be considered in the prognostic stratification, although specific studies are required to examine this in more detail.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Essential Thrombocytemia, Janus Kinase inhibitor, Myelofibrosis
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Even though there are predictive prognostic scores of thrombotic risk in patients with Essential Thrombocythemia (ET), there is no agreement established on the factors influencing the evolution of myelofibrosis in these patients, this is a factor that adversely affects their life expectancy, which is initially similar to that of the healthy population of the same age.
Aims
To analyse in a group of patients with ET the impact of parameters such as age, platelet count at diagnosis, number of leucocytes, time until cytoreductive therapy was needed, time under observation, presence of JAK2 V617F mutation and allelic burden on the risk of myelofibrotic transformation.
Methods
We analysed a total of 100 patients diagnosed in our centre between 1996 and 2013 based on bone marrow study. All patients received anti- platelet agregation and began cytoreductive therapy with hydroxyurea and / or anagrelide according to IPSET criteria. JAK2 V617F mutation was detected by allele - specific real- time quantitative in peripheral blood samples. Homozygous patients for the mutation occurred when the load allelic was > 50%, being the rest considered heterozygous. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 15.0 software, considering a statistical significant difference if p < 0.05.
Results
Average age of the study population was 63 years. 73% of patients had JAK2 V617F mutation, being homozygous for the same 7% of patients. 11% of patients progressed to myelofibrosis, with a median follow-up of 5 years from diagnosis to transformation. The transformed and untransformed groups were similar in platelet count at diagnosis, time under observation, time to need for cytoreductive treatment and presence of the mutation JAK2 V617F, although there is a tendency to older (74 vs. 63) and more number of leukocytes (15,1x10e9 /L vs. 9,6x10e9 /L) in the transformed versus non-transformed group. Patients with JAK2 V617F mutation and allelic burden above 40% had a higher risk of myelofibrotic transformation in the multivariate analysis, with an accumulated incidence at 5 years of 57.1 % (Figure 1), p = 0.04.
Conclusion
Patients with ET and JAK2 V617F mutation have an increased risk of myelofibrotic transformation when allelic burden is above 40 %, which is why specific therapeutic strategies will be needed aimed at reducing allelic burden to maintain an adequate life expectancy in young patients with this condition. Leucocytes cell count at diagnosis would be a variant to be considered in the prognostic stratification, although specific studies are required to examine this in more detail.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Essential Thrombocytemia, Janus Kinase inhibitor, Myelofibrosis
Abstract: E1367
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Even though there are predictive prognostic scores of thrombotic risk in patients with Essential Thrombocythemia (ET), there is no agreement established on the factors influencing the evolution of myelofibrosis in these patients, this is a factor that adversely affects their life expectancy, which is initially similar to that of the healthy population of the same age.
Aims
To analyse in a group of patients with ET the impact of parameters such as age, platelet count at diagnosis, number of leucocytes, time until cytoreductive therapy was needed, time under observation, presence of JAK2 V617F mutation and allelic burden on the risk of myelofibrotic transformation.
Methods
We analysed a total of 100 patients diagnosed in our centre between 1996 and 2013 based on bone marrow study. All patients received anti- platelet agregation and began cytoreductive therapy with hydroxyurea and / or anagrelide according to IPSET criteria. JAK2 V617F mutation was detected by allele - specific real- time quantitative in peripheral blood samples. Homozygous patients for the mutation occurred when the load allelic was > 50%, being the rest considered heterozygous. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 15.0 software, considering a statistical significant difference if p < 0.05.
Results
Average age of the study population was 63 years. 73% of patients had JAK2 V617F mutation, being homozygous for the same 7% of patients. 11% of patients progressed to myelofibrosis, with a median follow-up of 5 years from diagnosis to transformation. The transformed and untransformed groups were similar in platelet count at diagnosis, time under observation, time to need for cytoreductive treatment and presence of the mutation JAK2 V617F, although there is a tendency to older (74 vs. 63) and more number of leukocytes (15,1x10e9 /L vs. 9,6x10e9 /L) in the transformed versus non-transformed group. Patients with JAK2 V617F mutation and allelic burden above 40% had a higher risk of myelofibrotic transformation in the multivariate analysis, with an accumulated incidence at 5 years of 57.1 % (Figure 1), p = 0.04.
Conclusion
Patients with ET and JAK2 V617F mutation have an increased risk of myelofibrotic transformation when allelic burden is above 40 %, which is why specific therapeutic strategies will be needed aimed at reducing allelic burden to maintain an adequate life expectancy in young patients with this condition. Leucocytes cell count at diagnosis would be a variant to be considered in the prognostic stratification, although specific studies are required to examine this in more detail.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Essential Thrombocytemia, Janus Kinase inhibitor, Myelofibrosis
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Even though there are predictive prognostic scores of thrombotic risk in patients with Essential Thrombocythemia (ET), there is no agreement established on the factors influencing the evolution of myelofibrosis in these patients, this is a factor that adversely affects their life expectancy, which is initially similar to that of the healthy population of the same age.
Aims
To analyse in a group of patients with ET the impact of parameters such as age, platelet count at diagnosis, number of leucocytes, time until cytoreductive therapy was needed, time under observation, presence of JAK2 V617F mutation and allelic burden on the risk of myelofibrotic transformation.
Methods
We analysed a total of 100 patients diagnosed in our centre between 1996 and 2013 based on bone marrow study. All patients received anti- platelet agregation and began cytoreductive therapy with hydroxyurea and / or anagrelide according to IPSET criteria. JAK2 V617F mutation was detected by allele - specific real- time quantitative in peripheral blood samples. Homozygous patients for the mutation occurred when the load allelic was > 50%, being the rest considered heterozygous. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 15.0 software, considering a statistical significant difference if p < 0.05.
Results
Average age of the study population was 63 years. 73% of patients had JAK2 V617F mutation, being homozygous for the same 7% of patients. 11% of patients progressed to myelofibrosis, with a median follow-up of 5 years from diagnosis to transformation. The transformed and untransformed groups were similar in platelet count at diagnosis, time under observation, time to need for cytoreductive treatment and presence of the mutation JAK2 V617F, although there is a tendency to older (74 vs. 63) and more number of leukocytes (15,1x10e9 /L vs. 9,6x10e9 /L) in the transformed versus non-transformed group. Patients with JAK2 V617F mutation and allelic burden above 40% had a higher risk of myelofibrotic transformation in the multivariate analysis, with an accumulated incidence at 5 years of 57.1 % (Figure 1), p = 0.04.
Conclusion
Patients with ET and JAK2 V617F mutation have an increased risk of myelofibrotic transformation when allelic burden is above 40 %, which is why specific therapeutic strategies will be needed aimed at reducing allelic burden to maintain an adequate life expectancy in young patients with this condition. Leucocytes cell count at diagnosis would be a variant to be considered in the prognostic stratification, although specific studies are required to examine this in more detail.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Essential Thrombocytemia, Janus Kinase inhibitor, Myelofibrosis
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


