OUTCOMES FOR ASIAN PATIENTS WITH RELAPSED MULTIPLE MYELOMA TREATED WITH CARFILZOMIB AND DEXAMETHASONE VS BORTEZOMIB AND DEXAMETHASONE: A SUBGROUP ANALYSIS OF THE PHASE 3 ENDEAVOR STUDY (NCT01568866)
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Lee J. 06/09/16; 132877; E1328

Prof. Jae Hoon Lee
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: E1328
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Carfilzomib is a selective proteasome inhibitor that is approved as a single agent and in combination with dexamethasone or lenalidomide/dexamethasone for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM). The ENDEAVOR study (NCT01568866) demonstrated statistically and clinically significant improvements in progression-free survival (PFS) for carfilzomib and dexamethasone therapy (Kd) compared with bortezomib and dexamethasone therapy (Vd; median 18.7 vs 9.4 months [mo]; hazard ratio [HR], 0.53; 95% confidence interval [CI]:0.44–0.65; 1-sided P<0.001) (Dimopoulos et al, Lancet Oncol 2016).
Aims
This preplanned subgroup analysis evaluated the efficacy and safety outcomes in Asian patients (pts) with relapsed MM from the ENDEAVOR study.
Methods
Adult Asian pts with RRMM (1–3 prior regimens) were included. Patients in the Kd arm received carfilzomib at 20/56 mg/m2 IV of a 28-D cycle. The Vd arm received bortezomib 1.3 mg/m2 IV or SC of a 21-D cycle. Cycles were repeated until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The primary end point was PFS; secondary end points included overall survival (immature at the time), overall response rate (ORR), incidence of grade ≥2 peripheral neuropathy, and safety.
Results
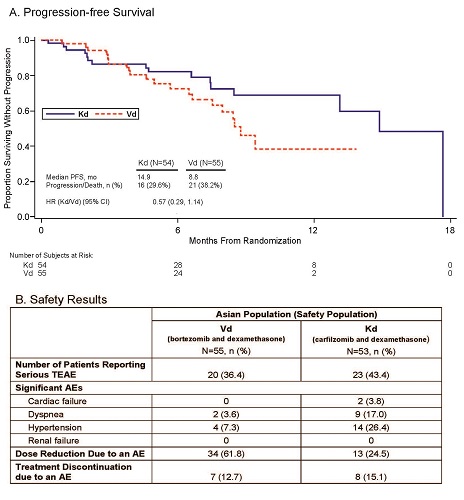
Of 929 pts randomized, 109 (11.7%) were of Asian ethnicity (Kd=54,Vd=55) from the JAPAC countries and received study treatment. The majority were from Japan (n=44; 40.4%) followed by Taiwan (n=24; 22.0%), Singapore (n=20; 18.3%), Republic of Korea (n=16; 14.7%), and Thailand (n=5; 4.6%). Median PFS follow-up was 8.4 mo (Kd) and 7.6 mo (Vd). Median PFS was 14.9 mo (Kd; 95% CI:13.1–17.7) vs 8.8 mo (Vd; 95% CI:6.6–NE [not estimable]) (HR=0.57, [95% CI:0.29–1.14]; Figure 1A), representing a greater than 6 mo improvement. The ORR was 79.6% (Kd; 95% CI:66.5–89.4) vs 70.9% (Vd; 95% CI:57.1–82.4) (odds ratio=1.604 [95% CI:0.664–3.872]). The proportion of pts who achieved a best overall response (OR) of ≥ complete response (CR) was higher in the Kd arm (9.3%) vs the Vd arm (1.8%). Also, the rate of ≥ very good partial response (VGPR) in the Kd arm (63.0%) was more than twice of that in the Vd arm (23.6%). Grade ≥2 peripheral neuropathy occurred in 0% of pts in the Kd arm and 29% in the Vd arm. Rates of serious treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAE), significant AEs of interest, and AEs leading to treatment reduction or discontinuation (Kd or Vd) are shown in Figure 1B. Similar pt incidence rates of AEs, ≥Grade 3 AEs, and ≥Grade 3 treatment-related AEs were observed between the Kd and Vd arms except for higher cardiovascular events and hypertension being observed in Kd arm.
Conclusion
In general, the efficacy and safety results from the Asian population analyses paralleled and are consistent with the results from the overall population of the ENDEAVOR study although the small sample size limits definitive conclusions regarding rates of AEs. For pts of Asian ethnicity, Kd therapy lead to clinically meaningful improvements in PFS, ORR, and CR/VGPR compared with the Vd arm.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Bortezomib, Multiple myeloma, Proteasome inhibitor, Race
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Carfilzomib is a selective proteasome inhibitor that is approved as a single agent and in combination with dexamethasone or lenalidomide/dexamethasone for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM). The ENDEAVOR study (NCT01568866) demonstrated statistically and clinically significant improvements in progression-free survival (PFS) for carfilzomib and dexamethasone therapy (Kd) compared with bortezomib and dexamethasone therapy (Vd; median 18.7 vs 9.4 months [mo]; hazard ratio [HR], 0.53; 95% confidence interval [CI]:0.44–0.65; 1-sided P<0.001) (Dimopoulos et al, Lancet Oncol 2016).
Aims
This preplanned subgroup analysis evaluated the efficacy and safety outcomes in Asian patients (pts) with relapsed MM from the ENDEAVOR study.
Methods
Adult Asian pts with RRMM (1–3 prior regimens) were included. Patients in the Kd arm received carfilzomib at 20/56 mg/m2 IV of a 28-D cycle. The Vd arm received bortezomib 1.3 mg/m2 IV or SC of a 21-D cycle. Cycles were repeated until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The primary end point was PFS; secondary end points included overall survival (immature at the time), overall response rate (ORR), incidence of grade ≥2 peripheral neuropathy, and safety.
Results
Of 929 pts randomized, 109 (11.7%) were of Asian ethnicity (Kd=54,Vd=55) from the JAPAC countries and received study treatment. The majority were from Japan (n=44; 40.4%) followed by Taiwan (n=24; 22.0%), Singapore (n=20; 18.3%), Republic of Korea (n=16; 14.7%), and Thailand (n=5; 4.6%). Median PFS follow-up was 8.4 mo (Kd) and 7.6 mo (Vd). Median PFS was 14.9 mo (Kd; 95% CI:13.1–17.7) vs 8.8 mo (Vd; 95% CI:6.6–NE [not estimable]) (HR=0.57, [95% CI:0.29–1.14]; Figure 1A), representing a greater than 6 mo improvement. The ORR was 79.6% (Kd; 95% CI:66.5–89.4) vs 70.9% (Vd; 95% CI:57.1–82.4) (odds ratio=1.604 [95% CI:0.664–3.872]). The proportion of pts who achieved a best overall response (OR) of ≥ complete response (CR) was higher in the Kd arm (9.3%) vs the Vd arm (1.8%). Also, the rate of ≥ very good partial response (VGPR) in the Kd arm (63.0%) was more than twice of that in the Vd arm (23.6%). Grade ≥2 peripheral neuropathy occurred in 0% of pts in the Kd arm and 29% in the Vd arm. Rates of serious treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAE), significant AEs of interest, and AEs leading to treatment reduction or discontinuation (Kd or Vd) are shown in Figure 1B. Similar pt incidence rates of AEs, ≥Grade 3 AEs, and ≥Grade 3 treatment-related AEs were observed between the Kd and Vd arms except for higher cardiovascular events and hypertension being observed in Kd arm.
Conclusion
In general, the efficacy and safety results from the Asian population analyses paralleled and are consistent with the results from the overall population of the ENDEAVOR study although the small sample size limits definitive conclusions regarding rates of AEs. For pts of Asian ethnicity, Kd therapy lead to clinically meaningful improvements in PFS, ORR, and CR/VGPR compared with the Vd arm.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Bortezomib, Multiple myeloma, Proteasome inhibitor, Race
Abstract: E1328
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Carfilzomib is a selective proteasome inhibitor that is approved as a single agent and in combination with dexamethasone or lenalidomide/dexamethasone for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM). The ENDEAVOR study (NCT01568866) demonstrated statistically and clinically significant improvements in progression-free survival (PFS) for carfilzomib and dexamethasone therapy (Kd) compared with bortezomib and dexamethasone therapy (Vd; median 18.7 vs 9.4 months [mo]; hazard ratio [HR], 0.53; 95% confidence interval [CI]:0.44–0.65; 1-sided P<0.001) (Dimopoulos et al, Lancet Oncol 2016).
Aims
This preplanned subgroup analysis evaluated the efficacy and safety outcomes in Asian patients (pts) with relapsed MM from the ENDEAVOR study.
Methods
Adult Asian pts with RRMM (1–3 prior regimens) were included. Patients in the Kd arm received carfilzomib at 20/56 mg/m2 IV of a 28-D cycle. The Vd arm received bortezomib 1.3 mg/m2 IV or SC of a 21-D cycle. Cycles were repeated until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The primary end point was PFS; secondary end points included overall survival (immature at the time), overall response rate (ORR), incidence of grade ≥2 peripheral neuropathy, and safety.
Results
Of 929 pts randomized, 109 (11.7%) were of Asian ethnicity (Kd=54,Vd=55) from the JAPAC countries and received study treatment. The majority were from Japan (n=44; 40.4%) followed by Taiwan (n=24; 22.0%), Singapore (n=20; 18.3%), Republic of Korea (n=16; 14.7%), and Thailand (n=5; 4.6%). Median PFS follow-up was 8.4 mo (Kd) and 7.6 mo (Vd). Median PFS was 14.9 mo (Kd; 95% CI:13.1–17.7) vs 8.8 mo (Vd; 95% CI:6.6–NE [not estimable]) (HR=0.57, [95% CI:0.29–1.14]; Figure 1A), representing a greater than 6 mo improvement. The ORR was 79.6% (Kd; 95% CI:66.5–89.4) vs 70.9% (Vd; 95% CI:57.1–82.4) (odds ratio=1.604 [95% CI:0.664–3.872]). The proportion of pts who achieved a best overall response (OR) of ≥ complete response (CR) was higher in the Kd arm (9.3%) vs the Vd arm (1.8%). Also, the rate of ≥ very good partial response (VGPR) in the Kd arm (63.0%) was more than twice of that in the Vd arm (23.6%). Grade ≥2 peripheral neuropathy occurred in 0% of pts in the Kd arm and 29% in the Vd arm. Rates of serious treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAE), significant AEs of interest, and AEs leading to treatment reduction or discontinuation (Kd or Vd) are shown in Figure 1B. Similar pt incidence rates of AEs, ≥Grade 3 AEs, and ≥Grade 3 treatment-related AEs were observed between the Kd and Vd arms except for higher cardiovascular events and hypertension being observed in Kd arm.
Conclusion
In general, the efficacy and safety results from the Asian population analyses paralleled and are consistent with the results from the overall population of the ENDEAVOR study although the small sample size limits definitive conclusions regarding rates of AEs. For pts of Asian ethnicity, Kd therapy lead to clinically meaningful improvements in PFS, ORR, and CR/VGPR compared with the Vd arm.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Bortezomib, Multiple myeloma, Proteasome inhibitor, Race
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Carfilzomib is a selective proteasome inhibitor that is approved as a single agent and in combination with dexamethasone or lenalidomide/dexamethasone for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM). The ENDEAVOR study (NCT01568866) demonstrated statistically and clinically significant improvements in progression-free survival (PFS) for carfilzomib and dexamethasone therapy (Kd) compared with bortezomib and dexamethasone therapy (Vd; median 18.7 vs 9.4 months [mo]; hazard ratio [HR], 0.53; 95% confidence interval [CI]:0.44–0.65; 1-sided P<0.001) (Dimopoulos et al, Lancet Oncol 2016).
Aims
This preplanned subgroup analysis evaluated the efficacy and safety outcomes in Asian patients (pts) with relapsed MM from the ENDEAVOR study.
Methods
Adult Asian pts with RRMM (1–3 prior regimens) were included. Patients in the Kd arm received carfilzomib at 20/56 mg/m2 IV of a 28-D cycle. The Vd arm received bortezomib 1.3 mg/m2 IV or SC of a 21-D cycle. Cycles were repeated until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The primary end point was PFS; secondary end points included overall survival (immature at the time), overall response rate (ORR), incidence of grade ≥2 peripheral neuropathy, and safety.
Results
Of 929 pts randomized, 109 (11.7%) were of Asian ethnicity (Kd=54,Vd=55) from the JAPAC countries and received study treatment. The majority were from Japan (n=44; 40.4%) followed by Taiwan (n=24; 22.0%), Singapore (n=20; 18.3%), Republic of Korea (n=16; 14.7%), and Thailand (n=5; 4.6%). Median PFS follow-up was 8.4 mo (Kd) and 7.6 mo (Vd). Median PFS was 14.9 mo (Kd; 95% CI:13.1–17.7) vs 8.8 mo (Vd; 95% CI:6.6–NE [not estimable]) (HR=0.57, [95% CI:0.29–1.14]; Figure 1A), representing a greater than 6 mo improvement. The ORR was 79.6% (Kd; 95% CI:66.5–89.4) vs 70.9% (Vd; 95% CI:57.1–82.4) (odds ratio=1.604 [95% CI:0.664–3.872]). The proportion of pts who achieved a best overall response (OR) of ≥ complete response (CR) was higher in the Kd arm (9.3%) vs the Vd arm (1.8%). Also, the rate of ≥ very good partial response (VGPR) in the Kd arm (63.0%) was more than twice of that in the Vd arm (23.6%). Grade ≥2 peripheral neuropathy occurred in 0% of pts in the Kd arm and 29% in the Vd arm. Rates of serious treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAE), significant AEs of interest, and AEs leading to treatment reduction or discontinuation (Kd or Vd) are shown in Figure 1B. Similar pt incidence rates of AEs, ≥Grade 3 AEs, and ≥Grade 3 treatment-related AEs were observed between the Kd and Vd arms except for higher cardiovascular events and hypertension being observed in Kd arm.
Conclusion
In general, the efficacy and safety results from the Asian population analyses paralleled and are consistent with the results from the overall population of the ENDEAVOR study although the small sample size limits definitive conclusions regarding rates of AEs. For pts of Asian ethnicity, Kd therapy lead to clinically meaningful improvements in PFS, ORR, and CR/VGPR compared with the Vd arm.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Bortezomib, Multiple myeloma, Proteasome inhibitor, Race
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


