PATTERNS OF HEMOGRAM CHANGES IN PATIENTS WITH RELAPSED/REFRACTORY INHL AND CLL TREATED WITH IDELALISIB
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Stilgenbauer S. 06/09/16; 132703; E1154

Prof. Dr. Stephan Stilgenbauer
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: E1154
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL) are B-cell malignancies associated with neutropenia, anemia and thrombocytopenia. Although the etiology of cytopenia is not well understood, bone marrow leukemia/lymphoma cell infiltrates are thought to contribute. Idelalisib (IDELA) is a selective, first-in-class oral PI3Kδ inhibitor. In preclinical studies, IDELA selectively targeted malignant B cells with minimal toxicity to nonmalignant B cells and other hematopoietic cell types. In clinical studies evaluating IDELA in B-cell malignancies, hematologic responses across all 3 lineages were observed in a majority of patients (pts) with baseline (BL) cytopenias.
Aims
The objective of this post hoc analysis was to evaluate hemogram changes in pts with relapsed or refractory (R/R) CLL or iNHL treated with IDELA in 2 pivotal studies.
Methods
In phase 3 Study 116, frail pts with CLL were randomized to receive rituximab (R) in combination with IDELA 150 mg BID or placebo (PBO). In phase 2 Study 101-09 (NCT01282424), pts with iNHL received IDELA monotherapy 150 mg BID. Trial inclusion criteria allowed enrollment of pts with BL cytopenias of any grade (CLL) or grade ˂3 (iNHL).Hematologic profiles for pts were categorized as normal or abnormal (any grade of cytopenia) at BL and assessed while on treatment. Supportive care utilization was assessed by use of blood product transfusions, hematopoietic growth factors, and immunosuppressant therapies. Treatment-emergent de novo autoimmune cytopenias (AIC) and/or worsening of pre-existing AIC were summarized. All analyses excluded pts from the iNHL study with PD at the first assessment to avoid confounding by underlying uncontrolled disease.
Results
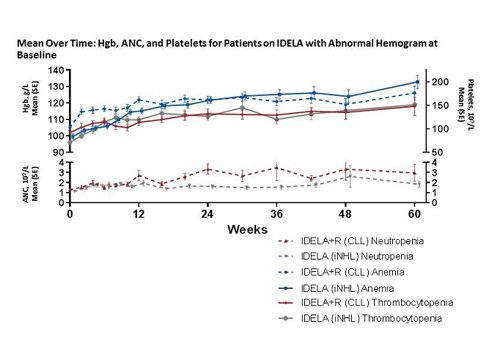
A total of 345 pts participated in these trials. The overall response rates for IDELA-treated patients in the CLL and iNHL studies were 84% and 58%, respectively. For pts with CLL on IDL+R (n=110), BL cytopenias (grade ≥1) included anemia (76%), thrombocytopenia (62%), and neutropenia (34%). For pts with iNHL on IDELA-monotherapy (n=115), BL cytopenias included anemia (50%), thrombocytopenia (36%), and neutropenia (24%). In patients with a normal hemogram at BL, median hematologic values remained unchanged over time with IDELA treatment. In patients with BL cytopenia, IDELA treatment was associated with improved Hgb and platelet counts and a reduction in supportive care utilization for anemia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia. For pts with CLL, median peak values for Hgb (24% above BL) and platelets (120% above BL) were observed within 6 months of IDELA initiation. For pts with iNHL, median peak values for Hgb (20% above BL) and platelets (64% above BL) were observed within 3 months of IDELA initiation. ANC remained stable over time in IDELA-treated pts with CLL and increased in pts with iNHL; a reduction in G-CSF utilization was observed for pts with CLL or iNHL and BL cytopenias while on treatment with IDELA.A history of AIC was reported in 6.4% and 16.4% of pts with CLL on IDELA+R and PBO+R, respectively. As of the data cutoff, no pt had experienced treatment-emergent AIC and/or worsening of pre-existing AIC.
Conclusion
This analysis indicates improved cytopenia in 2 lineages for pts with R/R CLL and iNHL treated with IDELA. Thus, pre-existing cytopenias, including those due to advanced disease, myelosuppression from prior chemotherapy, and AIC, do not by themselves preclude treatment with IDELA.Studies included in this analysis: 101-09: NCT01282424; GS-US-312-0116: NCT01539512
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Indolent non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, Randomized, Targeted therapy
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL) are B-cell malignancies associated with neutropenia, anemia and thrombocytopenia. Although the etiology of cytopenia is not well understood, bone marrow leukemia/lymphoma cell infiltrates are thought to contribute. Idelalisib (IDELA) is a selective, first-in-class oral PI3Kδ inhibitor. In preclinical studies, IDELA selectively targeted malignant B cells with minimal toxicity to nonmalignant B cells and other hematopoietic cell types. In clinical studies evaluating IDELA in B-cell malignancies, hematologic responses across all 3 lineages were observed in a majority of patients (pts) with baseline (BL) cytopenias.
Aims
The objective of this post hoc analysis was to evaluate hemogram changes in pts with relapsed or refractory (R/R) CLL or iNHL treated with IDELA in 2 pivotal studies.
Methods
In phase 3 Study 116, frail pts with CLL were randomized to receive rituximab (R) in combination with IDELA 150 mg BID or placebo (PBO). In phase 2 Study 101-09 (NCT01282424), pts with iNHL received IDELA monotherapy 150 mg BID. Trial inclusion criteria allowed enrollment of pts with BL cytopenias of any grade (CLL) or grade ˂3 (iNHL).Hematologic profiles for pts were categorized as normal or abnormal (any grade of cytopenia) at BL and assessed while on treatment. Supportive care utilization was assessed by use of blood product transfusions, hematopoietic growth factors, and immunosuppressant therapies. Treatment-emergent de novo autoimmune cytopenias (AIC) and/or worsening of pre-existing AIC were summarized. All analyses excluded pts from the iNHL study with PD at the first assessment to avoid confounding by underlying uncontrolled disease.
Results
A total of 345 pts participated in these trials. The overall response rates for IDELA-treated patients in the CLL and iNHL studies were 84% and 58%, respectively. For pts with CLL on IDL+R (n=110), BL cytopenias (grade ≥1) included anemia (76%), thrombocytopenia (62%), and neutropenia (34%). For pts with iNHL on IDELA-monotherapy (n=115), BL cytopenias included anemia (50%), thrombocytopenia (36%), and neutropenia (24%). In patients with a normal hemogram at BL, median hematologic values remained unchanged over time with IDELA treatment. In patients with BL cytopenia, IDELA treatment was associated with improved Hgb and platelet counts and a reduction in supportive care utilization for anemia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia. For pts with CLL, median peak values for Hgb (24% above BL) and platelets (120% above BL) were observed within 6 months of IDELA initiation. For pts with iNHL, median peak values for Hgb (20% above BL) and platelets (64% above BL) were observed within 3 months of IDELA initiation. ANC remained stable over time in IDELA-treated pts with CLL and increased in pts with iNHL; a reduction in G-CSF utilization was observed for pts with CLL or iNHL and BL cytopenias while on treatment with IDELA.A history of AIC was reported in 6.4% and 16.4% of pts with CLL on IDELA+R and PBO+R, respectively. As of the data cutoff, no pt had experienced treatment-emergent AIC and/or worsening of pre-existing AIC.
Conclusion
This analysis indicates improved cytopenia in 2 lineages for pts with R/R CLL and iNHL treated with IDELA. Thus, pre-existing cytopenias, including those due to advanced disease, myelosuppression from prior chemotherapy, and AIC, do not by themselves preclude treatment with IDELA.Studies included in this analysis: 101-09: NCT01282424; GS-US-312-0116: NCT01539512

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Indolent non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, Randomized, Targeted therapy
Abstract: E1154
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL) are B-cell malignancies associated with neutropenia, anemia and thrombocytopenia. Although the etiology of cytopenia is not well understood, bone marrow leukemia/lymphoma cell infiltrates are thought to contribute. Idelalisib (IDELA) is a selective, first-in-class oral PI3Kδ inhibitor. In preclinical studies, IDELA selectively targeted malignant B cells with minimal toxicity to nonmalignant B cells and other hematopoietic cell types. In clinical studies evaluating IDELA in B-cell malignancies, hematologic responses across all 3 lineages were observed in a majority of patients (pts) with baseline (BL) cytopenias.
Aims
The objective of this post hoc analysis was to evaluate hemogram changes in pts with relapsed or refractory (R/R) CLL or iNHL treated with IDELA in 2 pivotal studies.
Methods
In phase 3 Study 116, frail pts with CLL were randomized to receive rituximab (R) in combination with IDELA 150 mg BID or placebo (PBO). In phase 2 Study 101-09 (NCT01282424), pts with iNHL received IDELA monotherapy 150 mg BID. Trial inclusion criteria allowed enrollment of pts with BL cytopenias of any grade (CLL) or grade ˂3 (iNHL).Hematologic profiles for pts were categorized as normal or abnormal (any grade of cytopenia) at BL and assessed while on treatment. Supportive care utilization was assessed by use of blood product transfusions, hematopoietic growth factors, and immunosuppressant therapies. Treatment-emergent de novo autoimmune cytopenias (AIC) and/or worsening of pre-existing AIC were summarized. All analyses excluded pts from the iNHL study with PD at the first assessment to avoid confounding by underlying uncontrolled disease.
Results
A total of 345 pts participated in these trials. The overall response rates for IDELA-treated patients in the CLL and iNHL studies were 84% and 58%, respectively. For pts with CLL on IDL+R (n=110), BL cytopenias (grade ≥1) included anemia (76%), thrombocytopenia (62%), and neutropenia (34%). For pts with iNHL on IDELA-monotherapy (n=115), BL cytopenias included anemia (50%), thrombocytopenia (36%), and neutropenia (24%). In patients with a normal hemogram at BL, median hematologic values remained unchanged over time with IDELA treatment. In patients with BL cytopenia, IDELA treatment was associated with improved Hgb and platelet counts and a reduction in supportive care utilization for anemia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia. For pts with CLL, median peak values for Hgb (24% above BL) and platelets (120% above BL) were observed within 6 months of IDELA initiation. For pts with iNHL, median peak values for Hgb (20% above BL) and platelets (64% above BL) were observed within 3 months of IDELA initiation. ANC remained stable over time in IDELA-treated pts with CLL and increased in pts with iNHL; a reduction in G-CSF utilization was observed for pts with CLL or iNHL and BL cytopenias while on treatment with IDELA.A history of AIC was reported in 6.4% and 16.4% of pts with CLL on IDELA+R and PBO+R, respectively. As of the data cutoff, no pt had experienced treatment-emergent AIC and/or worsening of pre-existing AIC.
Conclusion
This analysis indicates improved cytopenia in 2 lineages for pts with R/R CLL and iNHL treated with IDELA. Thus, pre-existing cytopenias, including those due to advanced disease, myelosuppression from prior chemotherapy, and AIC, do not by themselves preclude treatment with IDELA.Studies included in this analysis: 101-09: NCT01282424; GS-US-312-0116: NCT01539512

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Indolent non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, Randomized, Targeted therapy
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL) are B-cell malignancies associated with neutropenia, anemia and thrombocytopenia. Although the etiology of cytopenia is not well understood, bone marrow leukemia/lymphoma cell infiltrates are thought to contribute. Idelalisib (IDELA) is a selective, first-in-class oral PI3Kδ inhibitor. In preclinical studies, IDELA selectively targeted malignant B cells with minimal toxicity to nonmalignant B cells and other hematopoietic cell types. In clinical studies evaluating IDELA in B-cell malignancies, hematologic responses across all 3 lineages were observed in a majority of patients (pts) with baseline (BL) cytopenias.
Aims
The objective of this post hoc analysis was to evaluate hemogram changes in pts with relapsed or refractory (R/R) CLL or iNHL treated with IDELA in 2 pivotal studies.
Methods
In phase 3 Study 116, frail pts with CLL were randomized to receive rituximab (R) in combination with IDELA 150 mg BID or placebo (PBO). In phase 2 Study 101-09 (NCT01282424), pts with iNHL received IDELA monotherapy 150 mg BID. Trial inclusion criteria allowed enrollment of pts with BL cytopenias of any grade (CLL) or grade ˂3 (iNHL).Hematologic profiles for pts were categorized as normal or abnormal (any grade of cytopenia) at BL and assessed while on treatment. Supportive care utilization was assessed by use of blood product transfusions, hematopoietic growth factors, and immunosuppressant therapies. Treatment-emergent de novo autoimmune cytopenias (AIC) and/or worsening of pre-existing AIC were summarized. All analyses excluded pts from the iNHL study with PD at the first assessment to avoid confounding by underlying uncontrolled disease.
Results
A total of 345 pts participated in these trials. The overall response rates for IDELA-treated patients in the CLL and iNHL studies were 84% and 58%, respectively. For pts with CLL on IDL+R (n=110), BL cytopenias (grade ≥1) included anemia (76%), thrombocytopenia (62%), and neutropenia (34%). For pts with iNHL on IDELA-monotherapy (n=115), BL cytopenias included anemia (50%), thrombocytopenia (36%), and neutropenia (24%). In patients with a normal hemogram at BL, median hematologic values remained unchanged over time with IDELA treatment. In patients with BL cytopenia, IDELA treatment was associated with improved Hgb and platelet counts and a reduction in supportive care utilization for anemia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia. For pts with CLL, median peak values for Hgb (24% above BL) and platelets (120% above BL) were observed within 6 months of IDELA initiation. For pts with iNHL, median peak values for Hgb (20% above BL) and platelets (64% above BL) were observed within 3 months of IDELA initiation. ANC remained stable over time in IDELA-treated pts with CLL and increased in pts with iNHL; a reduction in G-CSF utilization was observed for pts with CLL or iNHL and BL cytopenias while on treatment with IDELA.A history of AIC was reported in 6.4% and 16.4% of pts with CLL on IDELA+R and PBO+R, respectively. As of the data cutoff, no pt had experienced treatment-emergent AIC and/or worsening of pre-existing AIC.
Conclusion
This analysis indicates improved cytopenia in 2 lineages for pts with R/R CLL and iNHL treated with IDELA. Thus, pre-existing cytopenias, including those due to advanced disease, myelosuppression from prior chemotherapy, and AIC, do not by themselves preclude treatment with IDELA.Studies included in this analysis: 101-09: NCT01282424; GS-US-312-0116: NCT01539512

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Indolent non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, Randomized, Targeted therapy
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


