ADDITION OF ABSOLUTE LYMPHOCYTES/MONOCYTES RATIO IMPROVES THE STANDARD PROGNOSTIC SCORES FOR ADVANCED AND LOCALIZED HODGKIN LYMPHOMA PATIENTS TREATED WITH ABVD +/- RADIOTHERAPY.
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Herráez Balanzat I. 06/09/16; 132694; E1145

Mrs. Inés Herráez Balanzat
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: E1145
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a lymphoproliferative malignancy constituted by a few malignant cells (Reed-Sternberg cells) surrounded by an inflammatory microenvironment. The amount of monocytes infiltrating HL is a known prognostic factor but its study implies immunohistochemistry. Lymphopenia is a recognized adverse prognostic factor included in the International Prognostic Score (IPS). In the last years the clinical value of the absolute lymphocytes/monocytes ratio (LMR) has been reported as an alternative way to consider previous prognostic factors.
Aims
We aim to evaluate the combination of the absolute lymphocytes/monocytes ratio with the standard prognostic scores for advanced (IPS) and localized (GHSG) HL in order to improve definition of prognosis.
Methods
We retrospectively selected from the Pathology and Pharmacy registries of Son Espases University Hospital those patients with HL homogenously treated with ABVD +/- radiotherapy (RT). All standard prognostic factors were obtained from the records included in IPS and GHSG prognostic scores, as well as the absolute value of lymphocytes and monocytes. COR curves were used to determine the cutoff value for the LMR. IPS and GHSG scores were combined with LMR as follows: IPS 0-2=0; IPS>2=1; GHSG 0=0; GHSG>0=1; LMR≤cutoff=1; LMR>cutoff=0. LMR-IPS and LMR-GHSG were the sum of IPS or GHSG with LMR previous values (ranging from 0 to 2). Survival analysis was performed using Kaplan-Meier curves with the Log-rank test.
Results
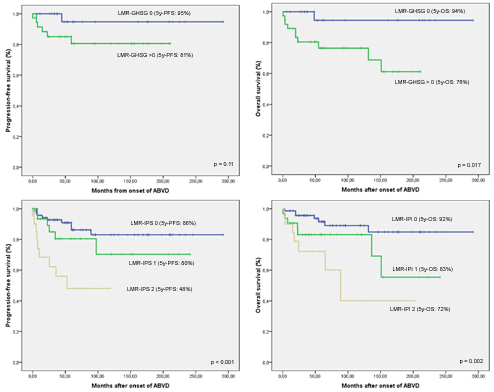
From January 1990 to June 2015, 124 patients fulfilled inclusion criteria. Median age was 37 years (15-75), 62% males, 48% Ann Arbor (AA) stage III-IV, 13% with ECOG performance status >1, 53% with IPS >2. Median LMR was 2.19 (0.2-7.7). Response was as follows: 105 (87%) achieved complete response (CR), 2 (2%) partial response (PR) and 17 (12%) stable disease or progression (SD/P). Using COR curves we set the cutoff for LMR in 1.56. Response rate, CR and SD/P were significantly better in patients with LMR >1.56: respectively 95% vs 72%, 94% vs 69% and 5% vs 29% (p=0.001); as well as patients younger than 45 (p=0.024) and 60 (p=0.003) years, with ECOG 0-1 (p=0.001), LMR-GHSG 0 (p=0.037) and LMR-IPS 0-1 (p=0.007). Univariate survival analysis showed several factors significantly influencing OS: age, ECOG PS, GHSG and IPS, ALC, AMC, LMR, LMR-IPS and LMR-GHSG (Figure 1). PFS was significantly influenced by age, AA stage, ECOG PS, IPS, LMR and LMR-IPS (Figure 1). In multivariate analysis for early HL age >45 (HR 13.1; p<0.001), ECOG PS>1 (HR 9.7; p=0.034) and LMR-GHSG>0 (HR 19.8; p=0.045) (Figure 1) where independent predictors of worse OS while in advanced HL only remained independent age>45 (HR 4.8; p=0.028) and LMR-IPS 2 (HR 14; p=0.041). In the PFS multivariate analysis only LMR-IPS showed to be an independent adverse prognostic factor both for the whole group (HR 4.5; p<0.001) and the advance HL patients (HR 3.5; p=0.013).
Conclusion
Addition of absolute LMR improved the ability of IPS and GHSG scores in identifying HL patients with worse responses and survival after standard ABVD +/- RT. Particularly, LMR-IPS was able to identify a high risk subgroup of patients with a 5y-PFS of 48% inside the patients with IPS>2.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Hodgkin's lymphoma, Prognostic factor
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a lymphoproliferative malignancy constituted by a few malignant cells (Reed-Sternberg cells) surrounded by an inflammatory microenvironment. The amount of monocytes infiltrating HL is a known prognostic factor but its study implies immunohistochemistry. Lymphopenia is a recognized adverse prognostic factor included in the International Prognostic Score (IPS). In the last years the clinical value of the absolute lymphocytes/monocytes ratio (LMR) has been reported as an alternative way to consider previous prognostic factors.
Aims
We aim to evaluate the combination of the absolute lymphocytes/monocytes ratio with the standard prognostic scores for advanced (IPS) and localized (GHSG) HL in order to improve definition of prognosis.
Methods
We retrospectively selected from the Pathology and Pharmacy registries of Son Espases University Hospital those patients with HL homogenously treated with ABVD +/- radiotherapy (RT). All standard prognostic factors were obtained from the records included in IPS and GHSG prognostic scores, as well as the absolute value of lymphocytes and monocytes. COR curves were used to determine the cutoff value for the LMR. IPS and GHSG scores were combined with LMR as follows: IPS 0-2=0; IPS>2=1; GHSG 0=0; GHSG>0=1; LMR≤cutoff=1; LMR>cutoff=0. LMR-IPS and LMR-GHSG were the sum of IPS or GHSG with LMR previous values (ranging from 0 to 2). Survival analysis was performed using Kaplan-Meier curves with the Log-rank test.
Results
From January 1990 to June 2015, 124 patients fulfilled inclusion criteria. Median age was 37 years (15-75), 62% males, 48% Ann Arbor (AA) stage III-IV, 13% with ECOG performance status >1, 53% with IPS >2. Median LMR was 2.19 (0.2-7.7). Response was as follows: 105 (87%) achieved complete response (CR), 2 (2%) partial response (PR) and 17 (12%) stable disease or progression (SD/P). Using COR curves we set the cutoff for LMR in 1.56. Response rate, CR and SD/P were significantly better in patients with LMR >1.56: respectively 95% vs 72%, 94% vs 69% and 5% vs 29% (p=0.001); as well as patients younger than 45 (p=0.024) and 60 (p=0.003) years, with ECOG 0-1 (p=0.001), LMR-GHSG 0 (p=0.037) and LMR-IPS 0-1 (p=0.007). Univariate survival analysis showed several factors significantly influencing OS: age, ECOG PS, GHSG and IPS, ALC, AMC, LMR, LMR-IPS and LMR-GHSG (Figure 1). PFS was significantly influenced by age, AA stage, ECOG PS, IPS, LMR and LMR-IPS (Figure 1). In multivariate analysis for early HL age >45 (HR 13.1; p<0.001), ECOG PS>1 (HR 9.7; p=0.034) and LMR-GHSG>0 (HR 19.8; p=0.045) (Figure 1) where independent predictors of worse OS while in advanced HL only remained independent age>45 (HR 4.8; p=0.028) and LMR-IPS 2 (HR 14; p=0.041). In the PFS multivariate analysis only LMR-IPS showed to be an independent adverse prognostic factor both for the whole group (HR 4.5; p<0.001) and the advance HL patients (HR 3.5; p=0.013).
Conclusion
Addition of absolute LMR improved the ability of IPS and GHSG scores in identifying HL patients with worse responses and survival after standard ABVD +/- RT. Particularly, LMR-IPS was able to identify a high risk subgroup of patients with a 5y-PFS of 48% inside the patients with IPS>2.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Hodgkin's lymphoma, Prognostic factor
Abstract: E1145
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a lymphoproliferative malignancy constituted by a few malignant cells (Reed-Sternberg cells) surrounded by an inflammatory microenvironment. The amount of monocytes infiltrating HL is a known prognostic factor but its study implies immunohistochemistry. Lymphopenia is a recognized adverse prognostic factor included in the International Prognostic Score (IPS). In the last years the clinical value of the absolute lymphocytes/monocytes ratio (LMR) has been reported as an alternative way to consider previous prognostic factors.
Aims
We aim to evaluate the combination of the absolute lymphocytes/monocytes ratio with the standard prognostic scores for advanced (IPS) and localized (GHSG) HL in order to improve definition of prognosis.
Methods
We retrospectively selected from the Pathology and Pharmacy registries of Son Espases University Hospital those patients with HL homogenously treated with ABVD +/- radiotherapy (RT). All standard prognostic factors were obtained from the records included in IPS and GHSG prognostic scores, as well as the absolute value of lymphocytes and monocytes. COR curves were used to determine the cutoff value for the LMR. IPS and GHSG scores were combined with LMR as follows: IPS 0-2=0; IPS>2=1; GHSG 0=0; GHSG>0=1; LMR≤cutoff=1; LMR>cutoff=0. LMR-IPS and LMR-GHSG were the sum of IPS or GHSG with LMR previous values (ranging from 0 to 2). Survival analysis was performed using Kaplan-Meier curves with the Log-rank test.
Results
From January 1990 to June 2015, 124 patients fulfilled inclusion criteria. Median age was 37 years (15-75), 62% males, 48% Ann Arbor (AA) stage III-IV, 13% with ECOG performance status >1, 53% with IPS >2. Median LMR was 2.19 (0.2-7.7). Response was as follows: 105 (87%) achieved complete response (CR), 2 (2%) partial response (PR) and 17 (12%) stable disease or progression (SD/P). Using COR curves we set the cutoff for LMR in 1.56. Response rate, CR and SD/P were significantly better in patients with LMR >1.56: respectively 95% vs 72%, 94% vs 69% and 5% vs 29% (p=0.001); as well as patients younger than 45 (p=0.024) and 60 (p=0.003) years, with ECOG 0-1 (p=0.001), LMR-GHSG 0 (p=0.037) and LMR-IPS 0-1 (p=0.007). Univariate survival analysis showed several factors significantly influencing OS: age, ECOG PS, GHSG and IPS, ALC, AMC, LMR, LMR-IPS and LMR-GHSG (Figure 1). PFS was significantly influenced by age, AA stage, ECOG PS, IPS, LMR and LMR-IPS (Figure 1). In multivariate analysis for early HL age >45 (HR 13.1; p<0.001), ECOG PS>1 (HR 9.7; p=0.034) and LMR-GHSG>0 (HR 19.8; p=0.045) (Figure 1) where independent predictors of worse OS while in advanced HL only remained independent age>45 (HR 4.8; p=0.028) and LMR-IPS 2 (HR 14; p=0.041). In the PFS multivariate analysis only LMR-IPS showed to be an independent adverse prognostic factor both for the whole group (HR 4.5; p<0.001) and the advance HL patients (HR 3.5; p=0.013).
Conclusion
Addition of absolute LMR improved the ability of IPS and GHSG scores in identifying HL patients with worse responses and survival after standard ABVD +/- RT. Particularly, LMR-IPS was able to identify a high risk subgroup of patients with a 5y-PFS of 48% inside the patients with IPS>2.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Hodgkin's lymphoma, Prognostic factor
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a lymphoproliferative malignancy constituted by a few malignant cells (Reed-Sternberg cells) surrounded by an inflammatory microenvironment. The amount of monocytes infiltrating HL is a known prognostic factor but its study implies immunohistochemistry. Lymphopenia is a recognized adverse prognostic factor included in the International Prognostic Score (IPS). In the last years the clinical value of the absolute lymphocytes/monocytes ratio (LMR) has been reported as an alternative way to consider previous prognostic factors.
Aims
We aim to evaluate the combination of the absolute lymphocytes/monocytes ratio with the standard prognostic scores for advanced (IPS) and localized (GHSG) HL in order to improve definition of prognosis.
Methods
We retrospectively selected from the Pathology and Pharmacy registries of Son Espases University Hospital those patients with HL homogenously treated with ABVD +/- radiotherapy (RT). All standard prognostic factors were obtained from the records included in IPS and GHSG prognostic scores, as well as the absolute value of lymphocytes and monocytes. COR curves were used to determine the cutoff value for the LMR. IPS and GHSG scores were combined with LMR as follows: IPS 0-2=0; IPS>2=1; GHSG 0=0; GHSG>0=1; LMR≤cutoff=1; LMR>cutoff=0. LMR-IPS and LMR-GHSG were the sum of IPS or GHSG with LMR previous values (ranging from 0 to 2). Survival analysis was performed using Kaplan-Meier curves with the Log-rank test.
Results
From January 1990 to June 2015, 124 patients fulfilled inclusion criteria. Median age was 37 years (15-75), 62% males, 48% Ann Arbor (AA) stage III-IV, 13% with ECOG performance status >1, 53% with IPS >2. Median LMR was 2.19 (0.2-7.7). Response was as follows: 105 (87%) achieved complete response (CR), 2 (2%) partial response (PR) and 17 (12%) stable disease or progression (SD/P). Using COR curves we set the cutoff for LMR in 1.56. Response rate, CR and SD/P were significantly better in patients with LMR >1.56: respectively 95% vs 72%, 94% vs 69% and 5% vs 29% (p=0.001); as well as patients younger than 45 (p=0.024) and 60 (p=0.003) years, with ECOG 0-1 (p=0.001), LMR-GHSG 0 (p=0.037) and LMR-IPS 0-1 (p=0.007). Univariate survival analysis showed several factors significantly influencing OS: age, ECOG PS, GHSG and IPS, ALC, AMC, LMR, LMR-IPS and LMR-GHSG (Figure 1). PFS was significantly influenced by age, AA stage, ECOG PS, IPS, LMR and LMR-IPS (Figure 1). In multivariate analysis for early HL age >45 (HR 13.1; p<0.001), ECOG PS>1 (HR 9.7; p=0.034) and LMR-GHSG>0 (HR 19.8; p=0.045) (Figure 1) where independent predictors of worse OS while in advanced HL only remained independent age>45 (HR 4.8; p=0.028) and LMR-IPS 2 (HR 14; p=0.041). In the PFS multivariate analysis only LMR-IPS showed to be an independent adverse prognostic factor both for the whole group (HR 4.5; p<0.001) and the advance HL patients (HR 3.5; p=0.013).
Conclusion
Addition of absolute LMR improved the ability of IPS and GHSG scores in identifying HL patients with worse responses and survival after standard ABVD +/- RT. Particularly, LMR-IPS was able to identify a high risk subgroup of patients with a 5y-PFS of 48% inside the patients with IPS>2.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Hodgkin's lymphoma, Prognostic factor
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


