TRIPLE-REGULATED ONCOLYTIC ADENOVIRUS-MEDIATED VSTM1 OVEREXPRESSION EXHIBITS POTENT ANTITUMOR ACTIVITY ON COMMON HUMAN LEUKEMIC CELL LINES
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Ruan G. 06/09/16; 132669; E1120

Prof. Guo-Rui Ruan
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: E1120
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
VSTM1 (V-set and transmembrane domain-containing 1), as a potential myeloid differentiation antigen gene, is downregulated in bone marrow cells from myeloid leukemia patients. Restoration of VSTM1 expression inhibited myeloid leukemia cells' growth. VSTM1 might provide a potential target for the diagnosis and treatment of leukemia.
Aims
The purpose of this study was to construct a triple-regulated oncolytic adenovirus carrying VSTM1 gene expression cassette, SG611-VSTM1, and to explore its antitumor efficacy on human leukemic cell lines.
Methods
In SG611-VSTM1, the E1a gene with a deletion of 24 nucleotides within CR2 region was controlled under the human telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter, the E1b gene expression was directed by the hypoxia response element, whereas the VSTM1 gene was controlled by the cytomegalovirus promoter. The insertion and orientation of all recombined plasmids were confirmed by restriction enzyme digestion and polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The relative VSTM1 expression level in human leukemic cell line K562 after infection with SG611-VSTM1 was detected by real-time quantitative PCR (RQ-PCR) and western blot. The tumor-selective replication of this virus and its antitumor efficacy were characterized in several leukemic cell lines with different multiplicities of infection (MOI) in vitro. Cell viability was detected by using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8). Cell apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry (FCM).
Results
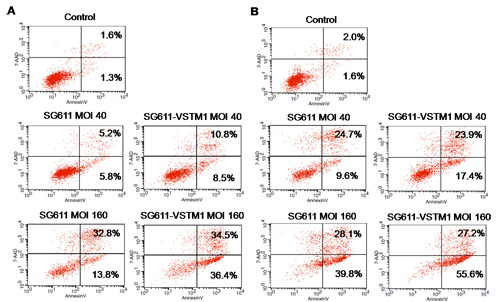
A triple-regulated oncolytic adenovirus carrying VSTM1 gene expression assette, SG611-VSTM1, was completed and confirmed. VSTM1, hTERTp, HRE, skeleton and fiber 11 of recombinant adenovirus SG611-VSTM1 were successfully amplified. SG611-VSTM1 expressed VSTM1 with high efficiency in leukemic cells as compared with SG611 (P < 0. 001). The expression level of VSTM1 increased gradually along with the increase of MOI. In CCK-8 assay, the cell viabilities were decreased gradually along with the increase of MOI in leukemic cells with SG611-VSTM1 in comparison with SG611, while the cell viabilities were maintained a relatively higher level in the normal cell lines BJ (about 50%) and L-02 (about 60%) with SG611-VSTM1. Similarly, the proapoptotic effect of SG611-VSTM1 on leukemic cells was superior to SG611. In K562 cells at 48 h after infection (Fig.1), the apoptotic percentage of SG611-VSTM1 at a MOI of 40 and 160 pfu/cell were 19.3% and 70.9%, significantly higher than that of SG611 (11.0% and 46.6%), respectively.Fig.1 Apoptosis of K562 cells infected with SG611-VSTM1 or SG611. A: at 48 h after infection; B: at 72 h after infection. The apoptotic percentage was increased gradually along with the increase of MOI and infection time prolonging, especially in the group treated with SG611-VSTM1.
Conclusion
It is concluded that the triple-regulated adenovirus of SG611-VSTM1 containing the VSTM1 has been successfully established with high VSTM1 expression level in leukemic cells. SG611-VSTM1 holds an increase of anticancer efficacy and might be an improvement of the safety as a new anticancer agent.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Adenovirus, Gene therapy, Leukemia
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
VSTM1 (V-set and transmembrane domain-containing 1), as a potential myeloid differentiation antigen gene, is downregulated in bone marrow cells from myeloid leukemia patients. Restoration of VSTM1 expression inhibited myeloid leukemia cells' growth. VSTM1 might provide a potential target for the diagnosis and treatment of leukemia.
Aims
The purpose of this study was to construct a triple-regulated oncolytic adenovirus carrying VSTM1 gene expression cassette, SG611-VSTM1, and to explore its antitumor efficacy on human leukemic cell lines.
Methods
In SG611-VSTM1, the E1a gene with a deletion of 24 nucleotides within CR2 region was controlled under the human telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter, the E1b gene expression was directed by the hypoxia response element, whereas the VSTM1 gene was controlled by the cytomegalovirus promoter. The insertion and orientation of all recombined plasmids were confirmed by restriction enzyme digestion and polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The relative VSTM1 expression level in human leukemic cell line K562 after infection with SG611-VSTM1 was detected by real-time quantitative PCR (RQ-PCR) and western blot. The tumor-selective replication of this virus and its antitumor efficacy were characterized in several leukemic cell lines with different multiplicities of infection (MOI) in vitro. Cell viability was detected by using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8). Cell apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry (FCM).
Results
A triple-regulated oncolytic adenovirus carrying VSTM1 gene expression assette, SG611-VSTM1, was completed and confirmed. VSTM1, hTERTp, HRE, skeleton and fiber 11 of recombinant adenovirus SG611-VSTM1 were successfully amplified. SG611-VSTM1 expressed VSTM1 with high efficiency in leukemic cells as compared with SG611 (P < 0. 001). The expression level of VSTM1 increased gradually along with the increase of MOI. In CCK-8 assay, the cell viabilities were decreased gradually along with the increase of MOI in leukemic cells with SG611-VSTM1 in comparison with SG611, while the cell viabilities were maintained a relatively higher level in the normal cell lines BJ (about 50%) and L-02 (about 60%) with SG611-VSTM1. Similarly, the proapoptotic effect of SG611-VSTM1 on leukemic cells was superior to SG611. In K562 cells at 48 h after infection (Fig.1), the apoptotic percentage of SG611-VSTM1 at a MOI of 40 and 160 pfu/cell were 19.3% and 70.9%, significantly higher than that of SG611 (11.0% and 46.6%), respectively.Fig.1 Apoptosis of K562 cells infected with SG611-VSTM1 or SG611. A: at 48 h after infection; B: at 72 h after infection. The apoptotic percentage was increased gradually along with the increase of MOI and infection time prolonging, especially in the group treated with SG611-VSTM1.
Conclusion
It is concluded that the triple-regulated adenovirus of SG611-VSTM1 containing the VSTM1 has been successfully established with high VSTM1 expression level in leukemic cells. SG611-VSTM1 holds an increase of anticancer efficacy and might be an improvement of the safety as a new anticancer agent.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Adenovirus, Gene therapy, Leukemia
Abstract: E1120
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
VSTM1 (V-set and transmembrane domain-containing 1), as a potential myeloid differentiation antigen gene, is downregulated in bone marrow cells from myeloid leukemia patients. Restoration of VSTM1 expression inhibited myeloid leukemia cells' growth. VSTM1 might provide a potential target for the diagnosis and treatment of leukemia.
Aims
The purpose of this study was to construct a triple-regulated oncolytic adenovirus carrying VSTM1 gene expression cassette, SG611-VSTM1, and to explore its antitumor efficacy on human leukemic cell lines.
Methods
In SG611-VSTM1, the E1a gene with a deletion of 24 nucleotides within CR2 region was controlled under the human telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter, the E1b gene expression was directed by the hypoxia response element, whereas the VSTM1 gene was controlled by the cytomegalovirus promoter. The insertion and orientation of all recombined plasmids were confirmed by restriction enzyme digestion and polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The relative VSTM1 expression level in human leukemic cell line K562 after infection with SG611-VSTM1 was detected by real-time quantitative PCR (RQ-PCR) and western blot. The tumor-selective replication of this virus and its antitumor efficacy were characterized in several leukemic cell lines with different multiplicities of infection (MOI) in vitro. Cell viability was detected by using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8). Cell apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry (FCM).
Results
A triple-regulated oncolytic adenovirus carrying VSTM1 gene expression assette, SG611-VSTM1, was completed and confirmed. VSTM1, hTERTp, HRE, skeleton and fiber 11 of recombinant adenovirus SG611-VSTM1 were successfully amplified. SG611-VSTM1 expressed VSTM1 with high efficiency in leukemic cells as compared with SG611 (P < 0. 001). The expression level of VSTM1 increased gradually along with the increase of MOI. In CCK-8 assay, the cell viabilities were decreased gradually along with the increase of MOI in leukemic cells with SG611-VSTM1 in comparison with SG611, while the cell viabilities were maintained a relatively higher level in the normal cell lines BJ (about 50%) and L-02 (about 60%) with SG611-VSTM1. Similarly, the proapoptotic effect of SG611-VSTM1 on leukemic cells was superior to SG611. In K562 cells at 48 h after infection (Fig.1), the apoptotic percentage of SG611-VSTM1 at a MOI of 40 and 160 pfu/cell were 19.3% and 70.9%, significantly higher than that of SG611 (11.0% and 46.6%), respectively.Fig.1 Apoptosis of K562 cells infected with SG611-VSTM1 or SG611. A: at 48 h after infection; B: at 72 h after infection. The apoptotic percentage was increased gradually along with the increase of MOI and infection time prolonging, especially in the group treated with SG611-VSTM1.
Conclusion
It is concluded that the triple-regulated adenovirus of SG611-VSTM1 containing the VSTM1 has been successfully established with high VSTM1 expression level in leukemic cells. SG611-VSTM1 holds an increase of anticancer efficacy and might be an improvement of the safety as a new anticancer agent.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Adenovirus, Gene therapy, Leukemia
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
VSTM1 (V-set and transmembrane domain-containing 1), as a potential myeloid differentiation antigen gene, is downregulated in bone marrow cells from myeloid leukemia patients. Restoration of VSTM1 expression inhibited myeloid leukemia cells' growth. VSTM1 might provide a potential target for the diagnosis and treatment of leukemia.
Aims
The purpose of this study was to construct a triple-regulated oncolytic adenovirus carrying VSTM1 gene expression cassette, SG611-VSTM1, and to explore its antitumor efficacy on human leukemic cell lines.
Methods
In SG611-VSTM1, the E1a gene with a deletion of 24 nucleotides within CR2 region was controlled under the human telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter, the E1b gene expression was directed by the hypoxia response element, whereas the VSTM1 gene was controlled by the cytomegalovirus promoter. The insertion and orientation of all recombined plasmids were confirmed by restriction enzyme digestion and polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The relative VSTM1 expression level in human leukemic cell line K562 after infection with SG611-VSTM1 was detected by real-time quantitative PCR (RQ-PCR) and western blot. The tumor-selective replication of this virus and its antitumor efficacy were characterized in several leukemic cell lines with different multiplicities of infection (MOI) in vitro. Cell viability was detected by using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8). Cell apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry (FCM).
Results
A triple-regulated oncolytic adenovirus carrying VSTM1 gene expression assette, SG611-VSTM1, was completed and confirmed. VSTM1, hTERTp, HRE, skeleton and fiber 11 of recombinant adenovirus SG611-VSTM1 were successfully amplified. SG611-VSTM1 expressed VSTM1 with high efficiency in leukemic cells as compared with SG611 (P < 0. 001). The expression level of VSTM1 increased gradually along with the increase of MOI. In CCK-8 assay, the cell viabilities were decreased gradually along with the increase of MOI in leukemic cells with SG611-VSTM1 in comparison with SG611, while the cell viabilities were maintained a relatively higher level in the normal cell lines BJ (about 50%) and L-02 (about 60%) with SG611-VSTM1. Similarly, the proapoptotic effect of SG611-VSTM1 on leukemic cells was superior to SG611. In K562 cells at 48 h after infection (Fig.1), the apoptotic percentage of SG611-VSTM1 at a MOI of 40 and 160 pfu/cell were 19.3% and 70.9%, significantly higher than that of SG611 (11.0% and 46.6%), respectively.Fig.1 Apoptosis of K562 cells infected with SG611-VSTM1 or SG611. A: at 48 h after infection; B: at 72 h after infection. The apoptotic percentage was increased gradually along with the increase of MOI and infection time prolonging, especially in the group treated with SG611-VSTM1.
Conclusion
It is concluded that the triple-regulated adenovirus of SG611-VSTM1 containing the VSTM1 has been successfully established with high VSTM1 expression level in leukemic cells. SG611-VSTM1 holds an increase of anticancer efficacy and might be an improvement of the safety as a new anticancer agent.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Adenovirus, Gene therapy, Leukemia
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


