COMPARISON OF PACE CLINICAL TRIAL VS REAL-WORLD PONATINIB PRESCRIBING AND DURATION OF THERAPY IN CHRONIC-PHASE CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA (CP-CML) PATIENTS
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Mauro M. 06/09/16; 132657; E1108

Dr. Michael Mauro
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: E1108
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Ponatinib demonstrated efficacy in patients with highly-resistant CP-CML in the pivotal phase 2 PACE trial (NCT01207440). Introduced to the US market in Dec’12, ponatinib was reintroduced in Jan’14 after an 11-week withdrawal to review data on vascular occlusive events and revise US prescribing information. In the US, ponatinib is available exclusively through a specialty pharmacy that maintains real-world prescribing data for all US patients treated with ponatinib since Jan’14.
Aims
Comparison of real-world pharmacy data to PACE trial data for patients with CP-CML, to identify any differences in duration of therapy due to potential noncompliance or availability of alternative therapies.
Methods
Data from patients with CP-CML enrolled Sep’10–Oct’11 into the PACE trial (all providing informed consent) were compared to real-world data for CP-CML patients starting ponatinib Jan’14–Dec’15. Real-world data source includes referring physicians, pharmacy intake forms and dispensing records. Patient characteristics and dosing were compared overall and by line of therapy using non-parametric tests; average dose was calculated, including therapy gaps as “zero” dose. Duration of therapy was assessed using Kaplan-Meier techniques and log-rank tests.
Results
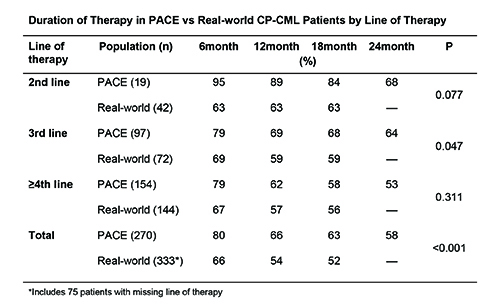
PACE enrolled 270 CP-CML patients; 333 US real-world CP-CML patients started treatment over the 2-year period. PACE patients were older (median 60 vs 55 years; p=0.004). Comparing PACE to 258 real-world patients with known line of therapy, 7% PACE vs 16% real-world were in 2nd line, 36% vs 28% 3rd line and 57% vs 56% ≥4th line (p=0.084). All PACE patients received 45 mg/day as the initial dose of ponatinib; in real-world ponatinib use, 48% of patients initially received 45 mg/day, 30% 30 mg/day, and 22% 15 mg/day; however, average ponatinib dose was similar in PACE vs real-world (2nd line: 29.4 vs 29.0 mg/day; 3rd line: 26.0 vs 25.9 mg/day; >4th line: 26.4 vs 26.9 mg/day; all p>0.05.) Duration of therapy was similar in 2nd line and >4th line patients in PACE vs real-world, but longer in PACE vs real-world for 3rd line patients (Table.)
Conclusion
Real-world CP-CML ponatinib patients are younger but otherwise similar to PACE patients. Real-world data suggests an increase in earlier (second) line ponatinib use and >50% of initial ponatinb dosing is below 45 mg/day. As expected, the real-world duration of therapy is somewhat shorter than in PACE; however, the majority of real-world ponatinib patients across all lines of therapy were on therapy for >1.5 years.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic myeloid leukemia, Clinical trial, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Ponatinib demonstrated efficacy in patients with highly-resistant CP-CML in the pivotal phase 2 PACE trial (NCT01207440). Introduced to the US market in Dec’12, ponatinib was reintroduced in Jan’14 after an 11-week withdrawal to review data on vascular occlusive events and revise US prescribing information. In the US, ponatinib is available exclusively through a specialty pharmacy that maintains real-world prescribing data for all US patients treated with ponatinib since Jan’14.
Aims
Comparison of real-world pharmacy data to PACE trial data for patients with CP-CML, to identify any differences in duration of therapy due to potential noncompliance or availability of alternative therapies.
Methods
Data from patients with CP-CML enrolled Sep’10–Oct’11 into the PACE trial (all providing informed consent) were compared to real-world data for CP-CML patients starting ponatinib Jan’14–Dec’15. Real-world data source includes referring physicians, pharmacy intake forms and dispensing records. Patient characteristics and dosing were compared overall and by line of therapy using non-parametric tests; average dose was calculated, including therapy gaps as “zero” dose. Duration of therapy was assessed using Kaplan-Meier techniques and log-rank tests.
Results
PACE enrolled 270 CP-CML patients; 333 US real-world CP-CML patients started treatment over the 2-year period. PACE patients were older (median 60 vs 55 years; p=0.004). Comparing PACE to 258 real-world patients with known line of therapy, 7% PACE vs 16% real-world were in 2nd line, 36% vs 28% 3rd line and 57% vs 56% ≥4th line (p=0.084). All PACE patients received 45 mg/day as the initial dose of ponatinib; in real-world ponatinib use, 48% of patients initially received 45 mg/day, 30% 30 mg/day, and 22% 15 mg/day; however, average ponatinib dose was similar in PACE vs real-world (2nd line: 29.4 vs 29.0 mg/day; 3rd line: 26.0 vs 25.9 mg/day; >4th line: 26.4 vs 26.9 mg/day; all p>0.05.) Duration of therapy was similar in 2nd line and >4th line patients in PACE vs real-world, but longer in PACE vs real-world for 3rd line patients (Table.)
Conclusion
Real-world CP-CML ponatinib patients are younger but otherwise similar to PACE patients. Real-world data suggests an increase in earlier (second) line ponatinib use and >50% of initial ponatinb dosing is below 45 mg/day. As expected, the real-world duration of therapy is somewhat shorter than in PACE; however, the majority of real-world ponatinib patients across all lines of therapy were on therapy for >1.5 years.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic myeloid leukemia, Clinical trial, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Abstract: E1108
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Ponatinib demonstrated efficacy in patients with highly-resistant CP-CML in the pivotal phase 2 PACE trial (NCT01207440). Introduced to the US market in Dec’12, ponatinib was reintroduced in Jan’14 after an 11-week withdrawal to review data on vascular occlusive events and revise US prescribing information. In the US, ponatinib is available exclusively through a specialty pharmacy that maintains real-world prescribing data for all US patients treated with ponatinib since Jan’14.
Aims
Comparison of real-world pharmacy data to PACE trial data for patients with CP-CML, to identify any differences in duration of therapy due to potential noncompliance or availability of alternative therapies.
Methods
Data from patients with CP-CML enrolled Sep’10–Oct’11 into the PACE trial (all providing informed consent) were compared to real-world data for CP-CML patients starting ponatinib Jan’14–Dec’15. Real-world data source includes referring physicians, pharmacy intake forms and dispensing records. Patient characteristics and dosing were compared overall and by line of therapy using non-parametric tests; average dose was calculated, including therapy gaps as “zero” dose. Duration of therapy was assessed using Kaplan-Meier techniques and log-rank tests.
Results
PACE enrolled 270 CP-CML patients; 333 US real-world CP-CML patients started treatment over the 2-year period. PACE patients were older (median 60 vs 55 years; p=0.004). Comparing PACE to 258 real-world patients with known line of therapy, 7% PACE vs 16% real-world were in 2nd line, 36% vs 28% 3rd line and 57% vs 56% ≥4th line (p=0.084). All PACE patients received 45 mg/day as the initial dose of ponatinib; in real-world ponatinib use, 48% of patients initially received 45 mg/day, 30% 30 mg/day, and 22% 15 mg/day; however, average ponatinib dose was similar in PACE vs real-world (2nd line: 29.4 vs 29.0 mg/day; 3rd line: 26.0 vs 25.9 mg/day; >4th line: 26.4 vs 26.9 mg/day; all p>0.05.) Duration of therapy was similar in 2nd line and >4th line patients in PACE vs real-world, but longer in PACE vs real-world for 3rd line patients (Table.)
Conclusion
Real-world CP-CML ponatinib patients are younger but otherwise similar to PACE patients. Real-world data suggests an increase in earlier (second) line ponatinib use and >50% of initial ponatinb dosing is below 45 mg/day. As expected, the real-world duration of therapy is somewhat shorter than in PACE; however, the majority of real-world ponatinib patients across all lines of therapy were on therapy for >1.5 years.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic myeloid leukemia, Clinical trial, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Ponatinib demonstrated efficacy in patients with highly-resistant CP-CML in the pivotal phase 2 PACE trial (NCT01207440). Introduced to the US market in Dec’12, ponatinib was reintroduced in Jan’14 after an 11-week withdrawal to review data on vascular occlusive events and revise US prescribing information. In the US, ponatinib is available exclusively through a specialty pharmacy that maintains real-world prescribing data for all US patients treated with ponatinib since Jan’14.
Aims
Comparison of real-world pharmacy data to PACE trial data for patients with CP-CML, to identify any differences in duration of therapy due to potential noncompliance or availability of alternative therapies.
Methods
Data from patients with CP-CML enrolled Sep’10–Oct’11 into the PACE trial (all providing informed consent) were compared to real-world data for CP-CML patients starting ponatinib Jan’14–Dec’15. Real-world data source includes referring physicians, pharmacy intake forms and dispensing records. Patient characteristics and dosing were compared overall and by line of therapy using non-parametric tests; average dose was calculated, including therapy gaps as “zero” dose. Duration of therapy was assessed using Kaplan-Meier techniques and log-rank tests.
Results
PACE enrolled 270 CP-CML patients; 333 US real-world CP-CML patients started treatment over the 2-year period. PACE patients were older (median 60 vs 55 years; p=0.004). Comparing PACE to 258 real-world patients with known line of therapy, 7% PACE vs 16% real-world were in 2nd line, 36% vs 28% 3rd line and 57% vs 56% ≥4th line (p=0.084). All PACE patients received 45 mg/day as the initial dose of ponatinib; in real-world ponatinib use, 48% of patients initially received 45 mg/day, 30% 30 mg/day, and 22% 15 mg/day; however, average ponatinib dose was similar in PACE vs real-world (2nd line: 29.4 vs 29.0 mg/day; 3rd line: 26.0 vs 25.9 mg/day; >4th line: 26.4 vs 26.9 mg/day; all p>0.05.) Duration of therapy was similar in 2nd line and >4th line patients in PACE vs real-world, but longer in PACE vs real-world for 3rd line patients (Table.)
Conclusion
Real-world CP-CML ponatinib patients are younger but otherwise similar to PACE patients. Real-world data suggests an increase in earlier (second) line ponatinib use and >50% of initial ponatinb dosing is below 45 mg/day. As expected, the real-world duration of therapy is somewhat shorter than in PACE; however, the majority of real-world ponatinib patients across all lines of therapy were on therapy for >1.5 years.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic myeloid leukemia, Clinical trial, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


