DIFFERENT SETS OF GENES WERE ASSOCIATED TO THE MOLECULAR RESPONSE AFTER 3 AND 6 MONTHS OF FIRST-LINE NILOTINIB TREATMENT BY MICROARRAY OF CD34+/LIN- CELLS OF CHRONIC PHASE CML PATIENTS AT DIAGNOSIS
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Cairoli R. 06/09/16; 132642; E1093

Roberto Cairoli
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: E1093
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a clonal myeloproliferative disorder and the biomolecular mechanisms of CML response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors are not fully defined.
Aims
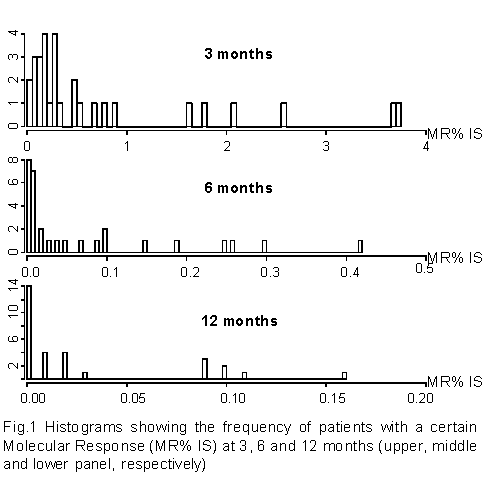
Thirty chronic phase CML patients were investigated at diagnosis and at 3, 6 and 12 months of first-line nilotinib treatment and optimal response was achieved at 3, 6 and 12 months after nilotinib in all the 30 patients (figure 1). We established cut off values of molecular response (MR) to define groups of patients, and to explore differences of gene expression profiles (GEP) between patients at diagnosis based on the MR achieved after 3, 6 and 12 months of nilotinib, respectively.
Methods
Cut off values were: 1% IS at 3 months of nilotinib, 0.1% IS at 6 months of nilotinib, and 0.01% IS at 12 months of nilotinib. We divided patients into 2 groups based on MR values of each patient at 3 months of nilotinib: group A (n=24) with MR≤1.0% IS and group B (n=6) with MR>1% IS. At 6 months of nilotinib, patients were divided into: group C (n=22) with MR≤0.1% IS and group D (n=8) with MR>0.1% IS. At 12 months of nilotinib, patients were divided into: group E (n=18) with MR≤0.01% IS and group F (n=12) with MR>0.01% IS. GEP on the selected bone marrow (BM) CD34+/lin- cells of 30 patients at diagnosis was performed using Affymetrix-GeneChip-HTA 2.0. RMA was used for preprocessing data. SAMR and GSEA detected differentially expressed genes and pathways associated with the different groups, respectively. MTC was performed using the FDR with a threshold 0.05 for SAMR and 0.25 for GSEA.
Results
GSEA identified significant differences in the transcriptional signature between group A and group B associated with the MR at 3 months as well as between group C and group D in respect to the MR at 6 months of nilotinib. Based on the MR at 3 months, Reactome-pathways-“P130-cascade” and “GRB2-SOS-linkage-to-MAPK-signaling-for-integrins” were significantly upregulated in group A. FGA, FGB, FGG, APBB1IP, ITGA2B and CRK genes contributed to call the pathways upregulated. From literature data, nilotinib inhibits BCR-ABL1 mediated phosphorilation of CKRL which acts in the CML hematopoietic stem cells in diverse signaling pathways playing an apoptotic role in CML. CRK was overexpressed in patients with a better MR≤1% IS at 3 months of nilotinib. Aminoacid-and-amine-transport-across-the-plasma-membrane-pathway was significantly overexpressed, whereas “lipid metabolism” was significantly downregulated (AKR1C1, ANGPTL3) in group A compared to group B, respectively. Based on the MR at 6 months, “positive-regulation-of-cytokine secretion” and “interleukin1-secretion” were significantly upregulated in group C compared to group D, involving PYCARD8, NLRP2, NLRC4, NLRP3 and CARD8 genes. PYCARD and CARD8 promote caspase-mediated-apoptosis processes involving the recruitment of recognition receptors: NLRP2, NLRP3 and NLRC4.
Conclusion
The study showed that MAPK-signaling-for-integrins and amine-transport-across-the-plasma-membrane were significantly overexpressed in CML patients with MR≤1.0% IS while lipid metabolism was significantly underexpressed in CML patients with MR≤1.0% IS after 3 months of nilotinib. Positive-regulation-of- cytokine-secretion-and-interleukin1-secretion was significantly overexpressed in CML patients who achieved MR≤0.1 IS after 6 months of nilotinib. In summary, distinct sets of genes involved in apoptosis were differentially expressed in 30 CML patients at diagnosis based on the MR at 3 and at 6 months of first-line nilotinib treatment.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic myeloid leukemia, Gene expression profile, Molecular response, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a clonal myeloproliferative disorder and the biomolecular mechanisms of CML response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors are not fully defined.
Aims
Thirty chronic phase CML patients were investigated at diagnosis and at 3, 6 and 12 months of first-line nilotinib treatment and optimal response was achieved at 3, 6 and 12 months after nilotinib in all the 30 patients (figure 1). We established cut off values of molecular response (MR) to define groups of patients, and to explore differences of gene expression profiles (GEP) between patients at diagnosis based on the MR achieved after 3, 6 and 12 months of nilotinib, respectively.
Methods
Cut off values were: 1% IS at 3 months of nilotinib, 0.1% IS at 6 months of nilotinib, and 0.01% IS at 12 months of nilotinib. We divided patients into 2 groups based on MR values of each patient at 3 months of nilotinib: group A (n=24) with MR≤1.0% IS and group B (n=6) with MR>1% IS. At 6 months of nilotinib, patients were divided into: group C (n=22) with MR≤0.1% IS and group D (n=8) with MR>0.1% IS. At 12 months of nilotinib, patients were divided into: group E (n=18) with MR≤0.01% IS and group F (n=12) with MR>0.01% IS. GEP on the selected bone marrow (BM) CD34+/lin- cells of 30 patients at diagnosis was performed using Affymetrix-GeneChip-HTA 2.0. RMA was used for preprocessing data. SAMR and GSEA detected differentially expressed genes and pathways associated with the different groups, respectively. MTC was performed using the FDR with a threshold 0.05 for SAMR and 0.25 for GSEA.
Results
GSEA identified significant differences in the transcriptional signature between group A and group B associated with the MR at 3 months as well as between group C and group D in respect to the MR at 6 months of nilotinib. Based on the MR at 3 months, Reactome-pathways-“P130-cascade” and “GRB2-SOS-linkage-to-MAPK-signaling-for-integrins” were significantly upregulated in group A. FGA, FGB, FGG, APBB1IP, ITGA2B and CRK genes contributed to call the pathways upregulated. From literature data, nilotinib inhibits BCR-ABL1 mediated phosphorilation of CKRL which acts in the CML hematopoietic stem cells in diverse signaling pathways playing an apoptotic role in CML. CRK was overexpressed in patients with a better MR≤1% IS at 3 months of nilotinib. Aminoacid-and-amine-transport-across-the-plasma-membrane-pathway was significantly overexpressed, whereas “lipid metabolism” was significantly downregulated (AKR1C1, ANGPTL3) in group A compared to group B, respectively. Based on the MR at 6 months, “positive-regulation-of-cytokine secretion” and “interleukin1-secretion” were significantly upregulated in group C compared to group D, involving PYCARD8, NLRP2, NLRC4, NLRP3 and CARD8 genes. PYCARD and CARD8 promote caspase-mediated-apoptosis processes involving the recruitment of recognition receptors: NLRP2, NLRP3 and NLRC4.
Conclusion
The study showed that MAPK-signaling-for-integrins and amine-transport-across-the-plasma-membrane were significantly overexpressed in CML patients with MR≤1.0% IS while lipid metabolism was significantly underexpressed in CML patients with MR≤1.0% IS after 3 months of nilotinib. Positive-regulation-of- cytokine-secretion-and-interleukin1-secretion was significantly overexpressed in CML patients who achieved MR≤0.1 IS after 6 months of nilotinib. In summary, distinct sets of genes involved in apoptosis were differentially expressed in 30 CML patients at diagnosis based on the MR at 3 and at 6 months of first-line nilotinib treatment.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic myeloid leukemia, Gene expression profile, Molecular response, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Abstract: E1093
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a clonal myeloproliferative disorder and the biomolecular mechanisms of CML response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors are not fully defined.
Aims
Thirty chronic phase CML patients were investigated at diagnosis and at 3, 6 and 12 months of first-line nilotinib treatment and optimal response was achieved at 3, 6 and 12 months after nilotinib in all the 30 patients (figure 1). We established cut off values of molecular response (MR) to define groups of patients, and to explore differences of gene expression profiles (GEP) between patients at diagnosis based on the MR achieved after 3, 6 and 12 months of nilotinib, respectively.
Methods
Cut off values were: 1% IS at 3 months of nilotinib, 0.1% IS at 6 months of nilotinib, and 0.01% IS at 12 months of nilotinib. We divided patients into 2 groups based on MR values of each patient at 3 months of nilotinib: group A (n=24) with MR≤1.0% IS and group B (n=6) with MR>1% IS. At 6 months of nilotinib, patients were divided into: group C (n=22) with MR≤0.1% IS and group D (n=8) with MR>0.1% IS. At 12 months of nilotinib, patients were divided into: group E (n=18) with MR≤0.01% IS and group F (n=12) with MR>0.01% IS. GEP on the selected bone marrow (BM) CD34+/lin- cells of 30 patients at diagnosis was performed using Affymetrix-GeneChip-HTA 2.0. RMA was used for preprocessing data. SAMR and GSEA detected differentially expressed genes and pathways associated with the different groups, respectively. MTC was performed using the FDR with a threshold 0.05 for SAMR and 0.25 for GSEA.
Results
GSEA identified significant differences in the transcriptional signature between group A and group B associated with the MR at 3 months as well as between group C and group D in respect to the MR at 6 months of nilotinib. Based on the MR at 3 months, Reactome-pathways-“P130-cascade” and “GRB2-SOS-linkage-to-MAPK-signaling-for-integrins” were significantly upregulated in group A. FGA, FGB, FGG, APBB1IP, ITGA2B and CRK genes contributed to call the pathways upregulated. From literature data, nilotinib inhibits BCR-ABL1 mediated phosphorilation of CKRL which acts in the CML hematopoietic stem cells in diverse signaling pathways playing an apoptotic role in CML. CRK was overexpressed in patients with a better MR≤1% IS at 3 months of nilotinib. Aminoacid-and-amine-transport-across-the-plasma-membrane-pathway was significantly overexpressed, whereas “lipid metabolism” was significantly downregulated (AKR1C1, ANGPTL3) in group A compared to group B, respectively. Based on the MR at 6 months, “positive-regulation-of-cytokine secretion” and “interleukin1-secretion” were significantly upregulated in group C compared to group D, involving PYCARD8, NLRP2, NLRC4, NLRP3 and CARD8 genes. PYCARD and CARD8 promote caspase-mediated-apoptosis processes involving the recruitment of recognition receptors: NLRP2, NLRP3 and NLRC4.
Conclusion
The study showed that MAPK-signaling-for-integrins and amine-transport-across-the-plasma-membrane were significantly overexpressed in CML patients with MR≤1.0% IS while lipid metabolism was significantly underexpressed in CML patients with MR≤1.0% IS after 3 months of nilotinib. Positive-regulation-of- cytokine-secretion-and-interleukin1-secretion was significantly overexpressed in CML patients who achieved MR≤0.1 IS after 6 months of nilotinib. In summary, distinct sets of genes involved in apoptosis were differentially expressed in 30 CML patients at diagnosis based on the MR at 3 and at 6 months of first-line nilotinib treatment.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic myeloid leukemia, Gene expression profile, Molecular response, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a clonal myeloproliferative disorder and the biomolecular mechanisms of CML response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors are not fully defined.
Aims
Thirty chronic phase CML patients were investigated at diagnosis and at 3, 6 and 12 months of first-line nilotinib treatment and optimal response was achieved at 3, 6 and 12 months after nilotinib in all the 30 patients (figure 1). We established cut off values of molecular response (MR) to define groups of patients, and to explore differences of gene expression profiles (GEP) between patients at diagnosis based on the MR achieved after 3, 6 and 12 months of nilotinib, respectively.
Methods
Cut off values were: 1% IS at 3 months of nilotinib, 0.1% IS at 6 months of nilotinib, and 0.01% IS at 12 months of nilotinib. We divided patients into 2 groups based on MR values of each patient at 3 months of nilotinib: group A (n=24) with MR≤1.0% IS and group B (n=6) with MR>1% IS. At 6 months of nilotinib, patients were divided into: group C (n=22) with MR≤0.1% IS and group D (n=8) with MR>0.1% IS. At 12 months of nilotinib, patients were divided into: group E (n=18) with MR≤0.01% IS and group F (n=12) with MR>0.01% IS. GEP on the selected bone marrow (BM) CD34+/lin- cells of 30 patients at diagnosis was performed using Affymetrix-GeneChip-HTA 2.0. RMA was used for preprocessing data. SAMR and GSEA detected differentially expressed genes and pathways associated with the different groups, respectively. MTC was performed using the FDR with a threshold 0.05 for SAMR and 0.25 for GSEA.
Results
GSEA identified significant differences in the transcriptional signature between group A and group B associated with the MR at 3 months as well as between group C and group D in respect to the MR at 6 months of nilotinib. Based on the MR at 3 months, Reactome-pathways-“P130-cascade” and “GRB2-SOS-linkage-to-MAPK-signaling-for-integrins” were significantly upregulated in group A. FGA, FGB, FGG, APBB1IP, ITGA2B and CRK genes contributed to call the pathways upregulated. From literature data, nilotinib inhibits BCR-ABL1 mediated phosphorilation of CKRL which acts in the CML hematopoietic stem cells in diverse signaling pathways playing an apoptotic role in CML. CRK was overexpressed in patients with a better MR≤1% IS at 3 months of nilotinib. Aminoacid-and-amine-transport-across-the-plasma-membrane-pathway was significantly overexpressed, whereas “lipid metabolism” was significantly downregulated (AKR1C1, ANGPTL3) in group A compared to group B, respectively. Based on the MR at 6 months, “positive-regulation-of-cytokine secretion” and “interleukin1-secretion” were significantly upregulated in group C compared to group D, involving PYCARD8, NLRP2, NLRC4, NLRP3 and CARD8 genes. PYCARD and CARD8 promote caspase-mediated-apoptosis processes involving the recruitment of recognition receptors: NLRP2, NLRP3 and NLRC4.
Conclusion
The study showed that MAPK-signaling-for-integrins and amine-transport-across-the-plasma-membrane were significantly overexpressed in CML patients with MR≤1.0% IS while lipid metabolism was significantly underexpressed in CML patients with MR≤1.0% IS after 3 months of nilotinib. Positive-regulation-of- cytokine-secretion-and-interleukin1-secretion was significantly overexpressed in CML patients who achieved MR≤0.1 IS after 6 months of nilotinib. In summary, distinct sets of genes involved in apoptosis were differentially expressed in 30 CML patients at diagnosis based on the MR at 3 and at 6 months of first-line nilotinib treatment.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic myeloid leukemia, Gene expression profile, Molecular response, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


