DROPLET DIGITAL PCR IMPROVE MINIMAL RESIDUAL DISEASE DETECTION IN > 35% OF SAMPLES COMPARING TO RQ-PCR
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Andrade-Campos M. 06/09/16; 132638; E1089
Disclosure(s): There is no need to disclose actual financial value.

Dr. Marcio Andrade-Campos
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: E1089
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
The gold standard for BCR-ABL quantification in chronic myeloid leukemia patients (CML) is the real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RQ-PCR), this technique has a limited sensibility to MR4.0 or MR4.5 in the majority of laboratories. Several discontinuation studies in chronic phase CML (CP-CML) patients reveal that both, the achievement a deeper response and a long time in this response seem the main factors for good outcomes. The droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) had shows more sensitivity to detect minimal amounts of BCR-ABL transcripts in patients with undetectable BCR-ABL transcripts by RQ-PCR, leading an opportunity to investigation in this field.
Aims
to evaluate the usefulness of the ddPCR in detect the presence of BCR-ABL transcripts in CP-CML patients under TKI therapy, compared with RQ-PCR.
Methods
Between August-2013 to Mar 2015, a total of 112 samples from 34 CP-CML patients under TKI therapy were analyzed. The blood samples were obtained in EDTA for RQ-PCR and in TempusTM tube for RNA isolation. The RQ-PCR was performed following the current recommendations. The RNA was obtained from peripheral blood using TempusTM Spin RNA isolation kit according manufacturer recommendations. The analysis by ddPCR for each sample was done using 5 μg of RNA obtained using One-step kit and processed in Qx100 Droplet Digital PCR, Biorad; using primers and probes described by Gabert et al., 2003, the results were analyzed using QuantaLife Biorad software and expressed in absolute number of BCR-ABL copies and positive droplets. Samples were processed per triplicate (3 wells). Positive samples: were considered when the sum of ≥3 positive droplets in minimum of 24,000 droplets.
Results
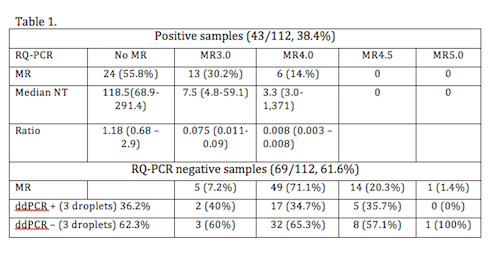
From the 112 samples analyzed by RQ-PCR, 69 (61.6%) were negative and 43 (38.4%) were positive. According molecular response the distribution by international scale (MR) and number of transcripts (NT). Table 1. The ddPCR analysis reveals that 65 (58.0%) of the samples were positive, median of positive droplets: 22.5 (3 – 35,529). Median BCR-ABL NT: 41.5 (5.5 – 11,129.3). For samples with a negative result by RQ-PCR (n=69), in 44 (63.7%) the analysis by ddPCR confirmed the negativity of the sample, however in 25 (36.2%) there were positivity in 3 or more droplets (median 4, 3-25), with a median NT 9.9 (5.5-44.7) copies. Table 1 exposed also the relation between the MR by RQ-PCR and the positivity by ddPCR. However if the threshold is settled in two positive droplets with a minimum of 3.5 NT, the number of positive samples increase to 38 (55.1%), with a median NT: 8.1 (3.6-44.7). There was a correlation in the number of copies between both techniques, but with a significant increase in the amount of NT copies.
Conclusion
The ddPCR offer a new way to assess CP-CML patients, in special for patients with MR4.0 or undetectable molecular response by RQ-PCR, and would offer a more secure alternative to select patient for discontinuation trials. In our cohort, at least an improving of 36% on identification of samples with presence of minimal residual disease has been founded. The use of this technique to monitoring and select patients for discontinuation trials is warranted.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Diagnosis, MRD, PCR
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
The gold standard for BCR-ABL quantification in chronic myeloid leukemia patients (CML) is the real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RQ-PCR), this technique has a limited sensibility to MR4.0 or MR4.5 in the majority of laboratories. Several discontinuation studies in chronic phase CML (CP-CML) patients reveal that both, the achievement a deeper response and a long time in this response seem the main factors for good outcomes. The droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) had shows more sensitivity to detect minimal amounts of BCR-ABL transcripts in patients with undetectable BCR-ABL transcripts by RQ-PCR, leading an opportunity to investigation in this field.
Aims
to evaluate the usefulness of the ddPCR in detect the presence of BCR-ABL transcripts in CP-CML patients under TKI therapy, compared with RQ-PCR.
Methods
Between August-2013 to Mar 2015, a total of 112 samples from 34 CP-CML patients under TKI therapy were analyzed. The blood samples were obtained in EDTA for RQ-PCR and in TempusTM tube for RNA isolation. The RQ-PCR was performed following the current recommendations. The RNA was obtained from peripheral blood using TempusTM Spin RNA isolation kit according manufacturer recommendations. The analysis by ddPCR for each sample was done using 5 μg of RNA obtained using One-step kit and processed in Qx100 Droplet Digital PCR, Biorad; using primers and probes described by Gabert et al., 2003, the results were analyzed using QuantaLife Biorad software and expressed in absolute number of BCR-ABL copies and positive droplets. Samples were processed per triplicate (3 wells). Positive samples: were considered when the sum of ≥3 positive droplets in minimum of 24,000 droplets.
Results
From the 112 samples analyzed by RQ-PCR, 69 (61.6%) were negative and 43 (38.4%) were positive. According molecular response the distribution by international scale (MR) and number of transcripts (NT). Table 1. The ddPCR analysis reveals that 65 (58.0%) of the samples were positive, median of positive droplets: 22.5 (3 – 35,529). Median BCR-ABL NT: 41.5 (5.5 – 11,129.3). For samples with a negative result by RQ-PCR (n=69), in 44 (63.7%) the analysis by ddPCR confirmed the negativity of the sample, however in 25 (36.2%) there were positivity in 3 or more droplets (median 4, 3-25), with a median NT 9.9 (5.5-44.7) copies. Table 1 exposed also the relation between the MR by RQ-PCR and the positivity by ddPCR. However if the threshold is settled in two positive droplets with a minimum of 3.5 NT, the number of positive samples increase to 38 (55.1%), with a median NT: 8.1 (3.6-44.7). There was a correlation in the number of copies between both techniques, but with a significant increase in the amount of NT copies.
Conclusion
The ddPCR offer a new way to assess CP-CML patients, in special for patients with MR4.0 or undetectable molecular response by RQ-PCR, and would offer a more secure alternative to select patient for discontinuation trials. In our cohort, at least an improving of 36% on identification of samples with presence of minimal residual disease has been founded. The use of this technique to monitoring and select patients for discontinuation trials is warranted.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Diagnosis, MRD, PCR
Abstract: E1089
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
The gold standard for BCR-ABL quantification in chronic myeloid leukemia patients (CML) is the real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RQ-PCR), this technique has a limited sensibility to MR4.0 or MR4.5 in the majority of laboratories. Several discontinuation studies in chronic phase CML (CP-CML) patients reveal that both, the achievement a deeper response and a long time in this response seem the main factors for good outcomes. The droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) had shows more sensitivity to detect minimal amounts of BCR-ABL transcripts in patients with undetectable BCR-ABL transcripts by RQ-PCR, leading an opportunity to investigation in this field.
Aims
to evaluate the usefulness of the ddPCR in detect the presence of BCR-ABL transcripts in CP-CML patients under TKI therapy, compared with RQ-PCR.
Methods
Between August-2013 to Mar 2015, a total of 112 samples from 34 CP-CML patients under TKI therapy were analyzed. The blood samples were obtained in EDTA for RQ-PCR and in TempusTM tube for RNA isolation. The RQ-PCR was performed following the current recommendations. The RNA was obtained from peripheral blood using TempusTM Spin RNA isolation kit according manufacturer recommendations. The analysis by ddPCR for each sample was done using 5 μg of RNA obtained using One-step kit and processed in Qx100 Droplet Digital PCR, Biorad; using primers and probes described by Gabert et al., 2003, the results were analyzed using QuantaLife Biorad software and expressed in absolute number of BCR-ABL copies and positive droplets. Samples were processed per triplicate (3 wells). Positive samples: were considered when the sum of ≥3 positive droplets in minimum of 24,000 droplets.
Results
From the 112 samples analyzed by RQ-PCR, 69 (61.6%) were negative and 43 (38.4%) were positive. According molecular response the distribution by international scale (MR) and number of transcripts (NT). Table 1. The ddPCR analysis reveals that 65 (58.0%) of the samples were positive, median of positive droplets: 22.5 (3 – 35,529). Median BCR-ABL NT: 41.5 (5.5 – 11,129.3). For samples with a negative result by RQ-PCR (n=69), in 44 (63.7%) the analysis by ddPCR confirmed the negativity of the sample, however in 25 (36.2%) there were positivity in 3 or more droplets (median 4, 3-25), with a median NT 9.9 (5.5-44.7) copies. Table 1 exposed also the relation between the MR by RQ-PCR and the positivity by ddPCR. However if the threshold is settled in two positive droplets with a minimum of 3.5 NT, the number of positive samples increase to 38 (55.1%), with a median NT: 8.1 (3.6-44.7). There was a correlation in the number of copies between both techniques, but with a significant increase in the amount of NT copies.
Conclusion
The ddPCR offer a new way to assess CP-CML patients, in special for patients with MR4.0 or undetectable molecular response by RQ-PCR, and would offer a more secure alternative to select patient for discontinuation trials. In our cohort, at least an improving of 36% on identification of samples with presence of minimal residual disease has been founded. The use of this technique to monitoring and select patients for discontinuation trials is warranted.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Diagnosis, MRD, PCR
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
The gold standard for BCR-ABL quantification in chronic myeloid leukemia patients (CML) is the real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RQ-PCR), this technique has a limited sensibility to MR4.0 or MR4.5 in the majority of laboratories. Several discontinuation studies in chronic phase CML (CP-CML) patients reveal that both, the achievement a deeper response and a long time in this response seem the main factors for good outcomes. The droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) had shows more sensitivity to detect minimal amounts of BCR-ABL transcripts in patients with undetectable BCR-ABL transcripts by RQ-PCR, leading an opportunity to investigation in this field.
Aims
to evaluate the usefulness of the ddPCR in detect the presence of BCR-ABL transcripts in CP-CML patients under TKI therapy, compared with RQ-PCR.
Methods
Between August-2013 to Mar 2015, a total of 112 samples from 34 CP-CML patients under TKI therapy were analyzed. The blood samples were obtained in EDTA for RQ-PCR and in TempusTM tube for RNA isolation. The RQ-PCR was performed following the current recommendations. The RNA was obtained from peripheral blood using TempusTM Spin RNA isolation kit according manufacturer recommendations. The analysis by ddPCR for each sample was done using 5 μg of RNA obtained using One-step kit and processed in Qx100 Droplet Digital PCR, Biorad; using primers and probes described by Gabert et al., 2003, the results were analyzed using QuantaLife Biorad software and expressed in absolute number of BCR-ABL copies and positive droplets. Samples were processed per triplicate (3 wells). Positive samples: were considered when the sum of ≥3 positive droplets in minimum of 24,000 droplets.
Results
From the 112 samples analyzed by RQ-PCR, 69 (61.6%) were negative and 43 (38.4%) were positive. According molecular response the distribution by international scale (MR) and number of transcripts (NT). Table 1. The ddPCR analysis reveals that 65 (58.0%) of the samples were positive, median of positive droplets: 22.5 (3 – 35,529). Median BCR-ABL NT: 41.5 (5.5 – 11,129.3). For samples with a negative result by RQ-PCR (n=69), in 44 (63.7%) the analysis by ddPCR confirmed the negativity of the sample, however in 25 (36.2%) there were positivity in 3 or more droplets (median 4, 3-25), with a median NT 9.9 (5.5-44.7) copies. Table 1 exposed also the relation between the MR by RQ-PCR and the positivity by ddPCR. However if the threshold is settled in two positive droplets with a minimum of 3.5 NT, the number of positive samples increase to 38 (55.1%), with a median NT: 8.1 (3.6-44.7). There was a correlation in the number of copies between both techniques, but with a significant increase in the amount of NT copies.
Conclusion
The ddPCR offer a new way to assess CP-CML patients, in special for patients with MR4.0 or undetectable molecular response by RQ-PCR, and would offer a more secure alternative to select patient for discontinuation trials. In our cohort, at least an improving of 36% on identification of samples with presence of minimal residual disease has been founded. The use of this technique to monitoring and select patients for discontinuation trials is warranted.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Diagnosis, MRD, PCR
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


