A SYSTEMATIC LITERATURE REVIEW OF RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIALS FOR THE TREATMENT OF RELAPSED OR REFRACTORY CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Thompson J. 06/09/16; 132619; E1070

Ms. Juliette Thompson
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: E1070
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) by chemotherapy is not curative, and patients receive multiple chemotherapy lines in an attempt to manage their disease along the years. Due to cumulative toxicity or resistance, treatment options following first-line therapy quickly become limited and new treatment options are needed. Idelalisib is a novel oral inhibitor of PK13K delta for the treatment of relapsed/refractory (R/R) CLL. This study reviewed randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of idelalisib and treatment options in the management of R/R CLL.
Aims
To review the efficacy and safety of idelalisib relative to other commonly used treatments for R/R CLL.
Methods
A systematic literature review was conducted to identify articles evaluating idelalisib (Id), ibrutinib (Ib), alemtuzumab (A), fludarabine (F), rituximab (R), ofatumumab (O), bendamustine (B), cyclophosphamide (C), methylprednisolone (Mp), chlorambucil (Ch), lenalidomide (L), doxorubicin (D), vincristine (V), prednisone (P), CHOP, and CVP as single agents or in combination, in adult patients with R/R CLL. Searches were conducted in the following literature databases: EMBASE, MEDLINE, MEDLINE In-Process and CENTRAL. Conference abstracts from ESMO, ASCO, EHA and ASH 2012–2015 were also searched. Screening was carried out independently by two reviewers. English language RCTs reporting overall, complete or partial response, stable or progressive disease, overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS) or safety were included.
Results
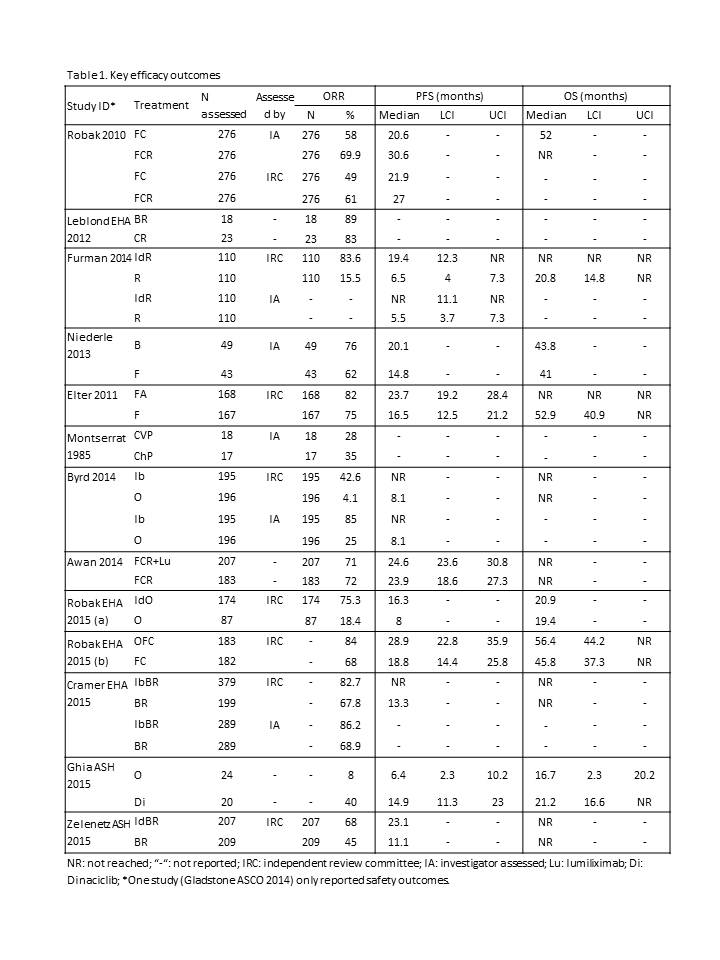
Of 2222 potential studies, 29 full papers were screened, eight of which were included in the final review. Nineteen conference abstracts were also included. Overall, data from 14 unique RCTs were included in the final analysis (Table 1). Three RCTs included Id; in combination with R, or O, or BR. The other 11 studies identified are outlined in table 1. Only eight studies reported baseline genetic characteristics. The included studies were heterogeneous with regards to CLL stage, cytogenetics, and prior lines of therapy; all of which are recognised as treatment modifiers.The median duration of progression-free survival (PFS) between treatment arms was available for nine studies and ranged from 5.5 months (R) to 30.6 months (FCR). Across all studies, the greatest difference in the median duration of PFS between treatment arms was 13 months (IdR vs. R; hazard ratio= 0.15; 95% CI 0.09–0.24). The Median duration of PFS in treatment arms that contained Id ranged from 16.3 months (IdO) to 23.1 months (IdBR). Median OS was reported in 11 studies and ranged from 16.7 months (O) to not reached.
Conclusion
This systematic literature review suggests that idelalisib (in combination with BR, O and R) is an acceptable alternative treatment compared to interventions currently used in clinical practice for R/R CLL patients.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Refractory, Relapse, Systematic review
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) by chemotherapy is not curative, and patients receive multiple chemotherapy lines in an attempt to manage their disease along the years. Due to cumulative toxicity or resistance, treatment options following first-line therapy quickly become limited and new treatment options are needed. Idelalisib is a novel oral inhibitor of PK13K delta for the treatment of relapsed/refractory (R/R) CLL. This study reviewed randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of idelalisib and treatment options in the management of R/R CLL.
Aims
To review the efficacy and safety of idelalisib relative to other commonly used treatments for R/R CLL.
Methods
A systematic literature review was conducted to identify articles evaluating idelalisib (Id), ibrutinib (Ib), alemtuzumab (A), fludarabine (F), rituximab (R), ofatumumab (O), bendamustine (B), cyclophosphamide (C), methylprednisolone (Mp), chlorambucil (Ch), lenalidomide (L), doxorubicin (D), vincristine (V), prednisone (P), CHOP, and CVP as single agents or in combination, in adult patients with R/R CLL. Searches were conducted in the following literature databases: EMBASE, MEDLINE, MEDLINE In-Process and CENTRAL. Conference abstracts from ESMO, ASCO, EHA and ASH 2012–2015 were also searched. Screening was carried out independently by two reviewers. English language RCTs reporting overall, complete or partial response, stable or progressive disease, overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS) or safety were included.
Results
Of 2222 potential studies, 29 full papers were screened, eight of which were included in the final review. Nineteen conference abstracts were also included. Overall, data from 14 unique RCTs were included in the final analysis (Table 1). Three RCTs included Id; in combination with R, or O, or BR. The other 11 studies identified are outlined in table 1. Only eight studies reported baseline genetic characteristics. The included studies were heterogeneous with regards to CLL stage, cytogenetics, and prior lines of therapy; all of which are recognised as treatment modifiers.The median duration of progression-free survival (PFS) between treatment arms was available for nine studies and ranged from 5.5 months (R) to 30.6 months (FCR). Across all studies, the greatest difference in the median duration of PFS between treatment arms was 13 months (IdR vs. R; hazard ratio= 0.15; 95% CI 0.09–0.24). The Median duration of PFS in treatment arms that contained Id ranged from 16.3 months (IdO) to 23.1 months (IdBR). Median OS was reported in 11 studies and ranged from 16.7 months (O) to not reached.
Conclusion
This systematic literature review suggests that idelalisib (in combination with BR, O and R) is an acceptable alternative treatment compared to interventions currently used in clinical practice for R/R CLL patients.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Refractory, Relapse, Systematic review
Abstract: E1070
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) by chemotherapy is not curative, and patients receive multiple chemotherapy lines in an attempt to manage their disease along the years. Due to cumulative toxicity or resistance, treatment options following first-line therapy quickly become limited and new treatment options are needed. Idelalisib is a novel oral inhibitor of PK13K delta for the treatment of relapsed/refractory (R/R) CLL. This study reviewed randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of idelalisib and treatment options in the management of R/R CLL.
Aims
To review the efficacy and safety of idelalisib relative to other commonly used treatments for R/R CLL.
Methods
A systematic literature review was conducted to identify articles evaluating idelalisib (Id), ibrutinib (Ib), alemtuzumab (A), fludarabine (F), rituximab (R), ofatumumab (O), bendamustine (B), cyclophosphamide (C), methylprednisolone (Mp), chlorambucil (Ch), lenalidomide (L), doxorubicin (D), vincristine (V), prednisone (P), CHOP, and CVP as single agents or in combination, in adult patients with R/R CLL. Searches were conducted in the following literature databases: EMBASE, MEDLINE, MEDLINE In-Process and CENTRAL. Conference abstracts from ESMO, ASCO, EHA and ASH 2012–2015 were also searched. Screening was carried out independently by two reviewers. English language RCTs reporting overall, complete or partial response, stable or progressive disease, overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS) or safety were included.
Results
Of 2222 potential studies, 29 full papers were screened, eight of which were included in the final review. Nineteen conference abstracts were also included. Overall, data from 14 unique RCTs were included in the final analysis (Table 1). Three RCTs included Id; in combination with R, or O, or BR. The other 11 studies identified are outlined in table 1. Only eight studies reported baseline genetic characteristics. The included studies were heterogeneous with regards to CLL stage, cytogenetics, and prior lines of therapy; all of which are recognised as treatment modifiers.The median duration of progression-free survival (PFS) between treatment arms was available for nine studies and ranged from 5.5 months (R) to 30.6 months (FCR). Across all studies, the greatest difference in the median duration of PFS between treatment arms was 13 months (IdR vs. R; hazard ratio= 0.15; 95% CI 0.09–0.24). The Median duration of PFS in treatment arms that contained Id ranged from 16.3 months (IdO) to 23.1 months (IdBR). Median OS was reported in 11 studies and ranged from 16.7 months (O) to not reached.
Conclusion
This systematic literature review suggests that idelalisib (in combination with BR, O and R) is an acceptable alternative treatment compared to interventions currently used in clinical practice for R/R CLL patients.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Refractory, Relapse, Systematic review
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) by chemotherapy is not curative, and patients receive multiple chemotherapy lines in an attempt to manage their disease along the years. Due to cumulative toxicity or resistance, treatment options following first-line therapy quickly become limited and new treatment options are needed. Idelalisib is a novel oral inhibitor of PK13K delta for the treatment of relapsed/refractory (R/R) CLL. This study reviewed randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of idelalisib and treatment options in the management of R/R CLL.
Aims
To review the efficacy and safety of idelalisib relative to other commonly used treatments for R/R CLL.
Methods
A systematic literature review was conducted to identify articles evaluating idelalisib (Id), ibrutinib (Ib), alemtuzumab (A), fludarabine (F), rituximab (R), ofatumumab (O), bendamustine (B), cyclophosphamide (C), methylprednisolone (Mp), chlorambucil (Ch), lenalidomide (L), doxorubicin (D), vincristine (V), prednisone (P), CHOP, and CVP as single agents or in combination, in adult patients with R/R CLL. Searches were conducted in the following literature databases: EMBASE, MEDLINE, MEDLINE In-Process and CENTRAL. Conference abstracts from ESMO, ASCO, EHA and ASH 2012–2015 were also searched. Screening was carried out independently by two reviewers. English language RCTs reporting overall, complete or partial response, stable or progressive disease, overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS) or safety were included.
Results
Of 2222 potential studies, 29 full papers were screened, eight of which were included in the final review. Nineteen conference abstracts were also included. Overall, data from 14 unique RCTs were included in the final analysis (Table 1). Three RCTs included Id; in combination with R, or O, or BR. The other 11 studies identified are outlined in table 1. Only eight studies reported baseline genetic characteristics. The included studies were heterogeneous with regards to CLL stage, cytogenetics, and prior lines of therapy; all of which are recognised as treatment modifiers.The median duration of progression-free survival (PFS) between treatment arms was available for nine studies and ranged from 5.5 months (R) to 30.6 months (FCR). Across all studies, the greatest difference in the median duration of PFS between treatment arms was 13 months (IdR vs. R; hazard ratio= 0.15; 95% CI 0.09–0.24). The Median duration of PFS in treatment arms that contained Id ranged from 16.3 months (IdO) to 23.1 months (IdBR). Median OS was reported in 11 studies and ranged from 16.7 months (O) to not reached.
Conclusion
This systematic literature review suggests that idelalisib (in combination with BR, O and R) is an acceptable alternative treatment compared to interventions currently used in clinical practice for R/R CLL patients.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Refractory, Relapse, Systematic review
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


