RESULTS OF PROSPECTIVE OBSERVATIONAL TRIAL OF POLISH ADULT LEUKEMIA GROUP (PALG) ON IBRUTINIB COMPASSIONATE USE IN RELAPSED OR REFRACTORY CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKAEMIA (CLL) IN POLAND.
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Jamroziak K. 06/09/16; 132617; E1068

Krzysztof Jamroziak
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: E1068
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Ibrutinib is a selective and covalent inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase approved for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Outcome and burden of adverse events of specific therapy reported in clinical trials may differ from routine clinical practice due to selection bias and different monitoring.
Aims
The aim of this observational study of Polish Adult Leukemia Study Group (PALG) was to prospectively assess the efficacy and toxicity of ibrutinib monotherapy in relapsed/refractory CLL patients treated within the ibrutinib compassionate use named patient program (NPP) in Poland.
Methods
Patients were eligible for ibrutinib compassionate use NPP if they met all following criteria a) relapsed or refractory CLL, b) active CLL/SLL requiring treatment, c) a minimum of 1 prior line of chemotherapy. Data on treatment outcome and complications were anonymously collected using electronic CRFs.
Results
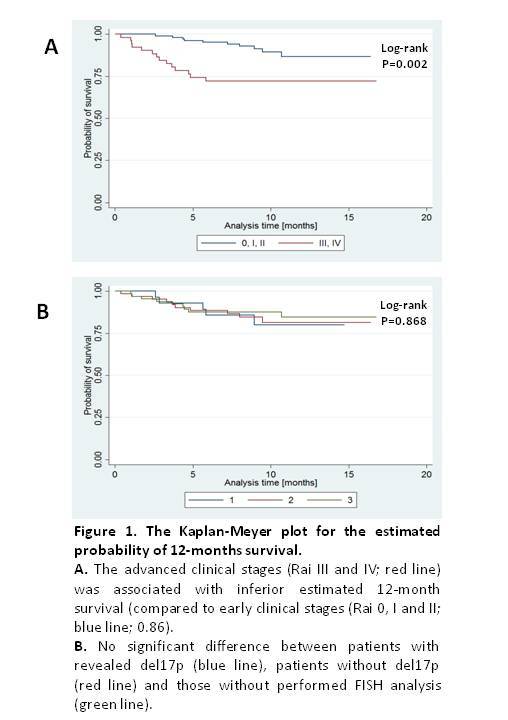
This report is based on data obtained for 163 patients (158 with CLL and 5 with SLL) treated in 15 hematology centers participating in the observational study of PALG. There were 91 male and 72 female patients with median age 63 (range 40-84). Fifty-two patients (32.5%) had advanced disease (III or IV Rai stage) at diagnosis. Median number of chemotherapy lines prior to ibrutinib was 3 (range 1-10). FISH cytogenetics at inclusion to NPP was conducted in 96 (60%) patients, and it revealed del17p in 30 patients (19%). The median follow-up time was 9.2 months (range 0.4-22.2 months). Overall response rate (complete remissions, partial remissions or partial remissions with lymphocytosis) was 73%. Median progression free survival and overall survival (OS) had not been reached with 24 deaths recorded during the time of observation. The estimated probability of 12-months OS was 0.83 (95%CI: 0.75 – 0.88) that appears inferior to 0.90 reported in RESONATE clinical trial (Byrd et al, NEJM 2014). Among parameters analyzed as potential prognostic factors, the advanced clinical stage (Rai III and IV) was associated with inferior OS, with estimated 12-months survival of 0.72 (95%CI: 0.577-0.826) (Fig 1A). Interestingly, no negative influence of del17p regarding OS was detected (Fig 1B). Regarding ibrutinib toxicity grade 3 or 4 side effects occurred in 43 patients (27%). Infections of any grade were diagnosed in 57 patients (36%), while atrial fibrillation of any grade was seen in 14 patients (8.8%). Thirty-three patients (20.2%) required ibrutinib dose reductions, mainly due to infections or hematological toxicity. Interestingly, in RESONATE trial with similar follow up time (median 9.4 months) ibrutinib dose reduction was reported only for 4% of patients.
Conclusion
This large analysis of refractory/relapsed CLL patients treated with ibrutinib monotherapy in real-world clinical practice shows satisfactory treatment results, however, patients’ outcome appears inferior as compared to that observed in the clinical trial. This difference could be partially due to relatively frequent ibrutinib dose reductions and treatment interruptions observed in this patient cohort. Furthermore, our report confirms efficacy of ibrutinib in relapsed/refractory CLL patients with del17p, but also shows that advanced CLL stage at diagnosis retains its prognostic value.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): B-CLL, P53, Relapse
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Ibrutinib is a selective and covalent inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase approved for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Outcome and burden of adverse events of specific therapy reported in clinical trials may differ from routine clinical practice due to selection bias and different monitoring.
Aims
The aim of this observational study of Polish Adult Leukemia Study Group (PALG) was to prospectively assess the efficacy and toxicity of ibrutinib monotherapy in relapsed/refractory CLL patients treated within the ibrutinib compassionate use named patient program (NPP) in Poland.
Methods
Patients were eligible for ibrutinib compassionate use NPP if they met all following criteria a) relapsed or refractory CLL, b) active CLL/SLL requiring treatment, c) a minimum of 1 prior line of chemotherapy. Data on treatment outcome and complications were anonymously collected using electronic CRFs.
Results
This report is based on data obtained for 163 patients (158 with CLL and 5 with SLL) treated in 15 hematology centers participating in the observational study of PALG. There were 91 male and 72 female patients with median age 63 (range 40-84). Fifty-two patients (32.5%) had advanced disease (III or IV Rai stage) at diagnosis. Median number of chemotherapy lines prior to ibrutinib was 3 (range 1-10). FISH cytogenetics at inclusion to NPP was conducted in 96 (60%) patients, and it revealed del17p in 30 patients (19%). The median follow-up time was 9.2 months (range 0.4-22.2 months). Overall response rate (complete remissions, partial remissions or partial remissions with lymphocytosis) was 73%. Median progression free survival and overall survival (OS) had not been reached with 24 deaths recorded during the time of observation. The estimated probability of 12-months OS was 0.83 (95%CI: 0.75 – 0.88) that appears inferior to 0.90 reported in RESONATE clinical trial (Byrd et al, NEJM 2014). Among parameters analyzed as potential prognostic factors, the advanced clinical stage (Rai III and IV) was associated with inferior OS, with estimated 12-months survival of 0.72 (95%CI: 0.577-0.826) (Fig 1A). Interestingly, no negative influence of del17p regarding OS was detected (Fig 1B). Regarding ibrutinib toxicity grade 3 or 4 side effects occurred in 43 patients (27%). Infections of any grade were diagnosed in 57 patients (36%), while atrial fibrillation of any grade was seen in 14 patients (8.8%). Thirty-three patients (20.2%) required ibrutinib dose reductions, mainly due to infections or hematological toxicity. Interestingly, in RESONATE trial with similar follow up time (median 9.4 months) ibrutinib dose reduction was reported only for 4% of patients.
Conclusion
This large analysis of refractory/relapsed CLL patients treated with ibrutinib monotherapy in real-world clinical practice shows satisfactory treatment results, however, patients’ outcome appears inferior as compared to that observed in the clinical trial. This difference could be partially due to relatively frequent ibrutinib dose reductions and treatment interruptions observed in this patient cohort. Furthermore, our report confirms efficacy of ibrutinib in relapsed/refractory CLL patients with del17p, but also shows that advanced CLL stage at diagnosis retains its prognostic value.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): B-CLL, P53, Relapse
Abstract: E1068
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Ibrutinib is a selective and covalent inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase approved for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Outcome and burden of adverse events of specific therapy reported in clinical trials may differ from routine clinical practice due to selection bias and different monitoring.
Aims
The aim of this observational study of Polish Adult Leukemia Study Group (PALG) was to prospectively assess the efficacy and toxicity of ibrutinib monotherapy in relapsed/refractory CLL patients treated within the ibrutinib compassionate use named patient program (NPP) in Poland.
Methods
Patients were eligible for ibrutinib compassionate use NPP if they met all following criteria a) relapsed or refractory CLL, b) active CLL/SLL requiring treatment, c) a minimum of 1 prior line of chemotherapy. Data on treatment outcome and complications were anonymously collected using electronic CRFs.
Results
This report is based on data obtained for 163 patients (158 with CLL and 5 with SLL) treated in 15 hematology centers participating in the observational study of PALG. There were 91 male and 72 female patients with median age 63 (range 40-84). Fifty-two patients (32.5%) had advanced disease (III or IV Rai stage) at diagnosis. Median number of chemotherapy lines prior to ibrutinib was 3 (range 1-10). FISH cytogenetics at inclusion to NPP was conducted in 96 (60%) patients, and it revealed del17p in 30 patients (19%). The median follow-up time was 9.2 months (range 0.4-22.2 months). Overall response rate (complete remissions, partial remissions or partial remissions with lymphocytosis) was 73%. Median progression free survival and overall survival (OS) had not been reached with 24 deaths recorded during the time of observation. The estimated probability of 12-months OS was 0.83 (95%CI: 0.75 – 0.88) that appears inferior to 0.90 reported in RESONATE clinical trial (Byrd et al, NEJM 2014). Among parameters analyzed as potential prognostic factors, the advanced clinical stage (Rai III and IV) was associated with inferior OS, with estimated 12-months survival of 0.72 (95%CI: 0.577-0.826) (Fig 1A). Interestingly, no negative influence of del17p regarding OS was detected (Fig 1B). Regarding ibrutinib toxicity grade 3 or 4 side effects occurred in 43 patients (27%). Infections of any grade were diagnosed in 57 patients (36%), while atrial fibrillation of any grade was seen in 14 patients (8.8%). Thirty-three patients (20.2%) required ibrutinib dose reductions, mainly due to infections or hematological toxicity. Interestingly, in RESONATE trial with similar follow up time (median 9.4 months) ibrutinib dose reduction was reported only for 4% of patients.
Conclusion
This large analysis of refractory/relapsed CLL patients treated with ibrutinib monotherapy in real-world clinical practice shows satisfactory treatment results, however, patients’ outcome appears inferior as compared to that observed in the clinical trial. This difference could be partially due to relatively frequent ibrutinib dose reductions and treatment interruptions observed in this patient cohort. Furthermore, our report confirms efficacy of ibrutinib in relapsed/refractory CLL patients with del17p, but also shows that advanced CLL stage at diagnosis retains its prognostic value.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): B-CLL, P53, Relapse
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Ibrutinib is a selective and covalent inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase approved for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Outcome and burden of adverse events of specific therapy reported in clinical trials may differ from routine clinical practice due to selection bias and different monitoring.
Aims
The aim of this observational study of Polish Adult Leukemia Study Group (PALG) was to prospectively assess the efficacy and toxicity of ibrutinib monotherapy in relapsed/refractory CLL patients treated within the ibrutinib compassionate use named patient program (NPP) in Poland.
Methods
Patients were eligible for ibrutinib compassionate use NPP if they met all following criteria a) relapsed or refractory CLL, b) active CLL/SLL requiring treatment, c) a minimum of 1 prior line of chemotherapy. Data on treatment outcome and complications were anonymously collected using electronic CRFs.
Results
This report is based on data obtained for 163 patients (158 with CLL and 5 with SLL) treated in 15 hematology centers participating in the observational study of PALG. There were 91 male and 72 female patients with median age 63 (range 40-84). Fifty-two patients (32.5%) had advanced disease (III or IV Rai stage) at diagnosis. Median number of chemotherapy lines prior to ibrutinib was 3 (range 1-10). FISH cytogenetics at inclusion to NPP was conducted in 96 (60%) patients, and it revealed del17p in 30 patients (19%). The median follow-up time was 9.2 months (range 0.4-22.2 months). Overall response rate (complete remissions, partial remissions or partial remissions with lymphocytosis) was 73%. Median progression free survival and overall survival (OS) had not been reached with 24 deaths recorded during the time of observation. The estimated probability of 12-months OS was 0.83 (95%CI: 0.75 – 0.88) that appears inferior to 0.90 reported in RESONATE clinical trial (Byrd et al, NEJM 2014). Among parameters analyzed as potential prognostic factors, the advanced clinical stage (Rai III and IV) was associated with inferior OS, with estimated 12-months survival of 0.72 (95%CI: 0.577-0.826) (Fig 1A). Interestingly, no negative influence of del17p regarding OS was detected (Fig 1B). Regarding ibrutinib toxicity grade 3 or 4 side effects occurred in 43 patients (27%). Infections of any grade were diagnosed in 57 patients (36%), while atrial fibrillation of any grade was seen in 14 patients (8.8%). Thirty-three patients (20.2%) required ibrutinib dose reductions, mainly due to infections or hematological toxicity. Interestingly, in RESONATE trial with similar follow up time (median 9.4 months) ibrutinib dose reduction was reported only for 4% of patients.
Conclusion
This large analysis of refractory/relapsed CLL patients treated with ibrutinib monotherapy in real-world clinical practice shows satisfactory treatment results, however, patients’ outcome appears inferior as compared to that observed in the clinical trial. This difference could be partially due to relatively frequent ibrutinib dose reductions and treatment interruptions observed in this patient cohort. Furthermore, our report confirms efficacy of ibrutinib in relapsed/refractory CLL patients with del17p, but also shows that advanced CLL stage at diagnosis retains its prognostic value.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): B-CLL, P53, Relapse
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


