PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF SIGNAL TRANSDUCER AND ACTIVATOR OF TRANSCRIPTION 5 AND 5B EXPRESSION IN EPSTEIN-BARR VIRUS POSITIVE PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Diamantopoulos P. 06/09/16; 132585; E1036

Dr. Panagiotis Diamantopoulos
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: E1036
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) proteins are cytosolic transcription factors that, upon activation, dimerize and migrate to the nucleus to control gene expression. Among them, STAT5 consists of two isoforms (STAT5A and STAT5B) that are 90% identical and are encoded by two adjacent genes on 17q11.2. Aberrant STAT5 activity has been linked to tumorigenesis, and the implication of STAT5 in leukemias and lymphomas that are correlated to viruses has been long speculated. EBV-related lymphomagenesis has not been thoroughly studied in correlation to the JAK-STAT pathway, although there are in vitro data supporting a constitutive activation of STATs in EBV positive lymphoma cell lines.
Aims
We investigated the expression of total STAT5 and STAT5b in patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) in correlation to the presence of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) and Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1).
Methods
Peripheral blood samples from patients with CLL and healthy blood donors were obtained. EBV DNA quantification was performed by real time PCR using the EBV R-gene Quantification Complete kit (bioMérieux, Paris, France). A conventional Real time PCR was used for the detection of LMP1-mRNA and LMP1 expression was verified by ELISA (LMP1 detection kit, MYBiosource, San Diego, CA, USA). Western-blotting was performed for STAT5 and STAT5B in protein extracts. The secondary antibodies used were Affinity Purified Antibody Peroxidase Labeled Goat anti-Rabbit and anti-Mouse IgG (H-L) (Kirkegaard & Perry Laboratories, USA). Gel Pro Analyzer 4 was used to analyze the results. IBM SPSS statistics, v19.0 (IBM Corporation, NY, USA) was used for the statistical analysis of the results.
Results
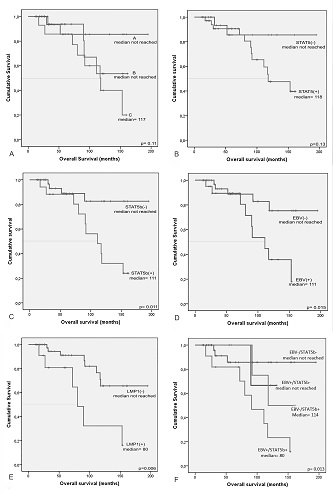
Sixty-three (63) patients with CLL and immunophenotypical comfirmed disease by peripheral blood at the time of sample collection were included in the study. The vast majority of the patients (81%) were treatment naïve, and the clinical stage according to the Binet staging system was: stage A 42.9%, B, 34.9%, and C 22.2%. Total STAT5 was expressed in 38 patients (60.3%) and STAT5b was expressed in patients only (18, 28.6%) but not in healthy subjects. Its expression was correlated to the detection of EBV (77.3% versus 51.2%, p=0.006) and the expression of LMP1 (58.3% versus 21.6%, p=0.011), (detailed results in Table 1). The expression of STAT5b and the presence of EBV and LMP1 were strongly negatively correlated to the overall survival (OS) of the patients (p=0.011, 0.015, 0.006 respectively). Double positive (for EBV and STAT5b) patients had the lowest OS (p=0.013), (Figure 1).Table IV. Correlation of EBV and LMP1 status with the expression of STAT5 and STAT5b.
* Pearson's chi-square test, 2-sided p
Conclusion
This is the first report of a survival disadvantage of EBV positivity in CLL, and the first correlation of STAT5b to OS. Moreover, double positivity (for EBV and STAT5b) was correlated to a worse prognosis, while double negative patients had the highest OS. The correlation of STAT5/5b expression with the presence of the virus and OS defines a subgroup of patients that may benefit from treatment with anti-STAT agents.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Epstein barr virus, STAT5
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) proteins are cytosolic transcription factors that, upon activation, dimerize and migrate to the nucleus to control gene expression. Among them, STAT5 consists of two isoforms (STAT5A and STAT5B) that are 90% identical and are encoded by two adjacent genes on 17q11.2. Aberrant STAT5 activity has been linked to tumorigenesis, and the implication of STAT5 in leukemias and lymphomas that are correlated to viruses has been long speculated. EBV-related lymphomagenesis has not been thoroughly studied in correlation to the JAK-STAT pathway, although there are in vitro data supporting a constitutive activation of STATs in EBV positive lymphoma cell lines.
Aims
We investigated the expression of total STAT5 and STAT5b in patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) in correlation to the presence of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) and Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1).
Methods
Peripheral blood samples from patients with CLL and healthy blood donors were obtained. EBV DNA quantification was performed by real time PCR using the EBV R-gene Quantification Complete kit (bioMérieux, Paris, France). A conventional Real time PCR was used for the detection of LMP1-mRNA and LMP1 expression was verified by ELISA (LMP1 detection kit, MYBiosource, San Diego, CA, USA). Western-blotting was performed for STAT5 and STAT5B in protein extracts. The secondary antibodies used were Affinity Purified Antibody Peroxidase Labeled Goat anti-Rabbit and anti-Mouse IgG (H-L) (Kirkegaard & Perry Laboratories, USA). Gel Pro Analyzer 4 was used to analyze the results. IBM SPSS statistics, v19.0 (IBM Corporation, NY, USA) was used for the statistical analysis of the results.
Results
Sixty-three (63) patients with CLL and immunophenotypical comfirmed disease by peripheral blood at the time of sample collection were included in the study. The vast majority of the patients (81%) were treatment naïve, and the clinical stage according to the Binet staging system was: stage A 42.9%, B, 34.9%, and C 22.2%. Total STAT5 was expressed in 38 patients (60.3%) and STAT5b was expressed in patients only (18, 28.6%) but not in healthy subjects. Its expression was correlated to the detection of EBV (77.3% versus 51.2%, p=0.006) and the expression of LMP1 (58.3% versus 21.6%, p=0.011), (detailed results in Table 1). The expression of STAT5b and the presence of EBV and LMP1 were strongly negatively correlated to the overall survival (OS) of the patients (p=0.011, 0.015, 0.006 respectively). Double positive (for EBV and STAT5b) patients had the lowest OS (p=0.013), (Figure 1).Table IV. Correlation of EBV and LMP1 status with the expression of STAT5 and STAT5b.
| Patients | EBV(+), N (%) | EBV(-), N (%) | P* |
| Expressing STAT5 Not expressing STAT5 | 17 (77.3)5 (22.7) | 21 (51.2)20 (48.8) | 0.044 |
| Expressing STAT5bNot expressing STAT5b | 11 (50.0)11 (50.0) | 7 (17.1)34 (82.9) | 0.006 |
| LMP1(+) | LMP1 (-) | ||
| Expressing STAT5 Not expressing STAT5 | 11 (91.7)1 (8.3) | 27 (52.9)24 (47.1) | 0.014 |
| Expressing STAT5bNot expressing STAT5b | 7 (58.3)5 (41.7) | 11 (21.6)40 (78.4) | 0.011 |
Conclusion
This is the first report of a survival disadvantage of EBV positivity in CLL, and the first correlation of STAT5b to OS. Moreover, double positivity (for EBV and STAT5b) was correlated to a worse prognosis, while double negative patients had the highest OS. The correlation of STAT5/5b expression with the presence of the virus and OS defines a subgroup of patients that may benefit from treatment with anti-STAT agents.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Epstein barr virus, STAT5
Abstract: E1036
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) proteins are cytosolic transcription factors that, upon activation, dimerize and migrate to the nucleus to control gene expression. Among them, STAT5 consists of two isoforms (STAT5A and STAT5B) that are 90% identical and are encoded by two adjacent genes on 17q11.2. Aberrant STAT5 activity has been linked to tumorigenesis, and the implication of STAT5 in leukemias and lymphomas that are correlated to viruses has been long speculated. EBV-related lymphomagenesis has not been thoroughly studied in correlation to the JAK-STAT pathway, although there are in vitro data supporting a constitutive activation of STATs in EBV positive lymphoma cell lines.
Aims
We investigated the expression of total STAT5 and STAT5b in patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) in correlation to the presence of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) and Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1).
Methods
Peripheral blood samples from patients with CLL and healthy blood donors were obtained. EBV DNA quantification was performed by real time PCR using the EBV R-gene Quantification Complete kit (bioMérieux, Paris, France). A conventional Real time PCR was used for the detection of LMP1-mRNA and LMP1 expression was verified by ELISA (LMP1 detection kit, MYBiosource, San Diego, CA, USA). Western-blotting was performed for STAT5 and STAT5B in protein extracts. The secondary antibodies used were Affinity Purified Antibody Peroxidase Labeled Goat anti-Rabbit and anti-Mouse IgG (H-L) (Kirkegaard & Perry Laboratories, USA). Gel Pro Analyzer 4 was used to analyze the results. IBM SPSS statistics, v19.0 (IBM Corporation, NY, USA) was used for the statistical analysis of the results.
Results
Sixty-three (63) patients with CLL and immunophenotypical comfirmed disease by peripheral blood at the time of sample collection were included in the study. The vast majority of the patients (81%) were treatment naïve, and the clinical stage according to the Binet staging system was: stage A 42.9%, B, 34.9%, and C 22.2%. Total STAT5 was expressed in 38 patients (60.3%) and STAT5b was expressed in patients only (18, 28.6%) but not in healthy subjects. Its expression was correlated to the detection of EBV (77.3% versus 51.2%, p=0.006) and the expression of LMP1 (58.3% versus 21.6%, p=0.011), (detailed results in Table 1). The expression of STAT5b and the presence of EBV and LMP1 were strongly negatively correlated to the overall survival (OS) of the patients (p=0.011, 0.015, 0.006 respectively). Double positive (for EBV and STAT5b) patients had the lowest OS (p=0.013), (Figure 1).Table IV. Correlation of EBV and LMP1 status with the expression of STAT5 and STAT5b.
* Pearson's chi-square test, 2-sided p
Conclusion
This is the first report of a survival disadvantage of EBV positivity in CLL, and the first correlation of STAT5b to OS. Moreover, double positivity (for EBV and STAT5b) was correlated to a worse prognosis, while double negative patients had the highest OS. The correlation of STAT5/5b expression with the presence of the virus and OS defines a subgroup of patients that may benefit from treatment with anti-STAT agents.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Epstein barr virus, STAT5
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) proteins are cytosolic transcription factors that, upon activation, dimerize and migrate to the nucleus to control gene expression. Among them, STAT5 consists of two isoforms (STAT5A and STAT5B) that are 90% identical and are encoded by two adjacent genes on 17q11.2. Aberrant STAT5 activity has been linked to tumorigenesis, and the implication of STAT5 in leukemias and lymphomas that are correlated to viruses has been long speculated. EBV-related lymphomagenesis has not been thoroughly studied in correlation to the JAK-STAT pathway, although there are in vitro data supporting a constitutive activation of STATs in EBV positive lymphoma cell lines.
Aims
We investigated the expression of total STAT5 and STAT5b in patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) in correlation to the presence of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) and Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1).
Methods
Peripheral blood samples from patients with CLL and healthy blood donors were obtained. EBV DNA quantification was performed by real time PCR using the EBV R-gene Quantification Complete kit (bioMérieux, Paris, France). A conventional Real time PCR was used for the detection of LMP1-mRNA and LMP1 expression was verified by ELISA (LMP1 detection kit, MYBiosource, San Diego, CA, USA). Western-blotting was performed for STAT5 and STAT5B in protein extracts. The secondary antibodies used were Affinity Purified Antibody Peroxidase Labeled Goat anti-Rabbit and anti-Mouse IgG (H-L) (Kirkegaard & Perry Laboratories, USA). Gel Pro Analyzer 4 was used to analyze the results. IBM SPSS statistics, v19.0 (IBM Corporation, NY, USA) was used for the statistical analysis of the results.
Results
Sixty-three (63) patients with CLL and immunophenotypical comfirmed disease by peripheral blood at the time of sample collection were included in the study. The vast majority of the patients (81%) were treatment naïve, and the clinical stage according to the Binet staging system was: stage A 42.9%, B, 34.9%, and C 22.2%. Total STAT5 was expressed in 38 patients (60.3%) and STAT5b was expressed in patients only (18, 28.6%) but not in healthy subjects. Its expression was correlated to the detection of EBV (77.3% versus 51.2%, p=0.006) and the expression of LMP1 (58.3% versus 21.6%, p=0.011), (detailed results in Table 1). The expression of STAT5b and the presence of EBV and LMP1 were strongly negatively correlated to the overall survival (OS) of the patients (p=0.011, 0.015, 0.006 respectively). Double positive (for EBV and STAT5b) patients had the lowest OS (p=0.013), (Figure 1).Table IV. Correlation of EBV and LMP1 status with the expression of STAT5 and STAT5b.
| Patients | EBV(+), N (%) | EBV(-), N (%) | P* |
| Expressing STAT5 Not expressing STAT5 | 17 (77.3)5 (22.7) | 21 (51.2)20 (48.8) | 0.044 |
| Expressing STAT5bNot expressing STAT5b | 11 (50.0)11 (50.0) | 7 (17.1)34 (82.9) | 0.006 |
| LMP1(+) | LMP1 (-) | ||
| Expressing STAT5 Not expressing STAT5 | 11 (91.7)1 (8.3) | 27 (52.9)24 (47.1) | 0.014 |
| Expressing STAT5bNot expressing STAT5b | 7 (58.3)5 (41.7) | 11 (21.6)40 (78.4) | 0.011 |
Conclusion
This is the first report of a survival disadvantage of EBV positivity in CLL, and the first correlation of STAT5b to OS. Moreover, double positivity (for EBV and STAT5b) was correlated to a worse prognosis, while double negative patients had the highest OS. The correlation of STAT5/5b expression with the presence of the virus and OS defines a subgroup of patients that may benefit from treatment with anti-STAT agents.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Epstein barr virus, STAT5
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


