OUTCOMES OF 34 PRIMARY BREAST DIFFUSE LARGE B-CELL LYMPHOMA IN RITUXIMAB ERA AT A SINGLE INSTITUTION
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Nishimura N. 06/09/16; 132523; E974
Disclosure(s): Chugai Pharmaceutical CO. LTD.

Dr. Noriko Nishimura
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: E974
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Primary breast lymphoma (PBL) is a rare subtype of lymphoma accounting for 1 to 2 % of extra-nodal lymphomas with the most subtype of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), thus the data of pathology and outcome is limited.
Aims
To elucidate the clinicopathological features and the outcomes including incidence of central nervous system (CNS) relapse in Rituximab-era.
Methods
Data were collected on patients with PBL diagnosed between January 1992 and 2016 at the Cancer Institute Hospital of JFCR, retrospectively. Patients with stage III and IV were excluded. Female DLBCL with stage I / II were also collected as a control in the matched case-control study.
Results
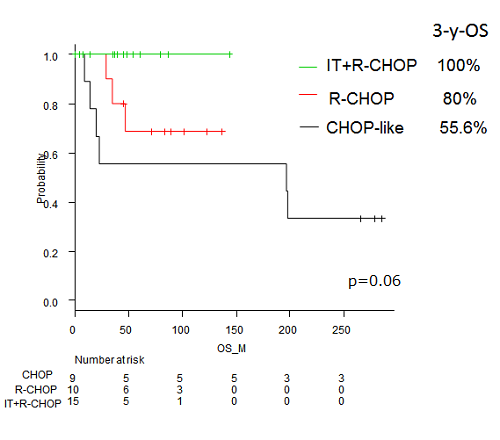
A total of 34 patients; 9 treated with CHOP-like regimens (CHOP group), 10 treated with rituximab-CHOP (R-CHOP group), and 15 treated with R-CHOP and intrathecal (IT) prophylaxis, were analyzed. Median age was 57 years. All patients were female with 21 patients (70.5%) of presenting with right breast tumor. Non-GC type defined by Hans algorithm had a higher proportion of 14 out of 24 analyzable patients (58.3%) without poor prognostic value. In comparison with early stage DLBCL treated with R-CHOP with or without IT prophylaxis except for breast, younger age (57 years v.s. 66 years) and higher CNS relapse rate (8.8% v.s. 0%) had significant difference between two groups. Then 1: 3 pair-matched case-control study limited in patients with stage I / II, female, and rituximab use, adjusted with age was carried out. Non-GC had higher rate in PBL than early stage DLBCL (66.7% v.s.44.4%), however, with no significant difference. On survival analysis with a median follow-up of 63months, PBL did not have poor prognosis with a 3-y-PFS (89.2% vs 90.2%, p=0.55) and 3-y-OS (90.0% vs 94.5%, p=0.87). Among patients with PBL, after a median follow-up of 47.5 months (range 1-286 months), the 3-year Progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) according to three groups; CHOP group, R-CHOP group, and IT+R-CHOP group were 55.6%, 80%, and 100% (p=0.058), and 55.6%, 80%, and 100% (p=0.06), respectively. CNS relapse had occurred in 3 out of 34 patients: all were stage II, one in CHOP group and two in R-CHOP group. Notably IT+ R-CHOP group had no relapse to date.
Conclusion
PBL patients are younger than early stage DLBCL, and still considered as a high-risk for CNS relapse in Rituximab era. Nevertheless, IT added to R-CHOP potentially improve outcomes including CNS relapse.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Breast, CNS, DLBCL, Germinal center
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Primary breast lymphoma (PBL) is a rare subtype of lymphoma accounting for 1 to 2 % of extra-nodal lymphomas with the most subtype of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), thus the data of pathology and outcome is limited.
Aims
To elucidate the clinicopathological features and the outcomes including incidence of central nervous system (CNS) relapse in Rituximab-era.
Methods
Data were collected on patients with PBL diagnosed between January 1992 and 2016 at the Cancer Institute Hospital of JFCR, retrospectively. Patients with stage III and IV were excluded. Female DLBCL with stage I / II were also collected as a control in the matched case-control study.
Results
A total of 34 patients; 9 treated with CHOP-like regimens (CHOP group), 10 treated with rituximab-CHOP (R-CHOP group), and 15 treated with R-CHOP and intrathecal (IT) prophylaxis, were analyzed. Median age was 57 years. All patients were female with 21 patients (70.5%) of presenting with right breast tumor. Non-GC type defined by Hans algorithm had a higher proportion of 14 out of 24 analyzable patients (58.3%) without poor prognostic value. In comparison with early stage DLBCL treated with R-CHOP with or without IT prophylaxis except for breast, younger age (57 years v.s. 66 years) and higher CNS relapse rate (8.8% v.s. 0%) had significant difference between two groups. Then 1: 3 pair-matched case-control study limited in patients with stage I / II, female, and rituximab use, adjusted with age was carried out. Non-GC had higher rate in PBL than early stage DLBCL (66.7% v.s.44.4%), however, with no significant difference. On survival analysis with a median follow-up of 63months, PBL did not have poor prognosis with a 3-y-PFS (89.2% vs 90.2%, p=0.55) and 3-y-OS (90.0% vs 94.5%, p=0.87). Among patients with PBL, after a median follow-up of 47.5 months (range 1-286 months), the 3-year Progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) according to three groups; CHOP group, R-CHOP group, and IT+R-CHOP group were 55.6%, 80%, and 100% (p=0.058), and 55.6%, 80%, and 100% (p=0.06), respectively. CNS relapse had occurred in 3 out of 34 patients: all were stage II, one in CHOP group and two in R-CHOP group. Notably IT+ R-CHOP group had no relapse to date.
Conclusion
PBL patients are younger than early stage DLBCL, and still considered as a high-risk for CNS relapse in Rituximab era. Nevertheless, IT added to R-CHOP potentially improve outcomes including CNS relapse.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Breast, CNS, DLBCL, Germinal center
Abstract: E974
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Primary breast lymphoma (PBL) is a rare subtype of lymphoma accounting for 1 to 2 % of extra-nodal lymphomas with the most subtype of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), thus the data of pathology and outcome is limited.
Aims
To elucidate the clinicopathological features and the outcomes including incidence of central nervous system (CNS) relapse in Rituximab-era.
Methods
Data were collected on patients with PBL diagnosed between January 1992 and 2016 at the Cancer Institute Hospital of JFCR, retrospectively. Patients with stage III and IV were excluded. Female DLBCL with stage I / II were also collected as a control in the matched case-control study.
Results
A total of 34 patients; 9 treated with CHOP-like regimens (CHOP group), 10 treated with rituximab-CHOP (R-CHOP group), and 15 treated with R-CHOP and intrathecal (IT) prophylaxis, were analyzed. Median age was 57 years. All patients were female with 21 patients (70.5%) of presenting with right breast tumor. Non-GC type defined by Hans algorithm had a higher proportion of 14 out of 24 analyzable patients (58.3%) without poor prognostic value. In comparison with early stage DLBCL treated with R-CHOP with or without IT prophylaxis except for breast, younger age (57 years v.s. 66 years) and higher CNS relapse rate (8.8% v.s. 0%) had significant difference between two groups. Then 1: 3 pair-matched case-control study limited in patients with stage I / II, female, and rituximab use, adjusted with age was carried out. Non-GC had higher rate in PBL than early stage DLBCL (66.7% v.s.44.4%), however, with no significant difference. On survival analysis with a median follow-up of 63months, PBL did not have poor prognosis with a 3-y-PFS (89.2% vs 90.2%, p=0.55) and 3-y-OS (90.0% vs 94.5%, p=0.87). Among patients with PBL, after a median follow-up of 47.5 months (range 1-286 months), the 3-year Progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) according to three groups; CHOP group, R-CHOP group, and IT+R-CHOP group were 55.6%, 80%, and 100% (p=0.058), and 55.6%, 80%, and 100% (p=0.06), respectively. CNS relapse had occurred in 3 out of 34 patients: all were stage II, one in CHOP group and two in R-CHOP group. Notably IT+ R-CHOP group had no relapse to date.
Conclusion
PBL patients are younger than early stage DLBCL, and still considered as a high-risk for CNS relapse in Rituximab era. Nevertheless, IT added to R-CHOP potentially improve outcomes including CNS relapse.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Breast, CNS, DLBCL, Germinal center
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Primary breast lymphoma (PBL) is a rare subtype of lymphoma accounting for 1 to 2 % of extra-nodal lymphomas with the most subtype of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), thus the data of pathology and outcome is limited.
Aims
To elucidate the clinicopathological features and the outcomes including incidence of central nervous system (CNS) relapse in Rituximab-era.
Methods
Data were collected on patients with PBL diagnosed between January 1992 and 2016 at the Cancer Institute Hospital of JFCR, retrospectively. Patients with stage III and IV were excluded. Female DLBCL with stage I / II were also collected as a control in the matched case-control study.
Results
A total of 34 patients; 9 treated with CHOP-like regimens (CHOP group), 10 treated with rituximab-CHOP (R-CHOP group), and 15 treated with R-CHOP and intrathecal (IT) prophylaxis, were analyzed. Median age was 57 years. All patients were female with 21 patients (70.5%) of presenting with right breast tumor. Non-GC type defined by Hans algorithm had a higher proportion of 14 out of 24 analyzable patients (58.3%) without poor prognostic value. In comparison with early stage DLBCL treated with R-CHOP with or without IT prophylaxis except for breast, younger age (57 years v.s. 66 years) and higher CNS relapse rate (8.8% v.s. 0%) had significant difference between two groups. Then 1: 3 pair-matched case-control study limited in patients with stage I / II, female, and rituximab use, adjusted with age was carried out. Non-GC had higher rate in PBL than early stage DLBCL (66.7% v.s.44.4%), however, with no significant difference. On survival analysis with a median follow-up of 63months, PBL did not have poor prognosis with a 3-y-PFS (89.2% vs 90.2%, p=0.55) and 3-y-OS (90.0% vs 94.5%, p=0.87). Among patients with PBL, after a median follow-up of 47.5 months (range 1-286 months), the 3-year Progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) according to three groups; CHOP group, R-CHOP group, and IT+R-CHOP group were 55.6%, 80%, and 100% (p=0.058), and 55.6%, 80%, and 100% (p=0.06), respectively. CNS relapse had occurred in 3 out of 34 patients: all were stage II, one in CHOP group and two in R-CHOP group. Notably IT+ R-CHOP group had no relapse to date.
Conclusion
PBL patients are younger than early stage DLBCL, and still considered as a high-risk for CNS relapse in Rituximab era. Nevertheless, IT added to R-CHOP potentially improve outcomes including CNS relapse.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Breast, CNS, DLBCL, Germinal center
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


