OUTCOMES WITH RITUXIMAB MONOTHERAPY VERSUS R-CHOP IN POST-TRANSPLANT LYMPHOPROLIFERATIVE DISEASE ARISING AFTER SOLID ORGAN TRANSPLANT: A UNITED KINGDOM MULTICENTRE STUDY
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Burns D. 06/09/16; 132493; E944

Dr. David Burns
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: E944
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD) remains an important complication of solid organ transplantation (SOT). There is currently a lack of data to guide selection between Rituximab monotherapy (R-mono) and R-CHOP as options for frontline therapy of B-cell PTLD.
Aims
To report outcomes and prognostic factors for patients with B-cell PTLD arising after SOT, comparing R-mono vs. R-CHOP as initial therapy.
Methods
This retrospective study included adult patients from 6 centres in the United Kingdom diagnosed with biopsy-proven PTLD between 2000-2013. Median follow-up was 4 years 2 months.
Results
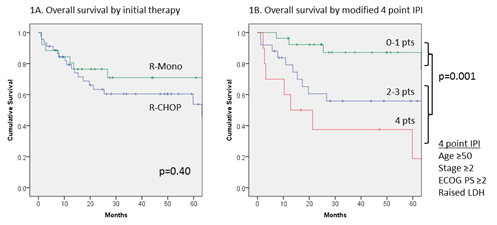
Of 116 cases of PTLD identified, 100 were categorised as B-cell PTLD and were included in this analysis. Histological subtypes were 67 DLBCL, 23 polymorphic and 10 B-cell PTLD otherwise unspecified. There were 62 renal, 30 liver, 7 cardiothoracic and 1 pancreatic transplant recipients. Median age at diagnosis was 48 years (range 16-84 years) and 65% of patients were male. Early onset disease, presenting ≤1 year after transplant, comprised 15% of cases. EBV-association was noted in 55/78 (71%) of evaluated cases and this was related to early onset disease (X2 p=0.004). Initial therapy was R-mono in 26/100 (26%) and R-CHOP in 45/100 (45%). Use of R-CHOP was associated with monomorphic histology (OR 18.3, p=0.001), ≥2 extranodal sites (OR 4.5, p=0.03), late onset disease (OR 6.2, p=0.01) and lack of EBV association (OR 0.08, p=0.002). Of patients treated with R-mono, 25/26 (96%) completed at least 4 infusions of Rituximab 375 mg/m2 weekly, with no treatment-related deaths. Of those treated with R-CHOP, 33/45 (73%) completed at least 6 cycles, although there were 4 treatment-related deaths. The overall response rate for R-mono was 20/26 (77%; 14 CR, 6 PR, 5 NR and 1 undetermined) compared to 36/45 (80%; 30 CR, 6 PR, 5 NR and 4 undetermined) for R-CHOP. Amongst patients treated with R-mono, 17/26 (65%) had no further therapy and remained disease free with median follow-up of 44 months; 6 other patients received R-CHOP for consolidation of response or relapsed/refractory disease. Overall survival (OS) was 71% and 61% at 3 years for R-mono and R-CHOP respectively (p=0.40; Figure 1A). Amongst all patients with B-cell PTLD, significant baseline predictors of inferior OS were age ≥50 years (HR 3.8, p<0.001), ECOG PS ≥2 (HR 1.9, p=0.04), elevated LDH (HR 2.0, p=0.08 borderline), stage ≥2 disease (HR 2.5, p=0.01) and ≥2 extranodal sites (HR 1.8, p=0.08 borderline). Overall response to R-mono or R-CHOP was also highly predictive of OS (HR 0.16, p=0.0001). B symptoms, onset time, extranodal disease, histology and EBV-association were not predictive. In multivariate testing, age ≥50 years (HR 5.3, p=0.0001) and advanced stage (HR 2.2, p=0.06 borderline) remained significant. Applying a 4 point modified prognostic index (comprising age ≥50 years, stage ≥2 disease, ECOG PS ≥2 and elevated LDH) to patients treated with R-mono or R-CHOP, those with low risk disease (0-1 points) had significantly improved survival compared to those with high risk disease (≥2 points), with 3 year OS of 87% vs. 51% (p=0.001; Figure 1B). Amongst patients with high risk disease, 13 treated with R-mono had an inferior complete response rate compared to 21 treated with R-CHOP (23% vs. 67%; OR 0.15, p=0.02), although a survival difference was not detected.
Conclusion
We report outcomes for R-mono vs. R-CHOP as initial therapy for PTLD arising after SOT. R-mono may deliver inferior response rates for patients with high risk disease. Using a modified prognostic index we identify a subset of patients with poor outcome for whom novel therapeutic strategies are required.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Lymphoma, Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder, Rituximab
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD) remains an important complication of solid organ transplantation (SOT). There is currently a lack of data to guide selection between Rituximab monotherapy (R-mono) and R-CHOP as options for frontline therapy of B-cell PTLD.
Aims
To report outcomes and prognostic factors for patients with B-cell PTLD arising after SOT, comparing R-mono vs. R-CHOP as initial therapy.
Methods
This retrospective study included adult patients from 6 centres in the United Kingdom diagnosed with biopsy-proven PTLD between 2000-2013. Median follow-up was 4 years 2 months.
Results
Of 116 cases of PTLD identified, 100 were categorised as B-cell PTLD and were included in this analysis. Histological subtypes were 67 DLBCL, 23 polymorphic and 10 B-cell PTLD otherwise unspecified. There were 62 renal, 30 liver, 7 cardiothoracic and 1 pancreatic transplant recipients. Median age at diagnosis was 48 years (range 16-84 years) and 65% of patients were male. Early onset disease, presenting ≤1 year after transplant, comprised 15% of cases. EBV-association was noted in 55/78 (71%) of evaluated cases and this was related to early onset disease (X2 p=0.004). Initial therapy was R-mono in 26/100 (26%) and R-CHOP in 45/100 (45%). Use of R-CHOP was associated with monomorphic histology (OR 18.3, p=0.001), ≥2 extranodal sites (OR 4.5, p=0.03), late onset disease (OR 6.2, p=0.01) and lack of EBV association (OR 0.08, p=0.002). Of patients treated with R-mono, 25/26 (96%) completed at least 4 infusions of Rituximab 375 mg/m2 weekly, with no treatment-related deaths. Of those treated with R-CHOP, 33/45 (73%) completed at least 6 cycles, although there were 4 treatment-related deaths. The overall response rate for R-mono was 20/26 (77%; 14 CR, 6 PR, 5 NR and 1 undetermined) compared to 36/45 (80%; 30 CR, 6 PR, 5 NR and 4 undetermined) for R-CHOP. Amongst patients treated with R-mono, 17/26 (65%) had no further therapy and remained disease free with median follow-up of 44 months; 6 other patients received R-CHOP for consolidation of response or relapsed/refractory disease. Overall survival (OS) was 71% and 61% at 3 years for R-mono and R-CHOP respectively (p=0.40; Figure 1A). Amongst all patients with B-cell PTLD, significant baseline predictors of inferior OS were age ≥50 years (HR 3.8, p<0.001), ECOG PS ≥2 (HR 1.9, p=0.04), elevated LDH (HR 2.0, p=0.08 borderline), stage ≥2 disease (HR 2.5, p=0.01) and ≥2 extranodal sites (HR 1.8, p=0.08 borderline). Overall response to R-mono or R-CHOP was also highly predictive of OS (HR 0.16, p=0.0001). B symptoms, onset time, extranodal disease, histology and EBV-association were not predictive. In multivariate testing, age ≥50 years (HR 5.3, p=0.0001) and advanced stage (HR 2.2, p=0.06 borderline) remained significant. Applying a 4 point modified prognostic index (comprising age ≥50 years, stage ≥2 disease, ECOG PS ≥2 and elevated LDH) to patients treated with R-mono or R-CHOP, those with low risk disease (0-1 points) had significantly improved survival compared to those with high risk disease (≥2 points), with 3 year OS of 87% vs. 51% (p=0.001; Figure 1B). Amongst patients with high risk disease, 13 treated with R-mono had an inferior complete response rate compared to 21 treated with R-CHOP (23% vs. 67%; OR 0.15, p=0.02), although a survival difference was not detected.
Conclusion
We report outcomes for R-mono vs. R-CHOP as initial therapy for PTLD arising after SOT. R-mono may deliver inferior response rates for patients with high risk disease. Using a modified prognostic index we identify a subset of patients with poor outcome for whom novel therapeutic strategies are required.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Lymphoma, Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder, Rituximab
Abstract: E944
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD) remains an important complication of solid organ transplantation (SOT). There is currently a lack of data to guide selection between Rituximab monotherapy (R-mono) and R-CHOP as options for frontline therapy of B-cell PTLD.
Aims
To report outcomes and prognostic factors for patients with B-cell PTLD arising after SOT, comparing R-mono vs. R-CHOP as initial therapy.
Methods
This retrospective study included adult patients from 6 centres in the United Kingdom diagnosed with biopsy-proven PTLD between 2000-2013. Median follow-up was 4 years 2 months.
Results
Of 116 cases of PTLD identified, 100 were categorised as B-cell PTLD and were included in this analysis. Histological subtypes were 67 DLBCL, 23 polymorphic and 10 B-cell PTLD otherwise unspecified. There were 62 renal, 30 liver, 7 cardiothoracic and 1 pancreatic transplant recipients. Median age at diagnosis was 48 years (range 16-84 years) and 65% of patients were male. Early onset disease, presenting ≤1 year after transplant, comprised 15% of cases. EBV-association was noted in 55/78 (71%) of evaluated cases and this was related to early onset disease (X2 p=0.004). Initial therapy was R-mono in 26/100 (26%) and R-CHOP in 45/100 (45%). Use of R-CHOP was associated with monomorphic histology (OR 18.3, p=0.001), ≥2 extranodal sites (OR 4.5, p=0.03), late onset disease (OR 6.2, p=0.01) and lack of EBV association (OR 0.08, p=0.002). Of patients treated with R-mono, 25/26 (96%) completed at least 4 infusions of Rituximab 375 mg/m2 weekly, with no treatment-related deaths. Of those treated with R-CHOP, 33/45 (73%) completed at least 6 cycles, although there were 4 treatment-related deaths. The overall response rate for R-mono was 20/26 (77%; 14 CR, 6 PR, 5 NR and 1 undetermined) compared to 36/45 (80%; 30 CR, 6 PR, 5 NR and 4 undetermined) for R-CHOP. Amongst patients treated with R-mono, 17/26 (65%) had no further therapy and remained disease free with median follow-up of 44 months; 6 other patients received R-CHOP for consolidation of response or relapsed/refractory disease. Overall survival (OS) was 71% and 61% at 3 years for R-mono and R-CHOP respectively (p=0.40; Figure 1A). Amongst all patients with B-cell PTLD, significant baseline predictors of inferior OS were age ≥50 years (HR 3.8, p<0.001), ECOG PS ≥2 (HR 1.9, p=0.04), elevated LDH (HR 2.0, p=0.08 borderline), stage ≥2 disease (HR 2.5, p=0.01) and ≥2 extranodal sites (HR 1.8, p=0.08 borderline). Overall response to R-mono or R-CHOP was also highly predictive of OS (HR 0.16, p=0.0001). B symptoms, onset time, extranodal disease, histology and EBV-association were not predictive. In multivariate testing, age ≥50 years (HR 5.3, p=0.0001) and advanced stage (HR 2.2, p=0.06 borderline) remained significant. Applying a 4 point modified prognostic index (comprising age ≥50 years, stage ≥2 disease, ECOG PS ≥2 and elevated LDH) to patients treated with R-mono or R-CHOP, those with low risk disease (0-1 points) had significantly improved survival compared to those with high risk disease (≥2 points), with 3 year OS of 87% vs. 51% (p=0.001; Figure 1B). Amongst patients with high risk disease, 13 treated with R-mono had an inferior complete response rate compared to 21 treated with R-CHOP (23% vs. 67%; OR 0.15, p=0.02), although a survival difference was not detected.
Conclusion
We report outcomes for R-mono vs. R-CHOP as initial therapy for PTLD arising after SOT. R-mono may deliver inferior response rates for patients with high risk disease. Using a modified prognostic index we identify a subset of patients with poor outcome for whom novel therapeutic strategies are required.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Lymphoma, Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder, Rituximab
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD) remains an important complication of solid organ transplantation (SOT). There is currently a lack of data to guide selection between Rituximab monotherapy (R-mono) and R-CHOP as options for frontline therapy of B-cell PTLD.
Aims
To report outcomes and prognostic factors for patients with B-cell PTLD arising after SOT, comparing R-mono vs. R-CHOP as initial therapy.
Methods
This retrospective study included adult patients from 6 centres in the United Kingdom diagnosed with biopsy-proven PTLD between 2000-2013. Median follow-up was 4 years 2 months.
Results
Of 116 cases of PTLD identified, 100 were categorised as B-cell PTLD and were included in this analysis. Histological subtypes were 67 DLBCL, 23 polymorphic and 10 B-cell PTLD otherwise unspecified. There were 62 renal, 30 liver, 7 cardiothoracic and 1 pancreatic transplant recipients. Median age at diagnosis was 48 years (range 16-84 years) and 65% of patients were male. Early onset disease, presenting ≤1 year after transplant, comprised 15% of cases. EBV-association was noted in 55/78 (71%) of evaluated cases and this was related to early onset disease (X2 p=0.004). Initial therapy was R-mono in 26/100 (26%) and R-CHOP in 45/100 (45%). Use of R-CHOP was associated with monomorphic histology (OR 18.3, p=0.001), ≥2 extranodal sites (OR 4.5, p=0.03), late onset disease (OR 6.2, p=0.01) and lack of EBV association (OR 0.08, p=0.002). Of patients treated with R-mono, 25/26 (96%) completed at least 4 infusions of Rituximab 375 mg/m2 weekly, with no treatment-related deaths. Of those treated with R-CHOP, 33/45 (73%) completed at least 6 cycles, although there were 4 treatment-related deaths. The overall response rate for R-mono was 20/26 (77%; 14 CR, 6 PR, 5 NR and 1 undetermined) compared to 36/45 (80%; 30 CR, 6 PR, 5 NR and 4 undetermined) for R-CHOP. Amongst patients treated with R-mono, 17/26 (65%) had no further therapy and remained disease free with median follow-up of 44 months; 6 other patients received R-CHOP for consolidation of response or relapsed/refractory disease. Overall survival (OS) was 71% and 61% at 3 years for R-mono and R-CHOP respectively (p=0.40; Figure 1A). Amongst all patients with B-cell PTLD, significant baseline predictors of inferior OS were age ≥50 years (HR 3.8, p<0.001), ECOG PS ≥2 (HR 1.9, p=0.04), elevated LDH (HR 2.0, p=0.08 borderline), stage ≥2 disease (HR 2.5, p=0.01) and ≥2 extranodal sites (HR 1.8, p=0.08 borderline). Overall response to R-mono or R-CHOP was also highly predictive of OS (HR 0.16, p=0.0001). B symptoms, onset time, extranodal disease, histology and EBV-association were not predictive. In multivariate testing, age ≥50 years (HR 5.3, p=0.0001) and advanced stage (HR 2.2, p=0.06 borderline) remained significant. Applying a 4 point modified prognostic index (comprising age ≥50 years, stage ≥2 disease, ECOG PS ≥2 and elevated LDH) to patients treated with R-mono or R-CHOP, those with low risk disease (0-1 points) had significantly improved survival compared to those with high risk disease (≥2 points), with 3 year OS of 87% vs. 51% (p=0.001; Figure 1B). Amongst patients with high risk disease, 13 treated with R-mono had an inferior complete response rate compared to 21 treated with R-CHOP (23% vs. 67%; OR 0.15, p=0.02), although a survival difference was not detected.
Conclusion
We report outcomes for R-mono vs. R-CHOP as initial therapy for PTLD arising after SOT. R-mono may deliver inferior response rates for patients with high risk disease. Using a modified prognostic index we identify a subset of patients with poor outcome for whom novel therapeutic strategies are required.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Lymphoma, Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder, Rituximab
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


