ASSESSMENT OF THE ALLELIC RATIO OF DNMT3A R882 MUTATIONS IN ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA BY DIGITAL DROPLET PCR
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Grimm J. 06/09/16; 132453; E904

Ms. Juliane Grimm
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: E904
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
In acute myeloid leukemia (AML) the allelic ratio (AR) of internal tandem duplication in the FLT3 gene (FLT3-ITD) has been shown to impact clinical outcomes.DNMT3A mutations (mut) occur in approximately 20% of AML patients (pts) & the majority is found in amino acid R882. These mut arise early in leukemogenesis & their presence is associated with worse prognosis in some AML subgroups. To date the biological & clinical impact of DNMT3Amut AR has not been investigated. Simultaneous absolute quantification of mut & wild type (wt) copies with the highly sensitive & specific digital droplet PCR (ddPCR) may represent an excellent tool for DNMT3A R882mut AR assessment.
Aims
To evaluate the feasibility of DNMT3A R882mut AR assessment by ddPCR at diagnosis & during disease course in AML pts.
Methods
AML pts treated at our institution between 2000 & 2015 with DNMT3A R882H or R882C mut & eligible diagnostic (n=33) &/or follow-up material (n=20) were analyzed by ddPCR. cDNA was applied to a duplex assay measuring DNMT3Amut & wt simultaneously. Absolute copy numbers of DNMT3Amut/DNMT3Awt defined the AR. Samples with an AR<0.0001 or <3 positive droplets were rated negative according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Mut in NPM1, CEPBA & presence of FLT3-ITD & -TKD were assessed at diagnosis. For pts receiving hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) data on bone marrow chimerism at day 28 & 56 after HSCT were collected.
Results
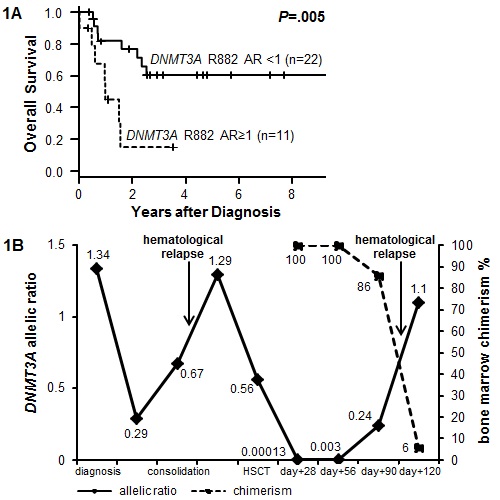
35 pts (median age 63 years [y], range 29-87y) were identified to have a DNMT3A R882H (71.4%) or R882Cmut (28.6%). All mut were determined to be heterozygous by visual inspection of the Sanger sequence traces.At diagnosis 31.4% of the AML pts had a DNMT3A R882mut AR>1 (median AR 0.92, range 0.0002-2.3). Pts with an AR>1 had more often secondary AML by trend (36.4% vs 8.3%, P=.06), were less frequently NPM1mut (18.2% vs 65.2%, P=.03), had fewer platelets by trend (P=.08) & more blasts in peripheral blood (P=.04). A DNMT3A R882mut AR>1 at diagnosis associated with shorter overall survival (Figure 1A, P=.005).27 pts received HSCT with 15 having available samples pre-HSCT. DNMT3A R882mut AR declined in all pts pre-HSCT (AR range 0-0.57, median 0.14; median AR reduction 67.3%, range 30.6-100%, P<.001). The majority of patients remained DNMT3A R882mut positive (86.7%) pre-HSCT. At day 28 after HSCT five pts had material available to assess DNMT3A R882mut AR. Four pts were positive for DNMT3A R882mut (AR range 0.0001-0.51) of whom three experienced relapse. One patient was negative for DNMT3A R882mut at day 28 & is in continuous remission.Figure 1B displays an exemplary AR course of one patient who experienced relapse after HSCT. Notably, the DNMT3A R882mut AR increased by two log-levels between day 28 & 56 after HSCT while the bone marrow total chimerism remained at 100%.
Conclusion
ddPCR is a feasible method to assess DNMT3Amut AR during disease course. In spite of the limited number of pts, our data suggest that the DNMT3A R882mut AR at diagnosis may associate with biological & clinical features & outcome of AML pts. DNMT3A R882mut AR may be useful for monitoring minimal residual disease (MRD) after HSCT. Assessment of DNMT3A R882mut AR by ddPCR will be included in future clinical trials to validate its prognostic impact & its feasibility as MRD marker after HSCT in AML.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Acute myeloid leukemia, Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant, MRD, Prognosis
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
In acute myeloid leukemia (AML) the allelic ratio (AR) of internal tandem duplication in the FLT3 gene (FLT3-ITD) has been shown to impact clinical outcomes.DNMT3A mutations (mut) occur in approximately 20% of AML patients (pts) & the majority is found in amino acid R882. These mut arise early in leukemogenesis & their presence is associated with worse prognosis in some AML subgroups. To date the biological & clinical impact of DNMT3Amut AR has not been investigated. Simultaneous absolute quantification of mut & wild type (wt) copies with the highly sensitive & specific digital droplet PCR (ddPCR) may represent an excellent tool for DNMT3A R882mut AR assessment.
Aims
To evaluate the feasibility of DNMT3A R882mut AR assessment by ddPCR at diagnosis & during disease course in AML pts.
Methods
AML pts treated at our institution between 2000 & 2015 with DNMT3A R882H or R882C mut & eligible diagnostic (n=33) &/or follow-up material (n=20) were analyzed by ddPCR. cDNA was applied to a duplex assay measuring DNMT3Amut & wt simultaneously. Absolute copy numbers of DNMT3Amut/DNMT3Awt defined the AR. Samples with an AR<0.0001 or <3 positive droplets were rated negative according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Mut in NPM1, CEPBA & presence of FLT3-ITD & -TKD were assessed at diagnosis. For pts receiving hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) data on bone marrow chimerism at day 28 & 56 after HSCT were collected.
Results
35 pts (median age 63 years [y], range 29-87y) were identified to have a DNMT3A R882H (71.4%) or R882Cmut (28.6%). All mut were determined to be heterozygous by visual inspection of the Sanger sequence traces.At diagnosis 31.4% of the AML pts had a DNMT3A R882mut AR>1 (median AR 0.92, range 0.0002-2.3). Pts with an AR>1 had more often secondary AML by trend (36.4% vs 8.3%, P=.06), were less frequently NPM1mut (18.2% vs 65.2%, P=.03), had fewer platelets by trend (P=.08) & more blasts in peripheral blood (P=.04). A DNMT3A R882mut AR>1 at diagnosis associated with shorter overall survival (Figure 1A, P=.005).27 pts received HSCT with 15 having available samples pre-HSCT. DNMT3A R882mut AR declined in all pts pre-HSCT (AR range 0-0.57, median 0.14; median AR reduction 67.3%, range 30.6-100%, P<.001). The majority of patients remained DNMT3A R882mut positive (86.7%) pre-HSCT. At day 28 after HSCT five pts had material available to assess DNMT3A R882mut AR. Four pts were positive for DNMT3A R882mut (AR range 0.0001-0.51) of whom three experienced relapse. One patient was negative for DNMT3A R882mut at day 28 & is in continuous remission.Figure 1B displays an exemplary AR course of one patient who experienced relapse after HSCT. Notably, the DNMT3A R882mut AR increased by two log-levels between day 28 & 56 after HSCT while the bone marrow total chimerism remained at 100%.
Conclusion
ddPCR is a feasible method to assess DNMT3Amut AR during disease course. In spite of the limited number of pts, our data suggest that the DNMT3A R882mut AR at diagnosis may associate with biological & clinical features & outcome of AML pts. DNMT3A R882mut AR may be useful for monitoring minimal residual disease (MRD) after HSCT. Assessment of DNMT3A R882mut AR by ddPCR will be included in future clinical trials to validate its prognostic impact & its feasibility as MRD marker after HSCT in AML.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Acute myeloid leukemia, Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant, MRD, Prognosis
Abstract: E904
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
In acute myeloid leukemia (AML) the allelic ratio (AR) of internal tandem duplication in the FLT3 gene (FLT3-ITD) has been shown to impact clinical outcomes.DNMT3A mutations (mut) occur in approximately 20% of AML patients (pts) & the majority is found in amino acid R882. These mut arise early in leukemogenesis & their presence is associated with worse prognosis in some AML subgroups. To date the biological & clinical impact of DNMT3Amut AR has not been investigated. Simultaneous absolute quantification of mut & wild type (wt) copies with the highly sensitive & specific digital droplet PCR (ddPCR) may represent an excellent tool for DNMT3A R882mut AR assessment.
Aims
To evaluate the feasibility of DNMT3A R882mut AR assessment by ddPCR at diagnosis & during disease course in AML pts.
Methods
AML pts treated at our institution between 2000 & 2015 with DNMT3A R882H or R882C mut & eligible diagnostic (n=33) &/or follow-up material (n=20) were analyzed by ddPCR. cDNA was applied to a duplex assay measuring DNMT3Amut & wt simultaneously. Absolute copy numbers of DNMT3Amut/DNMT3Awt defined the AR. Samples with an AR<0.0001 or <3 positive droplets were rated negative according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Mut in NPM1, CEPBA & presence of FLT3-ITD & -TKD were assessed at diagnosis. For pts receiving hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) data on bone marrow chimerism at day 28 & 56 after HSCT were collected.
Results
35 pts (median age 63 years [y], range 29-87y) were identified to have a DNMT3A R882H (71.4%) or R882Cmut (28.6%). All mut were determined to be heterozygous by visual inspection of the Sanger sequence traces.At diagnosis 31.4% of the AML pts had a DNMT3A R882mut AR>1 (median AR 0.92, range 0.0002-2.3). Pts with an AR>1 had more often secondary AML by trend (36.4% vs 8.3%, P=.06), were less frequently NPM1mut (18.2% vs 65.2%, P=.03), had fewer platelets by trend (P=.08) & more blasts in peripheral blood (P=.04). A DNMT3A R882mut AR>1 at diagnosis associated with shorter overall survival (Figure 1A, P=.005).27 pts received HSCT with 15 having available samples pre-HSCT. DNMT3A R882mut AR declined in all pts pre-HSCT (AR range 0-0.57, median 0.14; median AR reduction 67.3%, range 30.6-100%, P<.001). The majority of patients remained DNMT3A R882mut positive (86.7%) pre-HSCT. At day 28 after HSCT five pts had material available to assess DNMT3A R882mut AR. Four pts were positive for DNMT3A R882mut (AR range 0.0001-0.51) of whom three experienced relapse. One patient was negative for DNMT3A R882mut at day 28 & is in continuous remission.Figure 1B displays an exemplary AR course of one patient who experienced relapse after HSCT. Notably, the DNMT3A R882mut AR increased by two log-levels between day 28 & 56 after HSCT while the bone marrow total chimerism remained at 100%.
Conclusion
ddPCR is a feasible method to assess DNMT3Amut AR during disease course. In spite of the limited number of pts, our data suggest that the DNMT3A R882mut AR at diagnosis may associate with biological & clinical features & outcome of AML pts. DNMT3A R882mut AR may be useful for monitoring minimal residual disease (MRD) after HSCT. Assessment of DNMT3A R882mut AR by ddPCR will be included in future clinical trials to validate its prognostic impact & its feasibility as MRD marker after HSCT in AML.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Acute myeloid leukemia, Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant, MRD, Prognosis
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
In acute myeloid leukemia (AML) the allelic ratio (AR) of internal tandem duplication in the FLT3 gene (FLT3-ITD) has been shown to impact clinical outcomes.DNMT3A mutations (mut) occur in approximately 20% of AML patients (pts) & the majority is found in amino acid R882. These mut arise early in leukemogenesis & their presence is associated with worse prognosis in some AML subgroups. To date the biological & clinical impact of DNMT3Amut AR has not been investigated. Simultaneous absolute quantification of mut & wild type (wt) copies with the highly sensitive & specific digital droplet PCR (ddPCR) may represent an excellent tool for DNMT3A R882mut AR assessment.
Aims
To evaluate the feasibility of DNMT3A R882mut AR assessment by ddPCR at diagnosis & during disease course in AML pts.
Methods
AML pts treated at our institution between 2000 & 2015 with DNMT3A R882H or R882C mut & eligible diagnostic (n=33) &/or follow-up material (n=20) were analyzed by ddPCR. cDNA was applied to a duplex assay measuring DNMT3Amut & wt simultaneously. Absolute copy numbers of DNMT3Amut/DNMT3Awt defined the AR. Samples with an AR<0.0001 or <3 positive droplets were rated negative according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Mut in NPM1, CEPBA & presence of FLT3-ITD & -TKD were assessed at diagnosis. For pts receiving hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) data on bone marrow chimerism at day 28 & 56 after HSCT were collected.
Results
35 pts (median age 63 years [y], range 29-87y) were identified to have a DNMT3A R882H (71.4%) or R882Cmut (28.6%). All mut were determined to be heterozygous by visual inspection of the Sanger sequence traces.At diagnosis 31.4% of the AML pts had a DNMT3A R882mut AR>1 (median AR 0.92, range 0.0002-2.3). Pts with an AR>1 had more often secondary AML by trend (36.4% vs 8.3%, P=.06), were less frequently NPM1mut (18.2% vs 65.2%, P=.03), had fewer platelets by trend (P=.08) & more blasts in peripheral blood (P=.04). A DNMT3A R882mut AR>1 at diagnosis associated with shorter overall survival (Figure 1A, P=.005).27 pts received HSCT with 15 having available samples pre-HSCT. DNMT3A R882mut AR declined in all pts pre-HSCT (AR range 0-0.57, median 0.14; median AR reduction 67.3%, range 30.6-100%, P<.001). The majority of patients remained DNMT3A R882mut positive (86.7%) pre-HSCT. At day 28 after HSCT five pts had material available to assess DNMT3A R882mut AR. Four pts were positive for DNMT3A R882mut (AR range 0.0001-0.51) of whom three experienced relapse. One patient was negative for DNMT3A R882mut at day 28 & is in continuous remission.Figure 1B displays an exemplary AR course of one patient who experienced relapse after HSCT. Notably, the DNMT3A R882mut AR increased by two log-levels between day 28 & 56 after HSCT while the bone marrow total chimerism remained at 100%.
Conclusion
ddPCR is a feasible method to assess DNMT3Amut AR during disease course. In spite of the limited number of pts, our data suggest that the DNMT3A R882mut AR at diagnosis may associate with biological & clinical features & outcome of AML pts. DNMT3A R882mut AR may be useful for monitoring minimal residual disease (MRD) after HSCT. Assessment of DNMT3A R882mut AR by ddPCR will be included in future clinical trials to validate its prognostic impact & its feasibility as MRD marker after HSCT in AML.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Acute myeloid leukemia, Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant, MRD, Prognosis
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


