MANAGEMENT AND OUTCOME OF CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS) INVOLVEMENT IN ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMİA (ALL): PRE AND POST TRANSPLANT
(Abstract release date: 05/19/16)
EHA Library. Ataca P. 06/09/16; 132420; E871

Dr. Pinar Ataca
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: E871
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
The CNS is most common extramedullary site of involvement in ALL occurs in 4% to 8% of patients under chemotherapy. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (Allo-HSCT) has emerged the curative treatment of ALL. The data how and which patients respond to CNS involvement treatment in pre and post transplant period remain limited.
Aims
The objectives of this study is to examine the management and outcomes of CNS involvement in pre and posttransplant period.
Methods
This single-center retrospective analysis included 137 ALL patients who underwent Allo-HSCT at Ankara University School of Medicine between 2005 and 2015. CNS involvement/relapse included 1 or more of the following criterias: evidence of leukemic blasts in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), cranial nerve palsy or contrast-enhancing brain or spinal mass on imaging.
Results
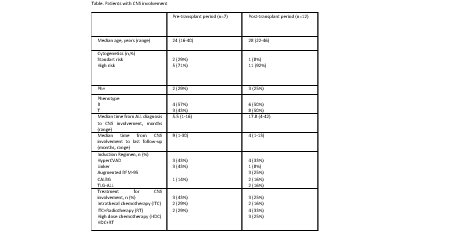
Pretransplant CNS involvement was diagnoesed in 7 (5%) patients whereas posttransplant CNS relapse was detected in 12 (9%) patients. The patient characteristics are shown in table. All induction regimens included prophylactic intrathecal chemotherapy (Methotrexate, ARA-C). None of the patients with pre-transplant involvement had post-transplant CNS relapse. Isolated CNS relapse was detected in 4 (33%) post-transplant patients. Median time to CNS relapse from Allo-HSCT was 8 months (range, 1-28). Twp pre-transplant (29%) and two post-transplant (16%) CNS involvement patients received reduced intensity conditioning. TBI based conditioning was prefered in 6 pre-transplant (86%) and 7 (58%) post-transplant CNS involvement patients. Peripheral blood was the stem cell source for 17 patients wheras two pre-transplant CNS involvement patients had received bone marrow from their matched relatives. None of the patients received CNS-directed prophylactic therapy after transplantation. All of the pre-transplant involvement patients were died due to disease relapse post-transplant. Two patients who received HDT and RT were alive in post-transplant CNS relapse group.
Conclusion
The prognosis is poor in CNS relapse detected in ALL patients posttransplant or pretransplant period. HDC and RT seems the most effective treatment strategy.
Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
The CNS is most common extramedullary site of involvement in ALL occurs in 4% to 8% of patients under chemotherapy. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (Allo-HSCT) has emerged the curative treatment of ALL. The data how and which patients respond to CNS involvement treatment in pre and post transplant period remain limited.
Aims
The objectives of this study is to examine the management and outcomes of CNS involvement in pre and posttransplant period.
Methods
This single-center retrospective analysis included 137 ALL patients who underwent Allo-HSCT at Ankara University School of Medicine between 2005 and 2015. CNS involvement/relapse included 1 or more of the following criterias: evidence of leukemic blasts in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), cranial nerve palsy or contrast-enhancing brain or spinal mass on imaging.
Results
Pretransplant CNS involvement was diagnoesed in 7 (5%) patients whereas posttransplant CNS relapse was detected in 12 (9%) patients. The patient characteristics are shown in table. All induction regimens included prophylactic intrathecal chemotherapy (Methotrexate, ARA-C). None of the patients with pre-transplant involvement had post-transplant CNS relapse. Isolated CNS relapse was detected in 4 (33%) post-transplant patients. Median time to CNS relapse from Allo-HSCT was 8 months (range, 1-28). Twp pre-transplant (29%) and two post-transplant (16%) CNS involvement patients received reduced intensity conditioning. TBI based conditioning was prefered in 6 pre-transplant (86%) and 7 (58%) post-transplant CNS involvement patients. Peripheral blood was the stem cell source for 17 patients wheras two pre-transplant CNS involvement patients had received bone marrow from their matched relatives. None of the patients received CNS-directed prophylactic therapy after transplantation. All of the pre-transplant involvement patients were died due to disease relapse post-transplant. Two patients who received HDT and RT were alive in post-transplant CNS relapse group.
Conclusion
The prognosis is poor in CNS relapse detected in ALL patients posttransplant or pretransplant period. HDC and RT seems the most effective treatment strategy.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant
Abstract: E871
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
The CNS is most common extramedullary site of involvement in ALL occurs in 4% to 8% of patients under chemotherapy. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (Allo-HSCT) has emerged the curative treatment of ALL. The data how and which patients respond to CNS involvement treatment in pre and post transplant period remain limited.
Aims
The objectives of this study is to examine the management and outcomes of CNS involvement in pre and posttransplant period.
Methods
This single-center retrospective analysis included 137 ALL patients who underwent Allo-HSCT at Ankara University School of Medicine between 2005 and 2015. CNS involvement/relapse included 1 or more of the following criterias: evidence of leukemic blasts in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), cranial nerve palsy or contrast-enhancing brain or spinal mass on imaging.
Results
Pretransplant CNS involvement was diagnoesed in 7 (5%) patients whereas posttransplant CNS relapse was detected in 12 (9%) patients. The patient characteristics are shown in table. All induction regimens included prophylactic intrathecal chemotherapy (Methotrexate, ARA-C). None of the patients with pre-transplant involvement had post-transplant CNS relapse. Isolated CNS relapse was detected in 4 (33%) post-transplant patients. Median time to CNS relapse from Allo-HSCT was 8 months (range, 1-28). Twp pre-transplant (29%) and two post-transplant (16%) CNS involvement patients received reduced intensity conditioning. TBI based conditioning was prefered in 6 pre-transplant (86%) and 7 (58%) post-transplant CNS involvement patients. Peripheral blood was the stem cell source for 17 patients wheras two pre-transplant CNS involvement patients had received bone marrow from their matched relatives. None of the patients received CNS-directed prophylactic therapy after transplantation. All of the pre-transplant involvement patients were died due to disease relapse post-transplant. Two patients who received HDT and RT were alive in post-transplant CNS relapse group.
Conclusion
The prognosis is poor in CNS relapse detected in ALL patients posttransplant or pretransplant period. HDC and RT seems the most effective treatment strategy.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant
Type: Eposter Presentation
Background
The CNS is most common extramedullary site of involvement in ALL occurs in 4% to 8% of patients under chemotherapy. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (Allo-HSCT) has emerged the curative treatment of ALL. The data how and which patients respond to CNS involvement treatment in pre and post transplant period remain limited.
Aims
The objectives of this study is to examine the management and outcomes of CNS involvement in pre and posttransplant period.
Methods
This single-center retrospective analysis included 137 ALL patients who underwent Allo-HSCT at Ankara University School of Medicine between 2005 and 2015. CNS involvement/relapse included 1 or more of the following criterias: evidence of leukemic blasts in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), cranial nerve palsy or contrast-enhancing brain or spinal mass on imaging.
Results
Pretransplant CNS involvement was diagnoesed in 7 (5%) patients whereas posttransplant CNS relapse was detected in 12 (9%) patients. The patient characteristics are shown in table. All induction regimens included prophylactic intrathecal chemotherapy (Methotrexate, ARA-C). None of the patients with pre-transplant involvement had post-transplant CNS relapse. Isolated CNS relapse was detected in 4 (33%) post-transplant patients. Median time to CNS relapse from Allo-HSCT was 8 months (range, 1-28). Twp pre-transplant (29%) and two post-transplant (16%) CNS involvement patients received reduced intensity conditioning. TBI based conditioning was prefered in 6 pre-transplant (86%) and 7 (58%) post-transplant CNS involvement patients. Peripheral blood was the stem cell source for 17 patients wheras two pre-transplant CNS involvement patients had received bone marrow from their matched relatives. None of the patients received CNS-directed prophylactic therapy after transplantation. All of the pre-transplant involvement patients were died due to disease relapse post-transplant. Two patients who received HDT and RT were alive in post-transplant CNS relapse group.
Conclusion
The prognosis is poor in CNS relapse detected in ALL patients posttransplant or pretransplant period. HDC and RT seems the most effective treatment strategy.

Session topic: E-poster
Keyword(s): Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


