
Contributions
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA20: From 14.06.2015 08:15 to 14.06.2015 08:30
Location: Room A2+3
Background
Lenalidomide is an immunomodulatory drug (IMiD) with high activity in multiple myeloma (MM). IMiD binding to the CRBN E3 ubiquitin ligase results in targeted ubiquitination and degradation of the lymphoid transcription factors IKZF1 and IKZF3 and constitutes a unique mechanism of action for a class of drugs.
Aims
To determine whether expression levels of CRBN, IKZF1, and IKZF3 are associated with outcome in lenalidomide treated patients (pts) with newly diagnosed MM.
Methods
We analyzed mRNA expression levels of IKZF1, IKZF3, and CRBN by real-time quantitative PCR (RQ-PCR) in CD138-selected pre-treatment samples from 60 pts with newly diagnosed MM uniformly treated within a phase II clinical trial of the German Myeloma Study Group (DSMM). Additionally, all pts were characterized for the presence of cytogenetic abnormalities using a comprehensive set of FISH probes. All patients received induction consisting of four cycles of lenalidomide, adriamycin and dexamethasone followed by high-dose melphalan (Mel-200) with autologous stem cell transplantation (aSCT). Genetically defined low- and intermediate risk patients received a second aSCT, while those pts with high-risk cytogenetics (presence of a del17p13, t(4;14) or t(14;16)) underwent allogeneic stem cell transplantation if a donor was available. All patients received lenalidomide maintenance for 12 months.
Results
Median expression levels normalized to plasma cells from healthy volunteers of CRBN, IKZF1, and IKZF3 were 0.66 (range, 0.12 - 2.86), 0.66 (0.16 – 2.92), and 0.52 (0.19 – 5.13), respectively. Expression levels of CRBN, IKZF1, and IKZF3 were not affected by the presence of chromosomal aberrations (del13q14, del17p13, del9q34, +1q21, t(4;14), t(11;14), t(14;16)).
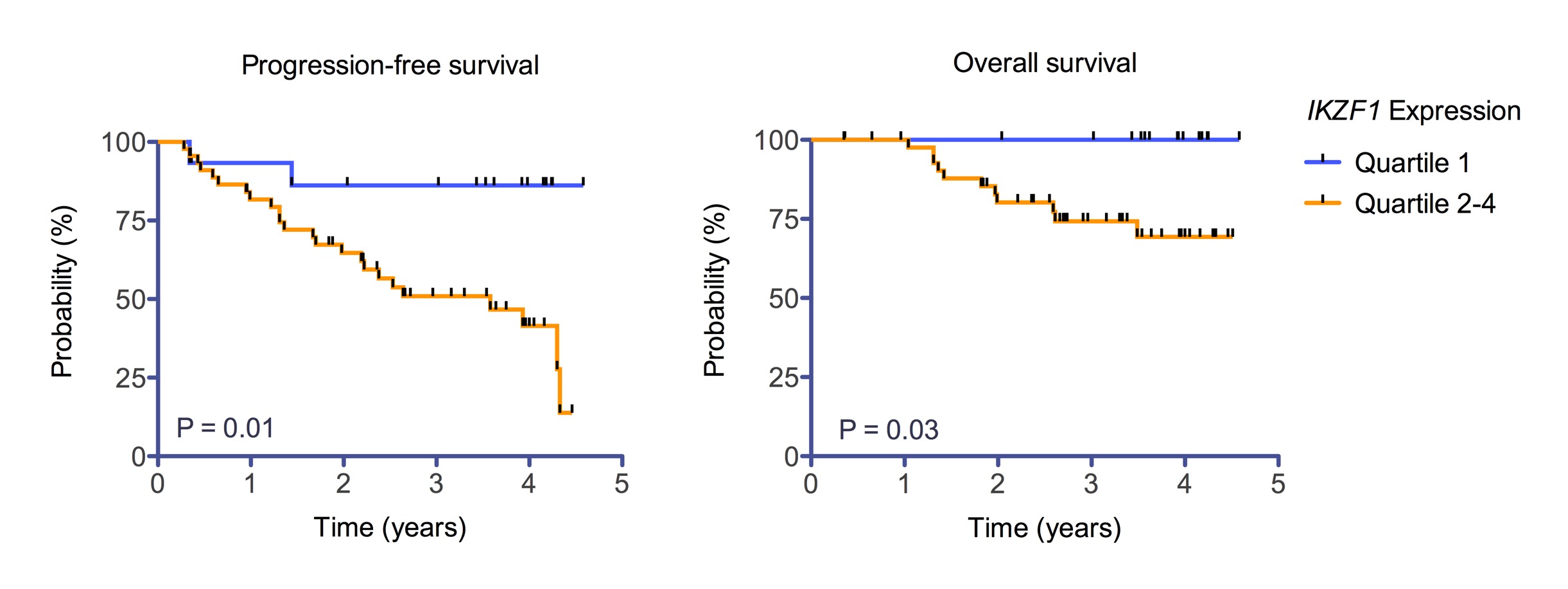
Patients achieving a complete response (CR) or very good partial response (VGPR) had a trend towards a lower IKZF1 expression than patients achieving a partial response (PR) (median IKZF1 expression: 0.62 vs 0.84, p=0.07). Consistently, lower IKZF1 expression levels were associated with a better outcome: when segregating IKZF1 expression levels into quartiles, pts with the lowest (Q1) quartile of IKZF1 expression had a 3 year progression-free survival (PFS) of 86% compared to 51% in patients of the remaining quartiles (Q2-Q4)(Log rank test, p=0.01). This translated into a better overall survival (OS) (IKZF1 Q1:100% vs IKZF1 Q2-4:74% after 3 years, log rank p=0.03). In contrast, CRBN and IKZF3 expression levels had no impact on response, PFS, or OS. Factors also associated with outcome included the presence of a del13q14 (PFS: p=n.s.; OS: p=0.04), del17p13 (PFS: p=0.001; OS=0.03), t(4;14) (PFS: p=0.009; OS: p=0.004) or +1q21 (PFS:p=n.s.; OS p=0.037).
Summary
In this cohort of uniformly treated newly diagnosed MM patients, IKZF1 but not IKZF3 or CRBN expression levels were associated with outcome. Low IKZF1 mRNA expression levels seem to identify a sub-group with a particularly good outcome.
Keyword(s): Ikaros, Imids, Multiple myeloma, Prognostic factor
Session topic: Multiple myeloma: Clinical studies 3
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA20: From 14.06.2015 08:15 to 14.06.2015 08:30
Location: Room A2+3
Background
Lenalidomide is an immunomodulatory drug (IMiD) with high activity in multiple myeloma (MM). IMiD binding to the CRBN E3 ubiquitin ligase results in targeted ubiquitination and degradation of the lymphoid transcription factors IKZF1 and IKZF3 and constitutes a unique mechanism of action for a class of drugs.
Aims
To determine whether expression levels of CRBN, IKZF1, and IKZF3 are associated with outcome in lenalidomide treated patients (pts) with newly diagnosed MM.
Methods
We analyzed mRNA expression levels of IKZF1, IKZF3, and CRBN by real-time quantitative PCR (RQ-PCR) in CD138-selected pre-treatment samples from 60 pts with newly diagnosed MM uniformly treated within a phase II clinical trial of the German Myeloma Study Group (DSMM). Additionally, all pts were characterized for the presence of cytogenetic abnormalities using a comprehensive set of FISH probes. All patients received induction consisting of four cycles of lenalidomide, adriamycin and dexamethasone followed by high-dose melphalan (Mel-200) with autologous stem cell transplantation (aSCT). Genetically defined low- and intermediate risk patients received a second aSCT, while those pts with high-risk cytogenetics (presence of a del17p13, t(4;14) or t(14;16)) underwent allogeneic stem cell transplantation if a donor was available. All patients received lenalidomide maintenance for 12 months.
Results
Median expression levels normalized to plasma cells from healthy volunteers of CRBN, IKZF1, and IKZF3 were 0.66 (range, 0.12 - 2.86), 0.66 (0.16 – 2.92), and 0.52 (0.19 – 5.13), respectively. Expression levels of CRBN, IKZF1, and IKZF3 were not affected by the presence of chromosomal aberrations (del13q14, del17p13, del9q34, +1q21, t(4;14), t(11;14), t(14;16)).
Patients achieving a complete response (CR) or very good partial response (VGPR) had a trend towards a lower IKZF1 expression than patients achieving a partial response (PR) (median IKZF1 expression: 0.62 vs 0.84, p=0.07). Consistently, lower IKZF1 expression levels were associated with a better outcome: when segregating IKZF1 expression levels into quartiles, pts with the lowest (Q1) quartile of IKZF1 expression had a 3 year progression-free survival (PFS) of 86% compared to 51% in patients of the remaining quartiles (Q2-Q4)(Log rank test, p=0.01). This translated into a better overall survival (OS) (IKZF1 Q1:100% vs IKZF1 Q2-4:74% after 3 years, log rank p=0.03). In contrast, CRBN and IKZF3 expression levels had no impact on response, PFS, or OS. Factors also associated with outcome included the presence of a del13q14 (PFS: p=n.s.; OS: p=0.04), del17p13 (PFS: p=0.001; OS=0.03), t(4;14) (PFS: p=0.009; OS: p=0.004) or +1q21 (PFS:p=n.s.; OS p=0.037).
Summary
In this cohort of uniformly treated newly diagnosed MM patients, IKZF1 but not IKZF3 or CRBN expression levels were associated with outcome. Low IKZF1 mRNA expression levels seem to identify a sub-group with a particularly good outcome.
Keyword(s): Ikaros, Imids, Multiple myeloma, Prognostic factor

Session topic: Multiple myeloma: Clinical studies 3


