Bing Center for Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia

Contributions
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA20: From 14.06.2015 08:00 to 14.06.2015 08:15
Location: Room A2+3
Background
MYD88L265P and CXCR4WHIM are highly prevalent somatic mutations in Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia (WM). MYD88L265P triggers WM growth via Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase, a target of ibrutinib. CXCR4WHIM mutations confer in vitro resistance to ibrutinib.
Aims
The primary aim of this study was to determine in a prospective, multicenter study the overall and major response rates of ibrutinib monotherapy in previously treated and symptomatic WM patients requiring therapy. Secondary aims of this study included determination of progression-free survival, drug safety, and impact of MYD88 and CXCR4 mutations on treatment outcome.
Methods
Symptomatic WM patients with > 1 prior therapies were eligible. Ibrutinib (420 mg) was administered daily until progression, or unacceptable toxicity. Dose modifications for toxicity were permitted. Central pathology review was performed in all patients. Genotyping for MYD88 L265P and CXCR4 WHIM mutation status was performed in 63 and 62 patients, respectively.
Results
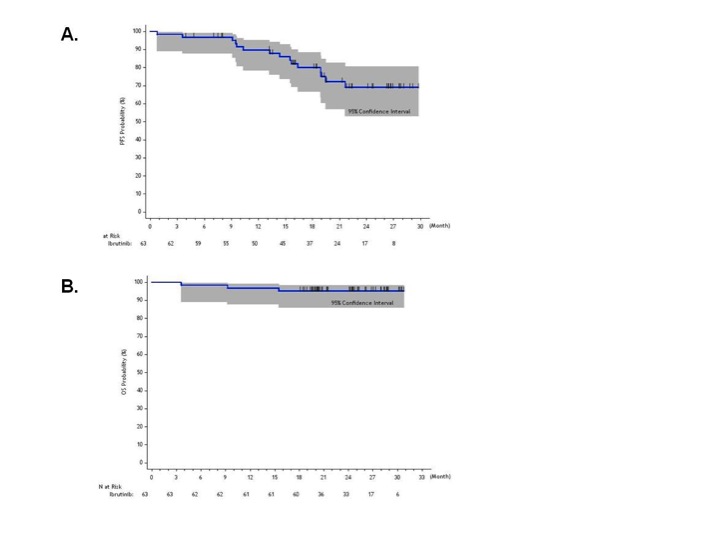
63 patients with a median of 2 prior therapies (40% with refractory disease) were enrolled. Post-therapy, median serum IgM levels declined from 3,520 to 880 mg/dL; hemoglobin rose from 10.5 to 13.8 g/dL, and bone marrow involvement declined from 60% to 25% (p < 0.01 for all comparisons). Overall and major response rates were 90.5% and 73.0%, and the median times to at least minor and major responses were 4 and 8 weeks, respectively. Overall responses were similar regardless of baseline age (<65 vs. >65 years), ECOG status (0 vs. >1), pre-therapy WM IPSS score, serum β2-microglobulin levels (<3.0 vs. >3.0 mg/L), hemoglobin (<11 vs. >11 g/dL), serum IgM (<4,000 vs. >4,000 mg/dL), BM disease involvement (<50% vs. > 50%), prior relapsed or refractory status, and prior lines of therapy (1-3 vs. >3). Fifty-six (88.9%) patients expressed MYD88L265P, and 21 (33.9%) had CXCR4WHIM mutations. Overall and major response rates were highest in patients with MYD88L265PCXCR4wild-type (WT) (100% and 91.2%), followed by MYD88L265PCXCR4WHIM (85.7% and 61.9%), and MYD88WTCXCR4WT (71.4% and 28.6%) mutation status. The 2-year PFS (Figure A) and overall survival rates (Figure B) were 69.1% and 95.2%, respectively. Subset analysis showed that >3 prior lines of therapy, high pre-therapy IPSS score, and MYD88WTCXCR4WT mutation status associated with inferior progression-free survival. Grade > 2 treatment-related toxicities included neutropenia (22.2%) and thrombocytopenia (14.3%) that were more common in heavily pre-treated patients; atrial fibrillation in patients with a prior arrhythmia history (3.2%); procedure-related bleeding (3.2%); and epistaxis related to marine oil supplements (3.2%). Serum IgA and IgG levels were unchanged, and treatment-related infections were infrequent.
Summary
Ibrutinib is highly active in previously treated WM patients. An overall response rate of 90.5%, and 2-year progression-free and overall survival rates of 69.1% and 95.2%, respectively, was achieved with ibrutinib monotherapy. Ibrutinib responses were influenced by MYD88 and CXCR4 mutation status. Overall, treatment toxicity was moderate and no unexpected toxicities were observed.
Keyword(s): CXCR4, Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia
Session topic: Multiple myeloma: Clinical studies 3
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA20: From 14.06.2015 08:00 to 14.06.2015 08:15
Location: Room A2+3
Background
MYD88L265P and CXCR4WHIM are highly prevalent somatic mutations in Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia (WM). MYD88L265P triggers WM growth via Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase, a target of ibrutinib. CXCR4WHIM mutations confer in vitro resistance to ibrutinib.
Aims
The primary aim of this study was to determine in a prospective, multicenter study the overall and major response rates of ibrutinib monotherapy in previously treated and symptomatic WM patients requiring therapy. Secondary aims of this study included determination of progression-free survival, drug safety, and impact of MYD88 and CXCR4 mutations on treatment outcome.
Methods
Symptomatic WM patients with > 1 prior therapies were eligible. Ibrutinib (420 mg) was administered daily until progression, or unacceptable toxicity. Dose modifications for toxicity were permitted. Central pathology review was performed in all patients. Genotyping for MYD88 L265P and CXCR4 WHIM mutation status was performed in 63 and 62 patients, respectively.
Results
63 patients with a median of 2 prior therapies (40% with refractory disease) were enrolled. Post-therapy, median serum IgM levels declined from 3,520 to 880 mg/dL; hemoglobin rose from 10.5 to 13.8 g/dL, and bone marrow involvement declined from 60% to 25% (p < 0.01 for all comparisons). Overall and major response rates were 90.5% and 73.0%, and the median times to at least minor and major responses were 4 and 8 weeks, respectively. Overall responses were similar regardless of baseline age (<65 vs. >65 years), ECOG status (0 vs. >1), pre-therapy WM IPSS score, serum β2-microglobulin levels (<3.0 vs. >3.0 mg/L), hemoglobin (<11 vs. >11 g/dL), serum IgM (<4,000 vs. >4,000 mg/dL), BM disease involvement (<50% vs. > 50%), prior relapsed or refractory status, and prior lines of therapy (1-3 vs. >3). Fifty-six (88.9%) patients expressed MYD88L265P, and 21 (33.9%) had CXCR4WHIM mutations. Overall and major response rates were highest in patients with MYD88L265PCXCR4wild-type (WT) (100% and 91.2%), followed by MYD88L265PCXCR4WHIM (85.7% and 61.9%), and MYD88WTCXCR4WT (71.4% and 28.6%) mutation status. The 2-year PFS (Figure A) and overall survival rates (Figure B) were 69.1% and 95.2%, respectively. Subset analysis showed that >3 prior lines of therapy, high pre-therapy IPSS score, and MYD88WTCXCR4WT mutation status associated with inferior progression-free survival. Grade > 2 treatment-related toxicities included neutropenia (22.2%) and thrombocytopenia (14.3%) that were more common in heavily pre-treated patients; atrial fibrillation in patients with a prior arrhythmia history (3.2%); procedure-related bleeding (3.2%); and epistaxis related to marine oil supplements (3.2%). Serum IgA and IgG levels were unchanged, and treatment-related infections were infrequent.
Summary
Ibrutinib is highly active in previously treated WM patients. An overall response rate of 90.5%, and 2-year progression-free and overall survival rates of 69.1% and 95.2%, respectively, was achieved with ibrutinib monotherapy. Ibrutinib responses were influenced by MYD88 and CXCR4 mutation status. Overall, treatment toxicity was moderate and no unexpected toxicities were observed.
Keyword(s): CXCR4, Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia

Session topic: Multiple myeloma: Clinical studies 3


