ADDITIONAL PROGNOSTIC VALUE OF CIRCULATING MIR-16 EXPRESSION OVER THE USUAL PROGNOSTIC PARAMETERS IN MULTIPLE MYELOMA PATIENTS
(Abstract release date: 05/21/15)
EHA Library. Rocci A. 06/13/15; 103196; S478
Disclosure(s): University of Torino, Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria Città della Salute e della Scienza di Torino, ItalyMyeloma Unit, Division of Hematology

Alberto Rocci
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: S478
Type: Oral Presentation + travel grant
Presentation during EHA20: From 13.06.2015 16:15 to 13.06.2015 16:30
Location: Room A2+3
Background
Current prognosis in multiple myeloma (MM) is based on International Staging System (ISS) and the presence of chromosomal abnormalities detected by Fluorescent in situ Hybridization (FISH). However, their ability to stratify patients is still suboptimal and novel biomarkers are required to better predict survival. We identified circulating miRNAs as a non-invasive biomarker to stratify MM patients.
Aims
Methods
Circulating miRNA expression has been evaluated in newly diagnosed MM patients enrolled in the GIMEMA clinical trial NCT#01063179. Patients were randomized to receive VMP (Velcade-Melphalan-Prednisone) or VMPT-VT (Velcade-Melphalan-Prednisolone-Thalidomide with Velcade-Thalidomide maintenance). We used NanoString assay to screen more than 800 miRNAs in serum at baseline and qRT-PCR to validate significant miRNAs as reported elsewhere (Rocci A et al., Leukemia 2014). High and low expression of miRNAs were defined using the 233 patients median value as a cut-off. We defined high risk FISH as the presence of del(17p) or t(4;14) or t(14;16) and standard risk as all other patients. Proportional hazard regression model was used, stratified by maintenance (to remove the effect of different chemotherapy regimens), with ISS treated as time-dependent covariate.
Results
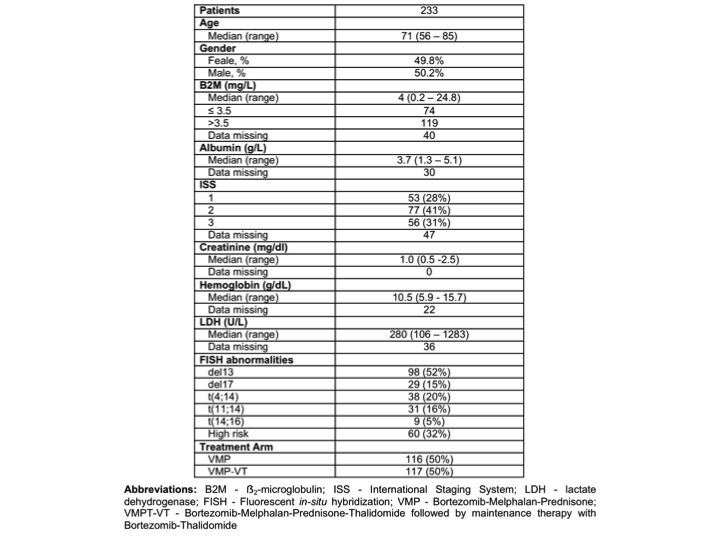
We analyzed serum from 233 evaluable patients, with a median follow-up of 71 months. Patient’s characteristics are reported in Table 1 and are balanced by age, treatment received and maintenance. Ten miRNAs were significantly expressed in serum (≥ 100 counts in at least 20% of patients) and confirmed by miRNA qRT-PCR. High expression of circulating miR-16 was confirmed as a strong predictor of better PFS (median PFS 32 vs 26 months, p=0.020) and OS (median OS unreached vs 58 months, p=0.006) when compared to low miR-16 in univariate analyses. High expression of miR-25 showed a trend for improved survival (PFS p=0.063; OS p=0.064). In multivariate analysis including age (>75 yrs vs ≤75 yrs), FISH (standard vs high risk), isolated Del17 by FISH, and ISS (I vs II and I vs III), miR-16 was a strong predictor of OS (p=0.014). Grouping miR-16, ISS and FISH identified those patients with a poor prognosis (miR-16 low, ISS 3, high risk FISH) versus good prognosis (miR-16 high, ISS 1, standard risk FISH) with a median OS of 18.4 months vs unreached respectively (p=0.0003). MiR-16 expression divides patients with standard FISH (n=127) into those with good outcome (high miR-16, 5 yrs OS: 68%) and those with poor outcome (low miR-16, 5 yrs OS: 47%, p=0.012). High miR-16 identifies patients with better outcome independently from treatment arm, however its effect was strongest in patients receiving VMPT-VT: patients with high miR-16 have a better 5-years PFS (38% vs 21%, p=0.07) and 5-year OS (76% vs 47%, p=0.0009).
Summary
Circulating miR-16 is a strong prognostic factor in newly diagnosed MM patients. It independently predicts overall survival in a model that includes ISS and FISH abnormalities. MiR-16 is independent from ISS and FISH and these three covariates together dichotomize the population in terms of overall survival.
Keyword(s): Epigenetic, Maintenance, Myeloma, Prognostic factor
Session topic: Multiple myeloma - Biology
Type: Oral Presentation + travel grant
Presentation during EHA20: From 13.06.2015 16:15 to 13.06.2015 16:30
Location: Room A2+3
Background
Current prognosis in multiple myeloma (MM) is based on International Staging System (ISS) and the presence of chromosomal abnormalities detected by Fluorescent in situ Hybridization (FISH). However, their ability to stratify patients is still suboptimal and novel biomarkers are required to better predict survival. We identified circulating miRNAs as a non-invasive biomarker to stratify MM patients.
Aims
To evaluate the role of circulating miRNA in combination with usual prognostic factors in MM. In details: 1) to confirm the prognostic value of circulating miRNAs in MM; 2) to investigate their relationship with classical prognostic parameters; 3) to evaluate the addition of circulating miRNAs into a prognostic model together with ISS and FISH.
Methods
Circulating miRNA expression has been evaluated in newly diagnosed MM patients enrolled in the GIMEMA clinical trial NCT#01063179. Patients were randomized to receive VMP (Velcade-Melphalan-Prednisone) or VMPT-VT (Velcade-Melphalan-Prednisolone-Thalidomide with Velcade-Thalidomide maintenance). We used NanoString assay to screen more than 800 miRNAs in serum at baseline and qRT-PCR to validate significant miRNAs as reported elsewhere (Rocci A et al., Leukemia 2014). High and low expression of miRNAs were defined using the 233 patients median value as a cut-off. We defined high risk FISH as the presence of del(17p) or t(4;14) or t(14;16) and standard risk as all other patients. Proportional hazard regression model was used, stratified by maintenance (to remove the effect of different chemotherapy regimens), with ISS treated as time-dependent covariate.
Results
We analyzed serum from 233 evaluable patients, with a median follow-up of 71 months. Patient’s characteristics are reported in Table 1 and are balanced by age, treatment received and maintenance. Ten miRNAs were significantly expressed in serum (≥ 100 counts in at least 20% of patients) and confirmed by miRNA qRT-PCR. High expression of circulating miR-16 was confirmed as a strong predictor of better PFS (median PFS 32 vs 26 months, p=0.020) and OS (median OS unreached vs 58 months, p=0.006) when compared to low miR-16 in univariate analyses. High expression of miR-25 showed a trend for improved survival (PFS p=0.063; OS p=0.064). In multivariate analysis including age (>75 yrs vs ≤75 yrs), FISH (standard vs high risk), isolated Del17 by FISH, and ISS (I vs II and I vs III), miR-16 was a strong predictor of OS (p=0.014). Grouping miR-16, ISS and FISH identified those patients with a poor prognosis (miR-16 low, ISS 3, high risk FISH) versus good prognosis (miR-16 high, ISS 1, standard risk FISH) with a median OS of 18.4 months vs unreached respectively (p=0.0003). MiR-16 expression divides patients with standard FISH (n=127) into those with good outcome (high miR-16, 5 yrs OS: 68%) and those with poor outcome (low miR-16, 5 yrs OS: 47%, p=0.012). High miR-16 identifies patients with better outcome independently from treatment arm, however its effect was strongest in patients receiving VMPT-VT: patients with high miR-16 have a better 5-years PFS (38% vs 21%, p=0.07) and 5-year OS (76% vs 47%, p=0.0009).
Summary
Circulating miR-16 is a strong prognostic factor in newly diagnosed MM patients. It independently predicts overall survival in a model that includes ISS and FISH abnormalities. MiR-16 is independent from ISS and FISH and these three covariates together dichotomize the population in terms of overall survival.
Keyword(s): Epigenetic, Maintenance, Myeloma, Prognostic factor

Session topic: Multiple myeloma - Biology
Abstract: S478
Type: Oral Presentation + travel grant
Presentation during EHA20: From 13.06.2015 16:15 to 13.06.2015 16:30
Location: Room A2+3
Background
Current prognosis in multiple myeloma (MM) is based on International Staging System (ISS) and the presence of chromosomal abnormalities detected by Fluorescent in situ Hybridization (FISH). However, their ability to stratify patients is still suboptimal and novel biomarkers are required to better predict survival. We identified circulating miRNAs as a non-invasive biomarker to stratify MM patients.
Aims
Methods
Circulating miRNA expression has been evaluated in newly diagnosed MM patients enrolled in the GIMEMA clinical trial NCT#01063179. Patients were randomized to receive VMP (Velcade-Melphalan-Prednisone) or VMPT-VT (Velcade-Melphalan-Prednisolone-Thalidomide with Velcade-Thalidomide maintenance). We used NanoString assay to screen more than 800 miRNAs in serum at baseline and qRT-PCR to validate significant miRNAs as reported elsewhere (Rocci A et al., Leukemia 2014). High and low expression of miRNAs were defined using the 233 patients median value as a cut-off. We defined high risk FISH as the presence of del(17p) or t(4;14) or t(14;16) and standard risk as all other patients. Proportional hazard regression model was used, stratified by maintenance (to remove the effect of different chemotherapy regimens), with ISS treated as time-dependent covariate.
Results
We analyzed serum from 233 evaluable patients, with a median follow-up of 71 months. Patient’s characteristics are reported in Table 1 and are balanced by age, treatment received and maintenance. Ten miRNAs were significantly expressed in serum (≥ 100 counts in at least 20% of patients) and confirmed by miRNA qRT-PCR. High expression of circulating miR-16 was confirmed as a strong predictor of better PFS (median PFS 32 vs 26 months, p=0.020) and OS (median OS unreached vs 58 months, p=0.006) when compared to low miR-16 in univariate analyses. High expression of miR-25 showed a trend for improved survival (PFS p=0.063; OS p=0.064). In multivariate analysis including age (>75 yrs vs ≤75 yrs), FISH (standard vs high risk), isolated Del17 by FISH, and ISS (I vs II and I vs III), miR-16 was a strong predictor of OS (p=0.014). Grouping miR-16, ISS and FISH identified those patients with a poor prognosis (miR-16 low, ISS 3, high risk FISH) versus good prognosis (miR-16 high, ISS 1, standard risk FISH) with a median OS of 18.4 months vs unreached respectively (p=0.0003). MiR-16 expression divides patients with standard FISH (n=127) into those with good outcome (high miR-16, 5 yrs OS: 68%) and those with poor outcome (low miR-16, 5 yrs OS: 47%, p=0.012). High miR-16 identifies patients with better outcome independently from treatment arm, however its effect was strongest in patients receiving VMPT-VT: patients with high miR-16 have a better 5-years PFS (38% vs 21%, p=0.07) and 5-year OS (76% vs 47%, p=0.0009).
Summary
Circulating miR-16 is a strong prognostic factor in newly diagnosed MM patients. It independently predicts overall survival in a model that includes ISS and FISH abnormalities. MiR-16 is independent from ISS and FISH and these three covariates together dichotomize the population in terms of overall survival.
Keyword(s): Epigenetic, Maintenance, Myeloma, Prognostic factor

Session topic: Multiple myeloma - Biology
Type: Oral Presentation + travel grant
Presentation during EHA20: From 13.06.2015 16:15 to 13.06.2015 16:30
Location: Room A2+3
Background
Current prognosis in multiple myeloma (MM) is based on International Staging System (ISS) and the presence of chromosomal abnormalities detected by Fluorescent in situ Hybridization (FISH). However, their ability to stratify patients is still suboptimal and novel biomarkers are required to better predict survival. We identified circulating miRNAs as a non-invasive biomarker to stratify MM patients.
Aims
To evaluate the role of circulating miRNA in combination with usual prognostic factors in MM. In details: 1) to confirm the prognostic value of circulating miRNAs in MM; 2) to investigate their relationship with classical prognostic parameters; 3) to evaluate the addition of circulating miRNAs into a prognostic model together with ISS and FISH.
Methods
Circulating miRNA expression has been evaluated in newly diagnosed MM patients enrolled in the GIMEMA clinical trial NCT#01063179. Patients were randomized to receive VMP (Velcade-Melphalan-Prednisone) or VMPT-VT (Velcade-Melphalan-Prednisolone-Thalidomide with Velcade-Thalidomide maintenance). We used NanoString assay to screen more than 800 miRNAs in serum at baseline and qRT-PCR to validate significant miRNAs as reported elsewhere (Rocci A et al., Leukemia 2014). High and low expression of miRNAs were defined using the 233 patients median value as a cut-off. We defined high risk FISH as the presence of del(17p) or t(4;14) or t(14;16) and standard risk as all other patients. Proportional hazard regression model was used, stratified by maintenance (to remove the effect of different chemotherapy regimens), with ISS treated as time-dependent covariate.
Results
We analyzed serum from 233 evaluable patients, with a median follow-up of 71 months. Patient’s characteristics are reported in Table 1 and are balanced by age, treatment received and maintenance. Ten miRNAs were significantly expressed in serum (≥ 100 counts in at least 20% of patients) and confirmed by miRNA qRT-PCR. High expression of circulating miR-16 was confirmed as a strong predictor of better PFS (median PFS 32 vs 26 months, p=0.020) and OS (median OS unreached vs 58 months, p=0.006) when compared to low miR-16 in univariate analyses. High expression of miR-25 showed a trend for improved survival (PFS p=0.063; OS p=0.064). In multivariate analysis including age (>75 yrs vs ≤75 yrs), FISH (standard vs high risk), isolated Del17 by FISH, and ISS (I vs II and I vs III), miR-16 was a strong predictor of OS (p=0.014). Grouping miR-16, ISS and FISH identified those patients with a poor prognosis (miR-16 low, ISS 3, high risk FISH) versus good prognosis (miR-16 high, ISS 1, standard risk FISH) with a median OS of 18.4 months vs unreached respectively (p=0.0003). MiR-16 expression divides patients with standard FISH (n=127) into those with good outcome (high miR-16, 5 yrs OS: 68%) and those with poor outcome (low miR-16, 5 yrs OS: 47%, p=0.012). High miR-16 identifies patients with better outcome independently from treatment arm, however its effect was strongest in patients receiving VMPT-VT: patients with high miR-16 have a better 5-years PFS (38% vs 21%, p=0.07) and 5-year OS (76% vs 47%, p=0.0009).
Summary
Circulating miR-16 is a strong prognostic factor in newly diagnosed MM patients. It independently predicts overall survival in a model that includes ISS and FISH abnormalities. MiR-16 is independent from ISS and FISH and these three covariates together dichotomize the population in terms of overall survival.
Keyword(s): Epigenetic, Maintenance, Myeloma, Prognostic factor

Session topic: Multiple myeloma - Biology
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


