A DOSE-ESCALATION STUDY OF THE BCL-2 INHIBITOR VENETOCLAX (ABT-199/GDC-0199) PLUS BENDAMUSTINE (B) AND RITUXIMAB (R) IN PATIENTS WITH RELAPSED/REFRACTORY (R/R) NON-HODGKIN?S LYMPHOMA (NHL)
(Abstract release date: 05/21/15)
EHA Library. deVos S. 06/12/15; 103123; S109

Sven deVos
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: S109
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA20: From 12.06.2015 12:15 to 12.06.2015 12:30
Location: Room A7
Background
Venetoclax is a selective, potent, orally bioavailable BCL-2 inhibitor that has shown single agent activity in patients with R/R NHL. The current study evaluates venetoclax in combination with an immunochemotherapy regimen, BR, an active regimen widely used to treat patients with NHL.
Aims
The primary objectives were to assess safety, pharmacokinetics (PK), and determine the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) and recommended Phase 2 dose of the combination. Secondary objectives evaluated preliminary efficacy.
Methods
Dose escalation used a 3+3 design on a 28 day (d) cycle (C) with 3 venetoclax schedules: 3, 7, and 28 d/C. The BR regimen was 6 C: B (2 d/C, 90mg/m2) and R (1 d/C, 375mg/m2). DLTs for dose escalation were assessed during C1. Responses were first assessed on C3 d1. Patients who completed venetoclax + BR with continued tolerability and without disease progression could continue venetoclax monotherapy up to 2 yrs.
Results
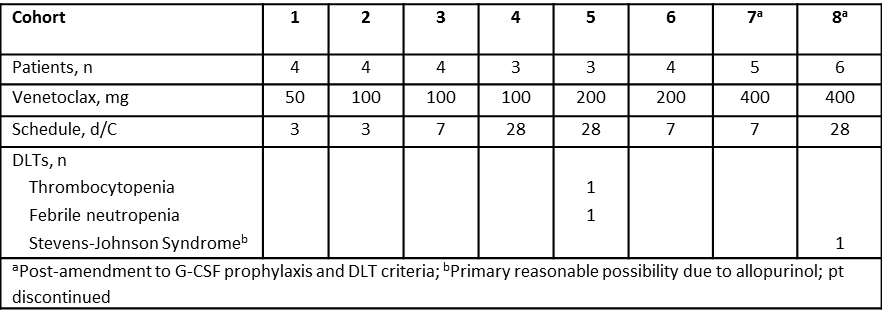
As of January 9 2015, 33 patients were treated: 20 (61%) FL, 10 (30%) DLBCL, and 3 (9%) MZL. The median age was 62 (29-90) yrs. All had prior R or R-combination, of which 32 (97%) had R-based chemotherapy and 8 (24%) had prior B or BR. Sixteen (48%) patients are active; 17 discontinued (12 PD, 2 AE, 1 withdrew consent, 1 non-compliance, and 1 completed the induction regimen). Median time on study was 90 d (1–876); 15 (45%) completed 6 C of the combination. The most common AEs (in >25%) were nausea (58%), anemia, neutropenia (each 42%), thrombocytopenia, diarrhea (each 39%), hyperglycemia (36%), and vomiting, hypokalemia, fatigue (each 27%). The most common grade 3/4 AEs (in >10%) were neutropenia (30%), leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia (each 21%), and anemia (18%). The most frequent SAE was febrile neutropenia (9%). There were no drug-related AEs that led to death. DLTs are summarized in the table. Preliminary PK results suggest that co-administration of BR did not significantly impact venetoclax PK. Twenty-nine patients were evaluable for objective response: 6 (21%) CR and 13 (45%) PR. The ORR was 66% in all patients and 74% in patients with FL.
Summary
Preliminary data demonstrate a tolerable safety profile of venetoclax + BR. Early responses were seen across all cohorts in this heavily pretreated patient population. The MTD has not been reached; cohort 9 is enrolling at 600 mg 28 d/C.
Keyword(s): BCL2, Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, Follicular lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Session topic: Treatment and outcome in non-Hodgkin lymphomas
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA20: From 12.06.2015 12:15 to 12.06.2015 12:30
Location: Room A7
Background
Venetoclax is a selective, potent, orally bioavailable BCL-2 inhibitor that has shown single agent activity in patients with R/R NHL. The current study evaluates venetoclax in combination with an immunochemotherapy regimen, BR, an active regimen widely used to treat patients with NHL.
Aims
The primary objectives were to assess safety, pharmacokinetics (PK), and determine the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) and recommended Phase 2 dose of the combination. Secondary objectives evaluated preliminary efficacy.
Methods
Dose escalation used a 3+3 design on a 28 day (d) cycle (C) with 3 venetoclax schedules: 3, 7, and 28 d/C. The BR regimen was 6 C: B (2 d/C, 90mg/m2) and R (1 d/C, 375mg/m2). DLTs for dose escalation were assessed during C1. Responses were first assessed on C3 d1. Patients who completed venetoclax + BR with continued tolerability and without disease progression could continue venetoclax monotherapy up to 2 yrs.
Results
As of January 9 2015, 33 patients were treated: 20 (61%) FL, 10 (30%) DLBCL, and 3 (9%) MZL. The median age was 62 (29-90) yrs. All had prior R or R-combination, of which 32 (97%) had R-based chemotherapy and 8 (24%) had prior B or BR. Sixteen (48%) patients are active; 17 discontinued (12 PD, 2 AE, 1 withdrew consent, 1 non-compliance, and 1 completed the induction regimen). Median time on study was 90 d (1–876); 15 (45%) completed 6 C of the combination. The most common AEs (in >25%) were nausea (58%), anemia, neutropenia (each 42%), thrombocytopenia, diarrhea (each 39%), hyperglycemia (36%), and vomiting, hypokalemia, fatigue (each 27%). The most common grade 3/4 AEs (in >10%) were neutropenia (30%), leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia (each 21%), and anemia (18%). The most frequent SAE was febrile neutropenia (9%). There were no drug-related AEs that led to death. DLTs are summarized in the table. Preliminary PK results suggest that co-administration of BR did not significantly impact venetoclax PK. Twenty-nine patients were evaluable for objective response: 6 (21%) CR and 13 (45%) PR. The ORR was 66% in all patients and 74% in patients with FL.
Summary
Preliminary data demonstrate a tolerable safety profile of venetoclax + BR. Early responses were seen across all cohorts in this heavily pretreated patient population. The MTD has not been reached; cohort 9 is enrolling at 600 mg 28 d/C.
Keyword(s): BCL2, Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, Follicular lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma

Session topic: Treatment and outcome in non-Hodgkin lymphomas
Abstract: S109
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA20: From 12.06.2015 12:15 to 12.06.2015 12:30
Location: Room A7
Background
Venetoclax is a selective, potent, orally bioavailable BCL-2 inhibitor that has shown single agent activity in patients with R/R NHL. The current study evaluates venetoclax in combination with an immunochemotherapy regimen, BR, an active regimen widely used to treat patients with NHL.
Aims
The primary objectives were to assess safety, pharmacokinetics (PK), and determine the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) and recommended Phase 2 dose of the combination. Secondary objectives evaluated preliminary efficacy.
Methods
Dose escalation used a 3+3 design on a 28 day (d) cycle (C) with 3 venetoclax schedules: 3, 7, and 28 d/C. The BR regimen was 6 C: B (2 d/C, 90mg/m2) and R (1 d/C, 375mg/m2). DLTs for dose escalation were assessed during C1. Responses were first assessed on C3 d1. Patients who completed venetoclax + BR with continued tolerability and without disease progression could continue venetoclax monotherapy up to 2 yrs.
Results
As of January 9 2015, 33 patients were treated: 20 (61%) FL, 10 (30%) DLBCL, and 3 (9%) MZL. The median age was 62 (29-90) yrs. All had prior R or R-combination, of which 32 (97%) had R-based chemotherapy and 8 (24%) had prior B or BR. Sixteen (48%) patients are active; 17 discontinued (12 PD, 2 AE, 1 withdrew consent, 1 non-compliance, and 1 completed the induction regimen). Median time on study was 90 d (1–876); 15 (45%) completed 6 C of the combination. The most common AEs (in >25%) were nausea (58%), anemia, neutropenia (each 42%), thrombocytopenia, diarrhea (each 39%), hyperglycemia (36%), and vomiting, hypokalemia, fatigue (each 27%). The most common grade 3/4 AEs (in >10%) were neutropenia (30%), leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia (each 21%), and anemia (18%). The most frequent SAE was febrile neutropenia (9%). There were no drug-related AEs that led to death. DLTs are summarized in the table. Preliminary PK results suggest that co-administration of BR did not significantly impact venetoclax PK. Twenty-nine patients were evaluable for objective response: 6 (21%) CR and 13 (45%) PR. The ORR was 66% in all patients and 74% in patients with FL.
Summary
Preliminary data demonstrate a tolerable safety profile of venetoclax + BR. Early responses were seen across all cohorts in this heavily pretreated patient population. The MTD has not been reached; cohort 9 is enrolling at 600 mg 28 d/C.
Keyword(s): BCL2, Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, Follicular lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma

Session topic: Treatment and outcome in non-Hodgkin lymphomas
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA20: From 12.06.2015 12:15 to 12.06.2015 12:30
Location: Room A7
Background
Venetoclax is a selective, potent, orally bioavailable BCL-2 inhibitor that has shown single agent activity in patients with R/R NHL. The current study evaluates venetoclax in combination with an immunochemotherapy regimen, BR, an active regimen widely used to treat patients with NHL.
Aims
The primary objectives were to assess safety, pharmacokinetics (PK), and determine the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) and recommended Phase 2 dose of the combination. Secondary objectives evaluated preliminary efficacy.
Methods
Dose escalation used a 3+3 design on a 28 day (d) cycle (C) with 3 venetoclax schedules: 3, 7, and 28 d/C. The BR regimen was 6 C: B (2 d/C, 90mg/m2) and R (1 d/C, 375mg/m2). DLTs for dose escalation were assessed during C1. Responses were first assessed on C3 d1. Patients who completed venetoclax + BR with continued tolerability and without disease progression could continue venetoclax monotherapy up to 2 yrs.
Results
As of January 9 2015, 33 patients were treated: 20 (61%) FL, 10 (30%) DLBCL, and 3 (9%) MZL. The median age was 62 (29-90) yrs. All had prior R or R-combination, of which 32 (97%) had R-based chemotherapy and 8 (24%) had prior B or BR. Sixteen (48%) patients are active; 17 discontinued (12 PD, 2 AE, 1 withdrew consent, 1 non-compliance, and 1 completed the induction regimen). Median time on study was 90 d (1–876); 15 (45%) completed 6 C of the combination. The most common AEs (in >25%) were nausea (58%), anemia, neutropenia (each 42%), thrombocytopenia, diarrhea (each 39%), hyperglycemia (36%), and vomiting, hypokalemia, fatigue (each 27%). The most common grade 3/4 AEs (in >10%) were neutropenia (30%), leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia (each 21%), and anemia (18%). The most frequent SAE was febrile neutropenia (9%). There were no drug-related AEs that led to death. DLTs are summarized in the table. Preliminary PK results suggest that co-administration of BR did not significantly impact venetoclax PK. Twenty-nine patients were evaluable for objective response: 6 (21%) CR and 13 (45%) PR. The ORR was 66% in all patients and 74% in patients with FL.
Summary
Preliminary data demonstrate a tolerable safety profile of venetoclax + BR. Early responses were seen across all cohorts in this heavily pretreated patient population. The MTD has not been reached; cohort 9 is enrolling at 600 mg 28 d/C.
Keyword(s): BCL2, Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, Follicular lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma

Session topic: Treatment and outcome in non-Hodgkin lymphomas
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


