
Contributions
Type: Publication Only
Background
Aspergillus species have emerged as an important cause of life-threatening infections in immunocompromised patients. Despite timely diagnosis and appropriate antifungal therapy, clinical outcome might be disappointing, necessitating treatment with a combination of antifungal agent.
Aims
in this study, we report the efficacy of voriconazole and caspofungin in pediatric acute leukemia.
Methods
We identified 30 pediatric acute leukemia patients who received the combination of CAS and VRC for invasive fungal infection (IFI) from April, 2009 to May, 2013 in pediatric department of Yeungnam university hospital. Medical records of patients were reviewed and analyzed retrospectively. We analyzed data that included the following: Demographic characteristics, underlying disease and disease state, radiological findings and outcome in patients with IFI.
Results
Of the 30 consecutive patients who receive CAS and VRC during study period, 8 patients were not evaluable for the following reasons: pneumonia not attributed to fungus (n=3), non-infectious pulmonary infiltration (n=5).
The study group comprised 11 boys and 11 girls, with mean age was 7 years (range, 0.8-13.3) years.
Underlying diseases were acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in 11 of these patients, acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in 11 of patients. No patient had received hematopoietic stem cell transplantation nor immunosuppressive treatment at the onset of IFD
IFD were classified as probable in 9 (41%) and possible in 13 (59%) patients, respectively.
All but 1 patients had received previous empirical antifungal monotherapy with conventional amphotericin B, liposomal amphotericin B and fluconazole (range 1-21 days) before start of VRC and CAS combination therapy. One patient had started de novo combination antifungal therapy.
The median duration of VRC and CAS combination therapy was 45 (range, 5 – 99 days) days. Loading and maintenance dose of CAS were 63.1 ± 7.7 mg/m2 and 47.2 ± 6.0 mg/m2 respectively. Those of VRC were 5.9 ± 0.5 mg/kg and 3.6 ± 0.60 mg/kg respectively.
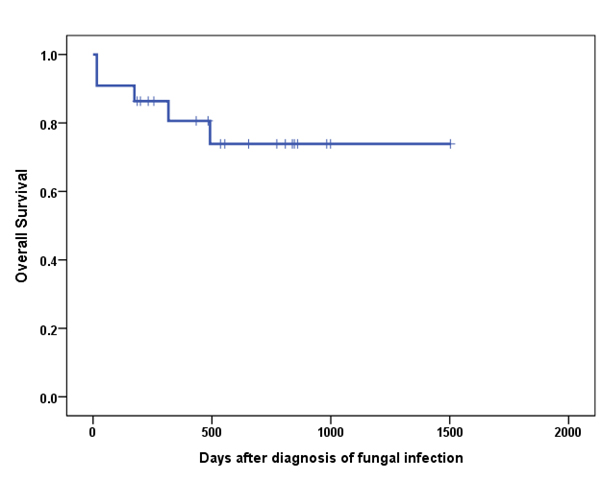
The survival rate of 100 days after initiation of combination therapy is 90.9%.
Twenty patient (90.9%) had response to combination therapy. (19 complete response and 1 partial response). Age, sex, underlying disease, disease state, treatment phase, oxygen and intravenous immunoglobulin therapy did not affect overall response and overall survival by univariate analysis
VRC and CAS combination therapy was well tolerated except for 2 patents. Two had mild increased in liver enzyme.
Summary
Voriconazole and caspofungin combination therapy is effective and safe treatment for serious invasive pulmonary fungal infections in pediatric acute leukemia
Keyword(s): Caspofungin, Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis, Leukemia, Voriconazole
Session topic: Publication Only
Type: Publication Only
Background
Aspergillus species have emerged as an important cause of life-threatening infections in immunocompromised patients. Despite timely diagnosis and appropriate antifungal therapy, clinical outcome might be disappointing, necessitating treatment with a combination of antifungal agent.
Aims
in this study, we report the efficacy of voriconazole and caspofungin in pediatric acute leukemia.
Methods
We identified 30 pediatric acute leukemia patients who received the combination of CAS and VRC for invasive fungal infection (IFI) from April, 2009 to May, 2013 in pediatric department of Yeungnam university hospital. Medical records of patients were reviewed and analyzed retrospectively. We analyzed data that included the following: Demographic characteristics, underlying disease and disease state, radiological findings and outcome in patients with IFI.
Results
Of the 30 consecutive patients who receive CAS and VRC during study period, 8 patients were not evaluable for the following reasons: pneumonia not attributed to fungus (n=3), non-infectious pulmonary infiltration (n=5).
The study group comprised 11 boys and 11 girls, with mean age was 7 years (range, 0.8-13.3) years.
Underlying diseases were acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in 11 of these patients, acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in 11 of patients. No patient had received hematopoietic stem cell transplantation nor immunosuppressive treatment at the onset of IFD
IFD were classified as probable in 9 (41%) and possible in 13 (59%) patients, respectively.
All but 1 patients had received previous empirical antifungal monotherapy with conventional amphotericin B, liposomal amphotericin B and fluconazole (range 1-21 days) before start of VRC and CAS combination therapy. One patient had started de novo combination antifungal therapy.
The median duration of VRC and CAS combination therapy was 45 (range, 5 – 99 days) days. Loading and maintenance dose of CAS were 63.1 ± 7.7 mg/m2 and 47.2 ± 6.0 mg/m2 respectively. Those of VRC were 5.9 ± 0.5 mg/kg and 3.6 ± 0.60 mg/kg respectively.
The survival rate of 100 days after initiation of combination therapy is 90.9%.
Twenty patient (90.9%) had response to combination therapy. (19 complete response and 1 partial response). Age, sex, underlying disease, disease state, treatment phase, oxygen and intravenous immunoglobulin therapy did not affect overall response and overall survival by univariate analysis
VRC and CAS combination therapy was well tolerated except for 2 patents. Two had mild increased in liver enzyme.
Summary
Voriconazole and caspofungin combination therapy is effective and safe treatment for serious invasive pulmonary fungal infections in pediatric acute leukemia
Keyword(s): Caspofungin, Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis, Leukemia, Voriconazole

Session topic: Publication Only


