HIGHER DOSE CD34+ CELLS AFFECT ABSOLUTE IMMATURE PLATELET COUNT BEFORE ENGRAFTMENT AND PLATELET COUNT AFTER ENGRAFTMENT IN CORD BLOOD TRANSPLANTATION: A SINGLE-INSTITUTIONAL STUDY
(Abstract release date: 05/21/15)
EHA Library. iwama K. 06/12/15; 103013; PB2034
Disclosure(s): TOKYO METROPOLITAN TAMA MEDICAL CENTERhematology

Kan-Ichi iwama
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: PB2034
Type: Publication Only
Background
Platelet recover is important to successful allogeneic stem cell transplantation and platelet is the last to be regenerated in bone marrow after stem cell transplantation. Especially, platelet increase is far slower in cord blood transplant(CBT). Recent retrospective studies suggested CD34+ cell and total nucleated cell affect blood cell recover. However, the impact of CD34+ cells dose on each blood cell lineages is not be sufficiently investigated. In addition, these studies mainly focus on engraftment.
Aims
Therefore, we analyzed cases in our database to evaluate the impact of CD34+ cell and total nucleated cell on each blood cell lineages in consecutive patients who were treated with CBT and achieved platelet engraftment over the past 6 years at our institution in Tokyo, Japan.
Methods
We included 95 consecutive patients treated at our institution between April 2008 and May 2014. The study population consisted of 58 male and 37 female patients with a median age of 53 years old (range: 16-69). Patient in this cohort underwent CBT as a part of therapy for myeloid malignancies(N=52) and lymphoid malignancies (N=43). 38 patients were treated with Flu+Cy+TBI(2gy), and 29 patients were treated with Flu+Bu+TBI(2Gy), and 29 patients were treated with AraC+CY+TBI(12gy). All patients received calcineurin inhibitor plus MMF for GVHD prophylaxis. Due to the influence of blood transfusion on blood cell counts and overall estimation of each blood cell movement, each blood cell lineages, and absolute Immature platelet count(ABPC) were assessed by the 5-day moving average,and then we checked movement of the 5-day moving average between patients receiving higher doses of CD34+ cells and patients receiving lower. The 5-day moving average was calculated from the time of day4 after transplantation until day 100 or death from any cause or the date on which the patient was received next chemotherapy.
Results
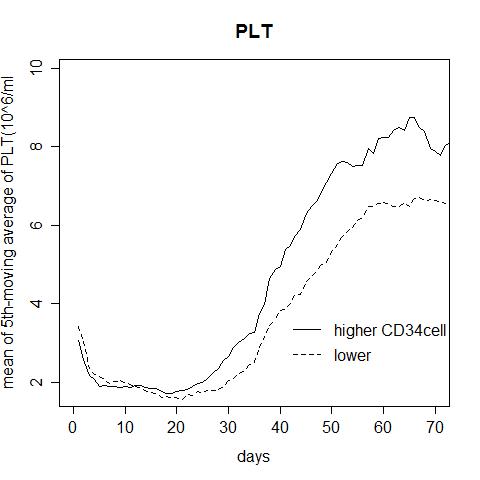
Among 95 patient, 69 patieunt achieved platelet engraftment. The median CD34+ cells doses and total nucleated cells doses were 0.8*10^5/kg and 2.0*10^7/kg. Among patients’ age, total cell count and CD34 cell count in donor cord blood and disease status and conditioning regimen, disease status and myeloablative regimen impacted on pletelet engraftment on multivariate analysis. But, as shown figure 1, the curve of ABPC in patients receiving higher doses of CD34+ cells is highter than the other from day +30 to day +50, and the curve of platlet counts in platelet patients receiving higher doses of CD34+ cells were raising after day +40. In patient who attained platelet engraftment, only age and CD34 cells affect over all survival rate.
Summary
The results of the present study highlighted the importance of CD34 cells on platelet recover and CD 34+ cell can be prognostic factor after engraftment in RIC-CBT.
Session topic: Publication Only
Type: Publication Only
Background
Platelet recover is important to successful allogeneic stem cell transplantation and platelet is the last to be regenerated in bone marrow after stem cell transplantation. Especially, platelet increase is far slower in cord blood transplant(CBT). Recent retrospective studies suggested CD34+ cell and total nucleated cell affect blood cell recover. However, the impact of CD34+ cells dose on each blood cell lineages is not be sufficiently investigated. In addition, these studies mainly focus on engraftment.
Aims
Therefore, we analyzed cases in our database to evaluate the impact of CD34+ cell and total nucleated cell on each blood cell lineages in consecutive patients who were treated with CBT and achieved platelet engraftment over the past 6 years at our institution in Tokyo, Japan.
Methods
We included 95 consecutive patients treated at our institution between April 2008 and May 2014. The study population consisted of 58 male and 37 female patients with a median age of 53 years old (range: 16-69). Patient in this cohort underwent CBT as a part of therapy for myeloid malignancies(N=52) and lymphoid malignancies (N=43). 38 patients were treated with Flu+Cy+TBI(2gy), and 29 patients were treated with Flu+Bu+TBI(2Gy), and 29 patients were treated with AraC+CY+TBI(12gy). All patients received calcineurin inhibitor plus MMF for GVHD prophylaxis. Due to the influence of blood transfusion on blood cell counts and overall estimation of each blood cell movement, each blood cell lineages, and absolute Immature platelet count(ABPC) were assessed by the 5-day moving average,and then we checked movement of the 5-day moving average between patients receiving higher doses of CD34+ cells and patients receiving lower. The 5-day moving average was calculated from the time of day4 after transplantation until day 100 or death from any cause or the date on which the patient was received next chemotherapy.
Results
Among 95 patient, 69 patieunt achieved platelet engraftment. The median CD34+ cells doses and total nucleated cells doses were 0.8*10^5/kg and 2.0*10^7/kg. Among patients’ age, total cell count and CD34 cell count in donor cord blood and disease status and conditioning regimen, disease status and myeloablative regimen impacted on pletelet engraftment on multivariate analysis. But, as shown figure 1, the curve of ABPC in patients receiving higher doses of CD34+ cells is highter than the other from day +30 to day +50, and the curve of platlet counts in platelet patients receiving higher doses of CD34+ cells were raising after day +40. In patient who attained platelet engraftment, only age and CD34 cells affect over all survival rate.
Summary
The results of the present study highlighted the importance of CD34 cells on platelet recover and CD 34+ cell can be prognostic factor after engraftment in RIC-CBT.

Session topic: Publication Only
Abstract: PB2034
Type: Publication Only
Background
Platelet recover is important to successful allogeneic stem cell transplantation and platelet is the last to be regenerated in bone marrow after stem cell transplantation. Especially, platelet increase is far slower in cord blood transplant(CBT). Recent retrospective studies suggested CD34+ cell and total nucleated cell affect blood cell recover. However, the impact of CD34+ cells dose on each blood cell lineages is not be sufficiently investigated. In addition, these studies mainly focus on engraftment.
Aims
Therefore, we analyzed cases in our database to evaluate the impact of CD34+ cell and total nucleated cell on each blood cell lineages in consecutive patients who were treated with CBT and achieved platelet engraftment over the past 6 years at our institution in Tokyo, Japan.
Methods
We included 95 consecutive patients treated at our institution between April 2008 and May 2014. The study population consisted of 58 male and 37 female patients with a median age of 53 years old (range: 16-69). Patient in this cohort underwent CBT as a part of therapy for myeloid malignancies(N=52) and lymphoid malignancies (N=43). 38 patients were treated with Flu+Cy+TBI(2gy), and 29 patients were treated with Flu+Bu+TBI(2Gy), and 29 patients were treated with AraC+CY+TBI(12gy). All patients received calcineurin inhibitor plus MMF for GVHD prophylaxis. Due to the influence of blood transfusion on blood cell counts and overall estimation of each blood cell movement, each blood cell lineages, and absolute Immature platelet count(ABPC) were assessed by the 5-day moving average,and then we checked movement of the 5-day moving average between patients receiving higher doses of CD34+ cells and patients receiving lower. The 5-day moving average was calculated from the time of day4 after transplantation until day 100 or death from any cause or the date on which the patient was received next chemotherapy.
Results
Among 95 patient, 69 patieunt achieved platelet engraftment. The median CD34+ cells doses and total nucleated cells doses were 0.8*10^5/kg and 2.0*10^7/kg. Among patients’ age, total cell count and CD34 cell count in donor cord blood and disease status and conditioning regimen, disease status and myeloablative regimen impacted on pletelet engraftment on multivariate analysis. But, as shown figure 1, the curve of ABPC in patients receiving higher doses of CD34+ cells is highter than the other from day +30 to day +50, and the curve of platlet counts in platelet patients receiving higher doses of CD34+ cells were raising after day +40. In patient who attained platelet engraftment, only age and CD34 cells affect over all survival rate.
Summary
The results of the present study highlighted the importance of CD34 cells on platelet recover and CD 34+ cell can be prognostic factor after engraftment in RIC-CBT.

Session topic: Publication Only
Type: Publication Only
Background
Platelet recover is important to successful allogeneic stem cell transplantation and platelet is the last to be regenerated in bone marrow after stem cell transplantation. Especially, platelet increase is far slower in cord blood transplant(CBT). Recent retrospective studies suggested CD34+ cell and total nucleated cell affect blood cell recover. However, the impact of CD34+ cells dose on each blood cell lineages is not be sufficiently investigated. In addition, these studies mainly focus on engraftment.
Aims
Therefore, we analyzed cases in our database to evaluate the impact of CD34+ cell and total nucleated cell on each blood cell lineages in consecutive patients who were treated with CBT and achieved platelet engraftment over the past 6 years at our institution in Tokyo, Japan.
Methods
We included 95 consecutive patients treated at our institution between April 2008 and May 2014. The study population consisted of 58 male and 37 female patients with a median age of 53 years old (range: 16-69). Patient in this cohort underwent CBT as a part of therapy for myeloid malignancies(N=52) and lymphoid malignancies (N=43). 38 patients were treated with Flu+Cy+TBI(2gy), and 29 patients were treated with Flu+Bu+TBI(2Gy), and 29 patients were treated with AraC+CY+TBI(12gy). All patients received calcineurin inhibitor plus MMF for GVHD prophylaxis. Due to the influence of blood transfusion on blood cell counts and overall estimation of each blood cell movement, each blood cell lineages, and absolute Immature platelet count(ABPC) were assessed by the 5-day moving average,and then we checked movement of the 5-day moving average between patients receiving higher doses of CD34+ cells and patients receiving lower. The 5-day moving average was calculated from the time of day4 after transplantation until day 100 or death from any cause or the date on which the patient was received next chemotherapy.
Results
Among 95 patient, 69 patieunt achieved platelet engraftment. The median CD34+ cells doses and total nucleated cells doses were 0.8*10^5/kg and 2.0*10^7/kg. Among patients’ age, total cell count and CD34 cell count in donor cord blood and disease status and conditioning regimen, disease status and myeloablative regimen impacted on pletelet engraftment on multivariate analysis. But, as shown figure 1, the curve of ABPC in patients receiving higher doses of CD34+ cells is highter than the other from day +30 to day +50, and the curve of platlet counts in platelet patients receiving higher doses of CD34+ cells were raising after day +40. In patient who attained platelet engraftment, only age and CD34 cells affect over all survival rate.
Summary
The results of the present study highlighted the importance of CD34 cells on platelet recover and CD 34+ cell can be prognostic factor after engraftment in RIC-CBT.

Session topic: Publication Only
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


