Hematology

Contributions
Type: Publication Only
Background
Nilotinib, a more potent and selective BCR-ABL-1 inhibitor than imatinib is approved by FDA and EMA for the treatment of newly-diagnosed Ph+ CML patients in the chronic phase (CML-CP).
Aims
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of nilotinib in a Turkish population of newly-diagnosed Ph+ CML-CP patients.
Methods
The study was a multicenter, open-label, single-arm phase II clinical trial. All patients were to be treated with nilotinib (AMN107, Tasigna®) 300 mg BID for 24 months.
Results
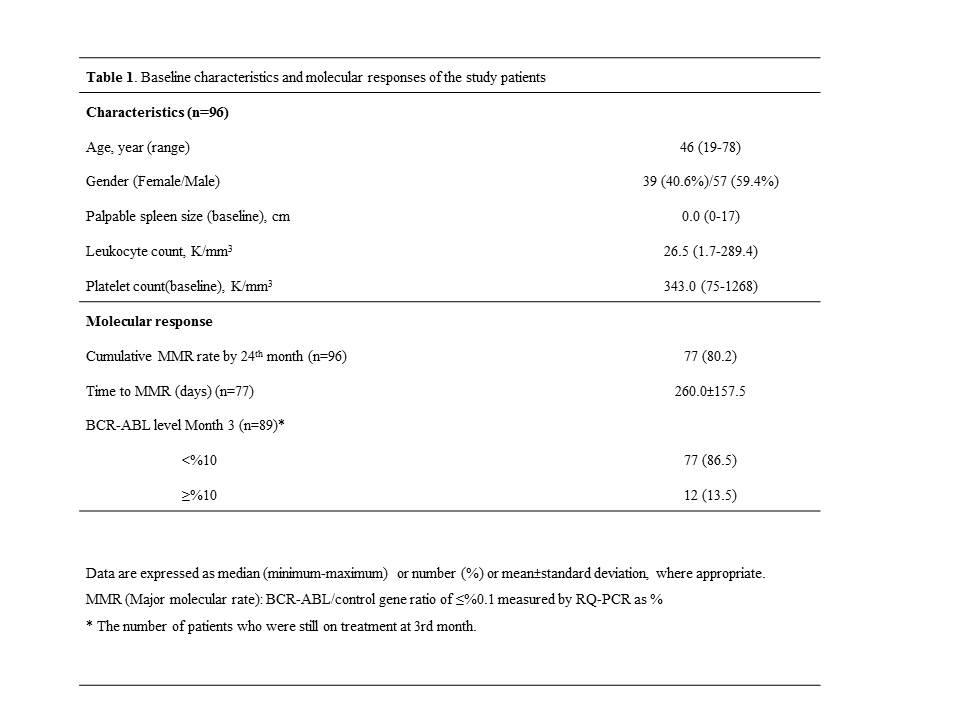
As of April 30, 2014, of the 96 patients out of a total 112 enrolled that had 24 month follow-up, 77 completed active treatment period. General characteristics of the patients at baseline and molecular response by 24 months are presented in Table 1.
Cumulative major molecular response rates at 3rd, 6th, 9th, 12th, 15th, 18th, 21st and 24th months were 23.4%, 47.9%, 56.4%, 61.7%, 71.9%, 79.2%, 82.2%, and 80.2%, respectively.
For the assessment of deeper molecular responses (defined as transcript levels of BCR–ABL on the International Scale [BCR–ABLIS] ≤0.0032%]), complete molecular response with a 4·5 log reduction required at least 32000 control genes. According to this evaluation, within 24 months follow-up 19 patients achieved MR4.5 (19.7%) by 12 months whereas 45 patients achieved increased MR4.5 (46.8%) ratio by 24 months in out of 96 patients.
Out of 96 patients, 39 patients had temporally or permanently discontinued treatment. Permanent discontinuation rate due to adverse event was 9.6% (9 patients) which was the most common reason among all patients (19.8%>19 patients) who permanently discontinued during 24 months. Thrombocytopenia was the most frequent (10.4%) AE, followed by hyperbilirubinemia (8.3%) and increased lipase level (7.3%). Despite published peripheral arterial occlusive disease (PAOD) reports related to nilotinib usage, there were no PAOD events reported at our cohort.
Summary
By 24 months, in Turkish patients with newly diagnosed CML, the cumulative MMR rate was 80.2%. Only one progression occurred, during the first year of therapy. Additionally results showing that 46.8% of these patients achieving MR4.5 by 2 years suggest that high efficacy was achieved with nilotinib, an approved first-line therapy for newly diagnosed chronic phase of CML (CP-CML) and can be an option for future candidate CML treatment regimen. Treatment free remission approach for the patients with sustainable responses during long term follow-up. This study contribute to well established nilotinib profile for chronic phase CML patients which is a licensed alternative for the treatment of newly diagnosed Ph+ CML-CP in Turkey.
Keyword(s): BCR-ABL, Molecular response, Ph+ ALL
Session topic: Publication Only
Type: Publication Only
Background
Nilotinib, a more potent and selective BCR-ABL-1 inhibitor than imatinib is approved by FDA and EMA for the treatment of newly-diagnosed Ph+ CML patients in the chronic phase (CML-CP).
Aims
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of nilotinib in a Turkish population of newly-diagnosed Ph+ CML-CP patients.
Methods
The study was a multicenter, open-label, single-arm phase II clinical trial. All patients were to be treated with nilotinib (AMN107, Tasigna®) 300 mg BID for 24 months.
Results
As of April 30, 2014, of the 96 patients out of a total 112 enrolled that had 24 month follow-up, 77 completed active treatment period. General characteristics of the patients at baseline and molecular response by 24 months are presented in Table 1.
Cumulative major molecular response rates at 3rd, 6th, 9th, 12th, 15th, 18th, 21st and 24th months were 23.4%, 47.9%, 56.4%, 61.7%, 71.9%, 79.2%, 82.2%, and 80.2%, respectively.
For the assessment of deeper molecular responses (defined as transcript levels of BCR–ABL on the International Scale [BCR–ABLIS] ≤0.0032%]), complete molecular response with a 4·5 log reduction required at least 32000 control genes. According to this evaluation, within 24 months follow-up 19 patients achieved MR4.5 (19.7%) by 12 months whereas 45 patients achieved increased MR4.5 (46.8%) ratio by 24 months in out of 96 patients.
Out of 96 patients, 39 patients had temporally or permanently discontinued treatment. Permanent discontinuation rate due to adverse event was 9.6% (9 patients) which was the most common reason among all patients (19.8%>19 patients) who permanently discontinued during 24 months. Thrombocytopenia was the most frequent (10.4%) AE, followed by hyperbilirubinemia (8.3%) and increased lipase level (7.3%). Despite published peripheral arterial occlusive disease (PAOD) reports related to nilotinib usage, there were no PAOD events reported at our cohort.
Summary
By 24 months, in Turkish patients with newly diagnosed CML, the cumulative MMR rate was 80.2%. Only one progression occurred, during the first year of therapy. Additionally results showing that 46.8% of these patients achieving MR4.5 by 2 years suggest that high efficacy was achieved with nilotinib, an approved first-line therapy for newly diagnosed chronic phase of CML (CP-CML) and can be an option for future candidate CML treatment regimen. Treatment free remission approach for the patients with sustainable responses during long term follow-up. This study contribute to well established nilotinib profile for chronic phase CML patients which is a licensed alternative for the treatment of newly diagnosed Ph+ CML-CP in Turkey.
Keyword(s): BCR-ABL, Molecular response, Ph+ ALL

Session topic: Publication Only


