Hematologic Oncology Clinic

Contributions
Type: Publication Only
Background
Rituximab in combination with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin and prednisolone (R-CHOP) has been a standard treatment for patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBL). Although complete response (CR) rate is up to 60~70%, 10~20% patients remained in PR after R-CHOP. Patients with PR are relatively chemo-sensitive compared to primary refractory diseases, but predictive factors and treatment strategy for these patients are in controversy.
Aims
We investigated the characteristics and prognosis for the patients who achieved PR after the first-line R-CHOP to analyze the survival of these patients and to define the prognostic factors affecting the clinical outcome of this specific patient group.
Methods
We performed a retrospective multicenter study on behalf of the Consortium for Improving Survival of Lymphoma (CISL). Patients who achieved PR by Cheson response criteria, and who had available PET scans at the end of R-CHOP were enrolled. Clinical parameters before and after R-CHOP were obtained to evaluate whether the patients’ dynamic condition after treatment could predict the outcome. For survival analysis, PFS2 (from the date PR was documented to disease progression or death) and OS2 (from the date PR was documented to death) were used.
Results
A total of 88 patients were enrolled. Median age was 53.5 years (21-88), and the number of patients with initial stage III-IV was 64 (72.7%). The International Prognostic Index (IPI) score at diagnosis was >2 in 46 (52.3%). At the time of PR documentation, secondary IPI scores (IPI2) assessed after R-CHOP were 0 in 33 (37.5%), 1 in 27(30.7%), and >1 in 28 (31.8%). The Deauville scores of PET scans after R-CHOP were ≤ 2 in 24 (28.2%), 3 in 26 (30.6%), ≥ 4 in 35 (41.2%), and unknown in 3 cases. As a second-line treatment, local radiation to residual lesion without any systemic treatment was performed in 33 (38.6%) patients. Intensive chemotherapy such as salvage chemotherapy or upfront ASCT was performed in 42 (47.7%) patients. Four (4.5%) patients received less intensive therapy such as rituximab or other oral agents.
With a median follow up of 47.8 months, 3-year PFS2 and OS2 rates were 57.9% and 68.1%. In the univariate analysis, age, bone marrow involvement, lymphopenia, and high IPI score at diagnosis were significantly associated with poor PFS2 and OS2.
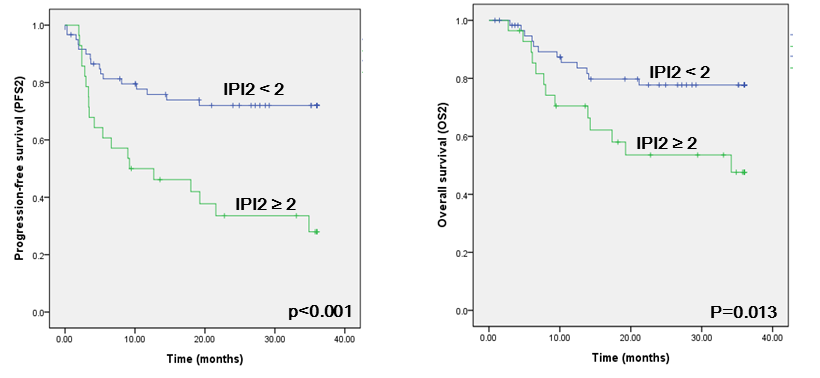
High IPI2 score (≥1) and the Deauville score (≥4) were significantly associated with worse PFS2 (p=0.001 and p=0.029, respectively). In the multivariate analysis, high IPI2 was an independent predictive factor for PFS2 (HR 2.40, 95% CI 1.08-5.269, p=0.031) after adjustment with initial IPI (p=0.163), bone marrow involvement (p=0.005), lymphopenia (p=0.124) at diagnosis and the Deauville score after R-CHOP (p=0.338).
For overall survival, high IPI2 score was also associated with poor OS2 in univariate analysis (p=0.013), but not the Deauville score (p=0.134). Only the initial IPI score >2 (p=0.041) and bone marrow involvement at diagnosis (p=0.001) remained significant in the multivariate analysis model.
Summary
IPI2 in patients with DLBL who achieved PR after R-CHOP was an important predictive factor for further survival outcomes. This suggests that the patient’s condition and residual tumor burden might be helpful when we are planning the next treatment.
Keyword(s): Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Session topic: Publication Only
Type: Publication Only
Background
Rituximab in combination with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin and prednisolone (R-CHOP) has been a standard treatment for patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBL). Although complete response (CR) rate is up to 60~70%, 10~20% patients remained in PR after R-CHOP. Patients with PR are relatively chemo-sensitive compared to primary refractory diseases, but predictive factors and treatment strategy for these patients are in controversy.
Aims
We investigated the characteristics and prognosis for the patients who achieved PR after the first-line R-CHOP to analyze the survival of these patients and to define the prognostic factors affecting the clinical outcome of this specific patient group.
Methods
We performed a retrospective multicenter study on behalf of the Consortium for Improving Survival of Lymphoma (CISL). Patients who achieved PR by Cheson response criteria, and who had available PET scans at the end of R-CHOP were enrolled. Clinical parameters before and after R-CHOP were obtained to evaluate whether the patients’ dynamic condition after treatment could predict the outcome. For survival analysis, PFS2 (from the date PR was documented to disease progression or death) and OS2 (from the date PR was documented to death) were used.
Results
A total of 88 patients were enrolled. Median age was 53.5 years (21-88), and the number of patients with initial stage III-IV was 64 (72.7%). The International Prognostic Index (IPI) score at diagnosis was >2 in 46 (52.3%). At the time of PR documentation, secondary IPI scores (IPI2) assessed after R-CHOP were 0 in 33 (37.5%), 1 in 27(30.7%), and >1 in 28 (31.8%). The Deauville scores of PET scans after R-CHOP were ≤ 2 in 24 (28.2%), 3 in 26 (30.6%), ≥ 4 in 35 (41.2%), and unknown in 3 cases. As a second-line treatment, local radiation to residual lesion without any systemic treatment was performed in 33 (38.6%) patients. Intensive chemotherapy such as salvage chemotherapy or upfront ASCT was performed in 42 (47.7%) patients. Four (4.5%) patients received less intensive therapy such as rituximab or other oral agents.
With a median follow up of 47.8 months, 3-year PFS2 and OS2 rates were 57.9% and 68.1%. In the univariate analysis, age, bone marrow involvement, lymphopenia, and high IPI score at diagnosis were significantly associated with poor PFS2 and OS2.
High IPI2 score (≥1) and the Deauville score (≥4) were significantly associated with worse PFS2 (p=0.001 and p=0.029, respectively). In the multivariate analysis, high IPI2 was an independent predictive factor for PFS2 (HR 2.40, 95% CI 1.08-5.269, p=0.031) after adjustment with initial IPI (p=0.163), bone marrow involvement (p=0.005), lymphopenia (p=0.124) at diagnosis and the Deauville score after R-CHOP (p=0.338).
For overall survival, high IPI2 score was also associated with poor OS2 in univariate analysis (p=0.013), but not the Deauville score (p=0.134). Only the initial IPI score >2 (p=0.041) and bone marrow involvement at diagnosis (p=0.001) remained significant in the multivariate analysis model.
Summary
IPI2 in patients with DLBL who achieved PR after R-CHOP was an important predictive factor for further survival outcomes. This suggests that the patient’s condition and residual tumor burden might be helpful when we are planning the next treatment.
Keyword(s): Diffuse large B cell lymphoma

Session topic: Publication Only


