HEMATOLOGY

Contributions
Type: Publication Only
Background
Prolonged survival in patients with Hodgkin's Lymphoma (HL) seems to be associated with an increased risk of developing secondary malignancies.
Aims
Ours objectives were to describe and analyze incidence of secondary malignancies, to detect predictors and their overall survival.
Methods
Single-center retrospective analysis of patients diagnosed and treated for LH in the period 1975 to 2015, at the General Hospital of Segovia (Spain). Statistical analysis was performed using SPSSâ (v.15).
Results
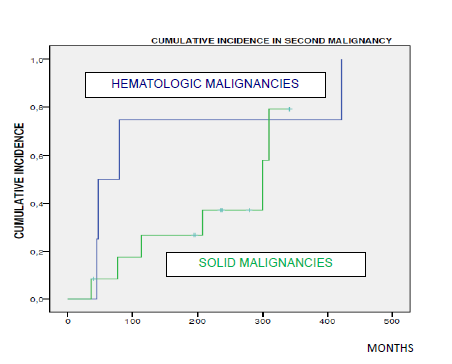
101 patients were analyzed. Median age was 33 years [10-88]. 59.4% were male. 60% had an advanced stage at diagnosis (IIB-IV). The most common histology was nodular sclerosis (n = 48). 82.2% patients had a favorable prognosis (Hasenclever ≤ 2). 87.1% patients were treated with chemotherapy (schedule ABVD the most used). 62.5% of patients received radiotherapy (RT) as first-line therapy. 10 patients only received RT as single therapy. The median follow-up was 88 months [0-422]. 16 second malignancies were detected. Median onset was 10 years [2-26]. Differences in median onset between hematologic malignancies and non-hematologic (4 vs16 years) were observed, but the difference was non stadistical significantly, perhaps due to small sample size. Comparing patients with secondary neoplasia against the global serie, only the stage (p=0.013) and number of deaths showed significant differences (p=0.005). Cumulative incidence (CI) was 35% at 300 months (CI in second malignancies is shown in Figure 1). The median overall survival stimated was 310 months in global serie (patients with second neoplasms: 300 months). Nowadays, 71 patients (70.3%) still alive, but only 6 affected by second neoplasia are alive.
Summary
HL is considered curable in a high percentage of patients, but carries a incidence of second malignancies in long survivors with an increased risk at 25 years of diagnosis, as happened in our series of a single center with median onset of 16 years. A previous publication (Kg, AK. Blood, 2014) describe an increased risk of hematologic neoplasia in patients who had received chemotherapy with alkylating agents type MOPP plus extensive radiotherapy later or with the combination chemotherapy (ABVD-MOPP). We found similar data in our serie featuring 2 cases who were treated with MOPP and mantle type RT, and other 2 with ABVD-MOPP. Another publication showed higher risk associated with BEACOPP schedule, results against to our findings: None of the 11 patients who received BEACOPP (standard or scalated) developed second neoplasia. In any case, the absence of these neoplasms along the track (last hematologic neoplasia in 1996), may be due to the change in therapeutic schemes and extent of RT (field involved vs extend field). Patients who developed non-hematological malignancies, 8 were treated with RT (all type Mantle). Therapeutic schemes were different, but in those patients who did not receive RT, all except one received ABVD scheme, no differences in both arms. Appearance of secondary neoplasms in field radiation is to be expected, as shown in our serie; however, there is also an increased risk in patients treated with alkylating agents.
In our retrospective study of single center, stage at diagnosis proved to be a predictor factor of development of second neoplasia related with higher mortality. Therefore, our data resemble previously publications as increase in the CI throughout evolution. Secondary malignancies may be lower with actual therapeutic schemes although longer follow-up would be necessary.
Keyword(s): Hodgkin's disease, Second malignancy, Survival prediction
Type: Publication Only
Background
Prolonged survival in patients with Hodgkin's Lymphoma (HL) seems to be associated with an increased risk of developing secondary malignancies.
Aims
Ours objectives were to describe and analyze incidence of secondary malignancies, to detect predictors and their overall survival.
Methods
Single-center retrospective analysis of patients diagnosed and treated for LH in the period 1975 to 2015, at the General Hospital of Segovia (Spain). Statistical analysis was performed using SPSSâ (v.15).
Results
101 patients were analyzed. Median age was 33 years [10-88]. 59.4% were male. 60% had an advanced stage at diagnosis (IIB-IV). The most common histology was nodular sclerosis (n = 48). 82.2% patients had a favorable prognosis (Hasenclever ≤ 2). 87.1% patients were treated with chemotherapy (schedule ABVD the most used). 62.5% of patients received radiotherapy (RT) as first-line therapy. 10 patients only received RT as single therapy. The median follow-up was 88 months [0-422]. 16 second malignancies were detected. Median onset was 10 years [2-26]. Differences in median onset between hematologic malignancies and non-hematologic (4 vs16 years) were observed, but the difference was non stadistical significantly, perhaps due to small sample size. Comparing patients with secondary neoplasia against the global serie, only the stage (p=0.013) and number of deaths showed significant differences (p=0.005). Cumulative incidence (CI) was 35% at 300 months (CI in second malignancies is shown in Figure 1). The median overall survival stimated was 310 months in global serie (patients with second neoplasms: 300 months). Nowadays, 71 patients (70.3%) still alive, but only 6 affected by second neoplasia are alive.
Summary
HL is considered curable in a high percentage of patients, but carries a incidence of second malignancies in long survivors with an increased risk at 25 years of diagnosis, as happened in our series of a single center with median onset of 16 years. A previous publication (Kg, AK. Blood, 2014) describe an increased risk of hematologic neoplasia in patients who had received chemotherapy with alkylating agents type MOPP plus extensive radiotherapy later or with the combination chemotherapy (ABVD-MOPP). We found similar data in our serie featuring 2 cases who were treated with MOPP and mantle type RT, and other 2 with ABVD-MOPP. Another publication showed higher risk associated with BEACOPP schedule, results against to our findings: None of the 11 patients who received BEACOPP (standard or scalated) developed second neoplasia. In any case, the absence of these neoplasms along the track (last hematologic neoplasia in 1996), may be due to the change in therapeutic schemes and extent of RT (field involved vs extend field). Patients who developed non-hematological malignancies, 8 were treated with RT (all type Mantle). Therapeutic schemes were different, but in those patients who did not receive RT, all except one received ABVD scheme, no differences in both arms. Appearance of secondary neoplasms in field radiation is to be expected, as shown in our serie; however, there is also an increased risk in patients treated with alkylating agents.
In our retrospective study of single center, stage at diagnosis proved to be a predictor factor of development of second neoplasia related with higher mortality. Therefore, our data resemble previously publications as increase in the CI throughout evolution. Secondary malignancies may be lower with actual therapeutic schemes although longer follow-up would be necessary.
Keyword(s): Hodgkin's disease, Second malignancy, Survival prediction



